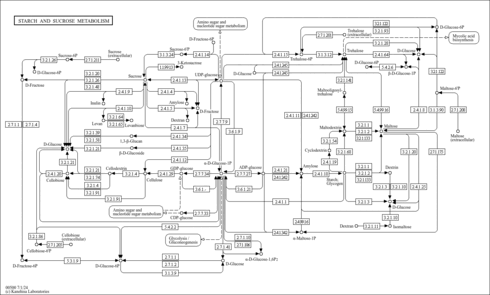
| Sucrose,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2813.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2849.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2809.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2790.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@@H]1O | 2802.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H]1O[C@]1(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2812.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2866.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2838.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2793.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2783.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2788.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2802.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #13 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2819.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #14 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2774.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #15 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2802.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #16 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2763.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #17 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2768.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #18 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2769.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #19 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2771.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2781.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #20 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2798.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #21 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2744.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #22 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2744.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #23 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2782.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #24 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2804.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #25 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2758.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #26 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H]1CO | 2783.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #27 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2811.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #28 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2798.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2751.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2761.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2767.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2802.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2780.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2793.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2772.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2718.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2700.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2690.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2691.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #13 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2685.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #14 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2725.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #15 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2702.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #16 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2696.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #17 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2742.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #18 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2720.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #19 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2736.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2706.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #20 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2716.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #21 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2742.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #22 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2727.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #23 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2736.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #24 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2706.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #25 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2714.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #26 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2709.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #27 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2705.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #28 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2704.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #29 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2728.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2715.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #30 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2740.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #31 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2718.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #32 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2746.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #33 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2747.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #34 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2741.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #35 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2743.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #36 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2740.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #37 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2727.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #38 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2714.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #39 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2723.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2715.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #40 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2714.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #41 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2724.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #42 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2732.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #43 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2727.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #44 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2696.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #45 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2699.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #46 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2704.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #47 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2724.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #48 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2717.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #49 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2714.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2740.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #50 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H]1CO | 2724.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #51 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2726.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #52 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2697.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #53 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2728.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #54 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H]1CO | 2730.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #55 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2739.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #56 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2729.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2728.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2698.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2727.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2688.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2635.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2650.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2676.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2665.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #13 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2648.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #14 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2640.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #15 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2662.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #16 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2670.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #17 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2636.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #18 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2661.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #19 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2637.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2648.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #20 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2654.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #21 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2675.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #22 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2656.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #23 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2638.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #24 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2642.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #25 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2651.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #26 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2648.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #27 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2674.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #28 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2661.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #29 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2665.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2635.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #30 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2650.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #31 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2673.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #32 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2673.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #33 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2659.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #34 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2696.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #35 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2676.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #36 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2669.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #37 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2656.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #38 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2677.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #39 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2660.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2654.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #40 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2656.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #41 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2676.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #42 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2664.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #43 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2642.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #44 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2646.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #45 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2656.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #46 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2657.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #47 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2673.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #48 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2679.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #49 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2666.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2644.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #50 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2667.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #51 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2672.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #52 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2675.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #53 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2678.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #54 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2690.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #55 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2669.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #56 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2670.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #57 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2682.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #58 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2673.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #59 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2664.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2653.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #60 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2659.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #61 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2666.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #62 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2665.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #63 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2661.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #64 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2673.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #65 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2649.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #66 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H]1CO | 2674.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #67 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2684.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #68 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H]1CO | 2671.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #69 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2683.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2642.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #70 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2688.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2646.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2633.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2603.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2622.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2615.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2647.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #13 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2626.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #14 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2633.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #15 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2611.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #16 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2616.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #17 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2638.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #18 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2617.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #19 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2635.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2595.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #20 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2612.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #21 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2625.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #22 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2646.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #23 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2629.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #24 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2622.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #25 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2615.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #26 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2628.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #27 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2636.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #28 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2629.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #29 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2646.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2629.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #30 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2613.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #31 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2648.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #32 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2635.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #33 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2654.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #34 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2639.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #35 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2646.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #36 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2622.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #37 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2645.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #38 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2627.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #39 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2629.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2596.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #40 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2626.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #41 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2635.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #42 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2644.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #43 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2638.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #44 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2652.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #45 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2611.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #46 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2633.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #47 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2655.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #48 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2649.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #49 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2636.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2615.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #50 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2641.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #51 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2644.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #52 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2635.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #53 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2652.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #54 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2632.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #55 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2650.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #56 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2654.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2650.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2617.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2613.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,5TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2606.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2578.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2596.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2634.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2614.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #13 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2613.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #14 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2598.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #15 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2601.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #16 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2606.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #17 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2605.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #18 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2622.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #19 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2615.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2595.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #20 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2624.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #21 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2626.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #22 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2605.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #23 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2608.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #24 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2617.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #25 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2611.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #26 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2629.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #27 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2626.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #28 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2622.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2583.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2596.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2588.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2607.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2615.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2606.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,6TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2627.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,7TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2616.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,7TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2615.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,7TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2630.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,7TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2632.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,7TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2640.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,7TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2626.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,7TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2634.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,7TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2633.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3026.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3038.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3019.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3018.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@@H]1O | 3019.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H]1O[C@]1(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3037.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3058.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,1TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3047.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3207.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3218.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3231.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3240.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3232.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3208.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #15 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3206.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #16 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3210.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #17 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3202.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #18 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3206.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #19 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3229.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3191.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #20 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3231.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #21 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3206.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #22 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3209.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #23 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3231.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #24 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3229.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #25 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3224.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #26 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H]1CO | 3241.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #27 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3243.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #28 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3236.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3206.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3207.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3216.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3224.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3222.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3200.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,2TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3218.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3368.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3375.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3368.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3379.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3380.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3403.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #15 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3399.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #16 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3394.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #17 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3411.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #18 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3409.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #19 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3418.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3381.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #20 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3410.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #21 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3411.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #22 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3392.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #23 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3384.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #24 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3388.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #25 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3381.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #26 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3376.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #27 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3388.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #28 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3389.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #29 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3418.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3390.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #30 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3408.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #31 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3405.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #32 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3427.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #33 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3418.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #34 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3432.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #35 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3420.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #36 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3419.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #37 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3394.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #38 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3405.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #39 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3401.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3395.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #40 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3394.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #41 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3405.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #42 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3398.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #43 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3392.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #44 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3380.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #45 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3374.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #46 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3374.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #47 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3422.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #48 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3407.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #49 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3410.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3397.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #50 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H]1CO | 3409.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #51 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3404.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #52 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3390.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #53 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3427.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #54 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H]1CO | 3421.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #55 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3420.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #56 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3432.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3397.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3376.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3381.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,3TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3380.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3544.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3553.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3570.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3566.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3570.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3560.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #15 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3578.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #16 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3555.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #17 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3550.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #18 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3558.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #19 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3540.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3552.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #20 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3561.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #21 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3562.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #22 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3545.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #23 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3531.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #24 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3525.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #25 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3529.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #26 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3536.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #27 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3553.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #28 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3551.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #29 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3553.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3547.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #30 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3549.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #31 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3567.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #32 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3566.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #33 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3561.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #34 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3577.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #35 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3579.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #36 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3557.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #37 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3561.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #38 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3566.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #39 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3551.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3548.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #40 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3560.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #41 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3563.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #42 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3548.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #43 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3532.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #44 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3525.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #45 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3530.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #46 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3536.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #47 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3560.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #48 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3557.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #49 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3559.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3535.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #50 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3555.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #51 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3570.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #52 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3572.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #53 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3566.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #54 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3582.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #55 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@@]1(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3582.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #56 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3559.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #57 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3561.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #58 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3546.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #59 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3550.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3543.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #60 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3543.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #61 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3549.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #62 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3548.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #63 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3541.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #64 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3544.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #65 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3523.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #66 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H]1CO | 3557.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #67 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3555.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #68 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H]1CO | 3555.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #69 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3552.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3542.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #70 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@]2(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3569.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3557.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Sucrose,4TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3549.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |