| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:00 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000305 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Vitamin A |
|---|
| Description | Vitamin A (retinol) is a yellow fat-soluble, antioxidant vitamin important in vision and bone growth. It belongs to the family of chemical compounds known as retinoids. Retinol is ingested in a precursor form; animal sources (milk and eggs) contain retinyl esters, whereas plants (carrots, spinach) contain pro-vitamin A carotenoids. Hydrolysis of retinyl esters results in retinol while pro-vitamin A carotenoids can be cleaved to produce retinal. Retinal, also known as retinaldehyde, can be reversibly reduced to produce retinol or it can be irreversibly oxidized to produce retinoic acid. Retinol and derivatives of retinol that play an essential role in metabolic functioning of the retina, the growth of and differentiation of epithelial tissue, the growth of bone, reproduction, and the immune response. Dietary vitamin A is derived from a variety of carotenoids found in plants. It is enriched in the liver, egg yolks, and the fat component of dairy products. |
|---|
| Structure | C\C(=C/CO)\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C InChI=1S/C20H30O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-13,21H,7,10,14-15H2,1-5H3/b9-6+,12-11+,16-8+,17-13+ |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraen-1-ol | ChEBI | | (all-e)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraen-1-ol | ChEBI | | all-trans Retinol | ChEBI | | all-trans-Retinyl alcohol | ChEBI | | all-trans-Vitamin a | ChEBI | | all-trans-Vitamin a alcohol | ChEBI | | Alphalin | ChEBI | | Aquasol a | ChEBI | | Chocola a | ChEBI | | Retinol | ChEBI | | Retinol (vit a) | ChEBI | | Retinolum | ChEBI | | trans-Retinol | ChEBI | | Vitamin a alcohol | ChEBI | | Vitamin a1 | ChEBI | | Vitamin a1 alcohol | ChEBI | | 11-cis-Retinol | MeSH | | 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraen-1-ol, (all-e)-isomer | MeSH | | all trans Retinol | MeSH | | all-trans-Retinol | MeSH | | b-Retinol | HMDB | | beta-Retinol | HMDB | | Vitamin a | ChEBI |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H30O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 286.4516 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 286.229665582 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraen-1-ol |
|---|
| Traditional Name | α-sol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 68-26-8 |
|---|
| SMILES | C\C(=C/CO)\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H30O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-13,21H,7,10,14-15H2,1-5H3/b9-6+,12-11+,16-8+,17-13+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | FPIPGXGPPPQFEQ-OVSJKPMPSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as retinoids. These are oxygenated derivatives of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene and derivatives thereof. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Retinoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Retinoids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Retinoid skeleton
- Diterpenoid
- Fatty alcohol
- Fatty acyl
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Not Available | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 61 - 63 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | 5.68 | BIOBYTE (1995) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized | Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Vitamin A GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00di-1190000000-7c2230ee88e04e8f3741 | 2017-08-28 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Vitamin A GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-7139000000-7242603c3f7f12c824cd | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Vitamin A GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Vitamin A GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Vitamin A GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-052r-2950000000-c24ec8ff8d0ba6c1f23f | 2014-09-20 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-000i-0290000000-25c523b646154b291da8 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-05gj-3900000000-a63c286f931608f650a3 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-05mo-9700000000-e627db30469c74bb037f | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00kr-0490000000-97ed49d705440e4d32e7 | 2017-07-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00ks-3930000000-7c5bfbd8b838b97dc2aa | 2017-07-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0fri-9820000000-6a49bab0c891ffe1e5b2 | 2017-07-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-0090000000-d0ff1cdc72141d0daa0e | 2017-07-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4r-0090000000-c0a067ff8ed271b80945 | 2017-07-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00ku-4590000000-cfc35aba420e707075f7 | 2017-07-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0090000000-fe93459d3069e264b77f | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-05mx-0190000000-f81760535f6050971f92 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00li-0960000000-4dbc516b202b90a6c265 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-015i-1890000000-fb68e645ac6c84dc722c | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-05a9-2910000000-aa07b89a9cfe132b8725 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Vitamin A 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-06dl-5900000000-6de72efc591b252620c9 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, CDCl3, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Membrane (predicted from logP)
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Adipose Tissue
- Epidermis
- Fibroblasts
- Intestine
- Kidney
- Liver
- Neuron
- Placenta
- Spleen
- Testis
|
|---|
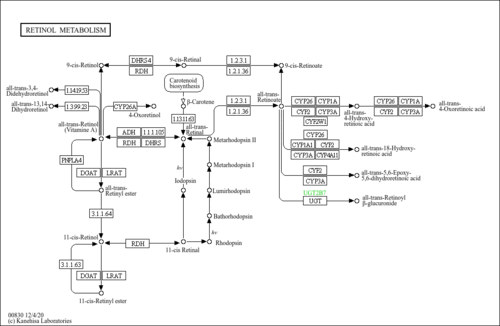
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.78 +/- 0.33 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.84 +/- 0.46 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.76 +/- 0.44 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.02 (0.34-2.1) uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.530-2.100 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0-2 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1-2 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1-2 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1-2 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.3 (1.2-3.5) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.0600 +/- 0.620 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.220 +/- 0.590 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.580 +/- 0.710 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.720 +/- 0.790 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.770 +/- 0.740 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.390 +/- 0.800 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.310 +/- 0.960 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.470 +/- 0.770 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.831 +/- 0.499 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.0736 +/- 0.485 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.220 +/- 0.496 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.580 +/- 0.360 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.0841 +/- 0.499 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.182 +/- 0.499 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.200 +/- 0.634 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.3 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.740 +/- 0.540 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.790 +/- 0.530 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.790 +/- 0.540 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.800 +/- 0.500 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.810 +/- 0.550 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.820 +/- 0.510 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.820 +/- 0.560 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.840 +/- 0.530 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.850 +/- 0.530 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.860 +/- 0.450 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.870 +/- 0.510 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.880 +/- 0.430 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.880 +/- 0.470 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.880 +/- 0.480 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.890 +/- 0.420 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.950 +/- 0.470 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.951 +/- 0.520 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 5.732 +/- 2.217 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 6.113 +/- 2.594 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 6.249 +/- 1.850 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.42 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.63 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.993 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.18 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.445 +/- 0.384 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.910 +/- 0.430 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.950 +/- 0.610 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.970 +/- 0.650 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.391 +/- 0.782 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.700 +/- 1.100 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 5.781 +/- 2.356 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 5.861 +/- 2.726 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.99 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.18 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.47 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.980 +/- 0.540 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.0800 +/- 0.620 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.130 +/- 0.380 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.400 +/- 0.900 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 5.666 +/- 2.0387 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 6.553 +/- 2.315 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 0.015 +/- 0.010 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Bladder cancer | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.50 +/- 0.86 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Hemodialysis | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.45 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Abetalipoproteinemia | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.0 (1.2-2.5) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Endometrial cancer | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.466 +/- 0.349 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Pregnancy | | details |
|
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Hemodialysis |
|---|
- Cabral PC, Diniz Ada S, de Arruda IK: Vitamin A and zinc status in patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrology (Carlton). 2005 Oct;10(5):459-63. [PubMed:16221095 ]
| | Endometrial cancer |
|---|
- Jeong NH, Song ES, Lee JM, Lee KB, Kim MK, Yun YM, Lee JK, Son SK, Lee JP, Kim JH, Hur SY, Kwon YI: Preoperative levels of plasma micronutrients are related to endometrial cancer risk. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2009;88(4):434-9. doi: 10.1080/00016340902767187. [PubMed:19235557 ]
| | Pregnancy |
|---|
- Mikkelsen TB, Osler M, Olsen SF: Validity of protein, retinol, folic acid and n-3 fatty acid intakes estimated from the food-frequency questionnaire used in the Danish National Birth Cohort. Public Health Nutr. 2006 Sep;9(6):771-8. [PubMed:16925883 ]
| | Abetalipoproteinemia |
|---|
- Lazaro RP, Dentinger MP, Rodichok LD, Barron KD, Satya-Murti S: Muscle pathology in Bassen-Kornzweig syndrome and vitamin E deficiency. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Sep;86(3):378-87. [PubMed:2944375 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00162 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB023841 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00031437 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C17276 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CPD-13524 |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Vitamin_A |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 445354 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 17336 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | RETINOL |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000141 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | rw1131351 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Isler, O.; Ronco, A.; Guex, W.; Hindley, N. C.; Huber, W.; Dialer, K.; Kofler, M. Esters and ethers of synthetic vitamin A. Helvetica Chimica Acta (1949), 32 489-505. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) |
|---|
| General References | - Norum KR, Blomhoff R: McCollum Award Lecture, 1992: vitamin A absorption, transport, cellular uptake, and storage. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992 Oct;56(4):735-44. [PubMed:1414975 ]
- Graham-Maar RC, Schall JI, Stettler N, Zemel BS, Stallings VA: Elevated vitamin A intake and serum retinol in preadolescent children with cystic fibrosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006 Jul;84(1):174-82. [PubMed:16825693 ]
- Sorenson AW, Delhumeau C, Bernstein MS, Costanza MC, Morabia A: Impact of 'Mad Cow Disease' publicity on trends in meat and total vitamin A consumption in Geneva between 1993 and 2000. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2003 Jan;57(1):177-85. [PubMed:12548314 ]
- Alberts D, Ranger-Moore J, Einspahr J, Saboda K, Bozzo P, Liu Y, Xu XC, Lotan R, Warneke J, Salasche S, Stratton S, Levine N, Goldman R, Islas M, Duckett L, Thompson D, Bartels P, Foote J: Safety and efficacy of dose-intensive oral vitamin A in subjects with sun-damaged skin. Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Mar 15;10(6):1875-80. [PubMed:15041701 ]
- Wieringa FT, Dijkhuizen MA, West CE, Thurnham DI, Muhilal, Van der Meer JW: Redistribution of vitamin A after iron supplementation in Indonesian infants. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003 Mar;77(3):651-7. [PubMed:12600856 ]
- Egeland GM, Berti P, Soueida R, Arbour LT, Receveur O, Kuhnlein HV: Age differences in vitamin A intake among Canadian Inuit. Can J Public Health. 2004 Nov-Dec;95(6):465-9. [PubMed:15622799 ]
- Ribaya-Mercado JD, Solon FS, Fermin LS, Perfecto CS, Solon JA, Dolnikowski GG, Russell RM: Dietary vitamin A intakes of Filipino elders with adequate or low liver vitamin A concentrations as assessed by the deuterated-retinol-dilution method: implications for dietary requirements. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004 Apr;79(4):633-41. [PubMed:15051608 ]
- Kieu NT, Yurie K, Hung NT, Yamamoto S, Chuyen NV: Simultaneous analysis of retinol, beta-carotene and tocopherol levels in serum of Vietnamese populations with different incomes. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2002;11(2):92-7. [PubMed:12074187 ]
- Torma H, Vahlquist A: Vitamin A esterification in human epidermis: a relation to keratinocyte differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jan;94(1):132-8. [PubMed:2295828 ]
- Allen LH, Haskell M: Estimating the potential for vitamin A toxicity in women and young children. J Nutr. 2002 Sep;132(9 Suppl):2907S-2919S. [PubMed:12221269 ]
- Ribaya-Mercado JD, Solomons NW, Medrano Y, Bulux J, Dolnikowski GG, Russell RM, Wallace CB: Use of the deuterated-retinol-dilution technique to monitor the vitamin A status of Nicaraguan schoolchildren 1 y after initiation of the Nicaraguan national program of sugar fortification with vitamin A. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004 Nov;80(5):1291-8. [PubMed:15531678 ]
- Marquez M, Yepez CE, Sutil-Naranjo R, Rincon M: [Basic aspects and measurement of the antioxidant vitamins A and E]. Invest Clin. 2002 Sep;43(3):191-204. [PubMed:12229281 ]
- Mills JP, Penniston KL, Tanumihardjo SA: Extra-hepatic vitamin A concentrations in captive Rhesus (Macaca mulatta) and Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) monkeys fed excess vitamin A. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2005 Mar;75(2):126-32. [PubMed:15929633 ]
- Penniston KL, Tanumihardjo SA: The acute and chronic toxic effects of vitamin A. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006 Feb;83(2):191-201. [PubMed:16469975 ]
- Jumpsen JA, Brown NE, Thomson AB, Paul Man SF, Goh YK, Ma D, Clandinin MT: Fatty acids in blood and intestine following docosahexaenoic acid supplementation in adults with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2006 May;5(2):77-84. Epub 2006 Feb 28. [PubMed:16507353 ]
| Show more...
|---|