| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_1_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_1_6) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_1_7) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_6) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_7) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_8) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_9) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_10) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_11) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_12) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_13) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_14) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_15) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_16) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_17) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - NAD GC-MS (TMS_2_18) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-03di-0000029000-870aa620464a4fedbe8d | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-002r-0930610000-ccd233f26036136ba3e8 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-000i-0900000000-ec77ba41ae7dbcfd08a2 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-00dl-0219003700-2f52e3c5db41066a112c | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0uk9-0301009000-a3d0c464e56f6e320c80 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-00dl-0000090000-c18a7719161c63a71938 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0000009000-1dde5b221786fe375304 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0002-0911001000-bd16ca8021ab63e9e290 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-001i-0900000000-662adda5a00fce5c5017 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-a2724dbab2ca6eb7e8da | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-00dl-0400090000-19bb49ef6fe960f224d2 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-006x-0011297400-efee4fe3a4cf024c960a | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0028900000-8ec9bcaf25513495b979 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0011953000-577487fb6aff29c77330 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-0000009000-e1d0afb4e7926a0f845e | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-0001092010-1dcbca7a5ffe61f23e50 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0028900000-764e3ecea72fe178a87e | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0018900000-3b774fba9b96129baa6c | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-0000090000-d4236efb9eec36017416 | 2019-11-22 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-0000009000-3cb1cc8e613a3e179149 | 2016-08-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014j-0000009000-4bd400c0be81ab938465 | 2016-08-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-6920102000-5fc300f474c5dc2b8600 | 2016-08-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0000009000-96d7faa48cdd181798a0 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-1100109000-f496601a0ac75ae3d4a5 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - NAD 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-003s-9201000000-c06274c9b4d1b70a9ce2 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2019-11-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
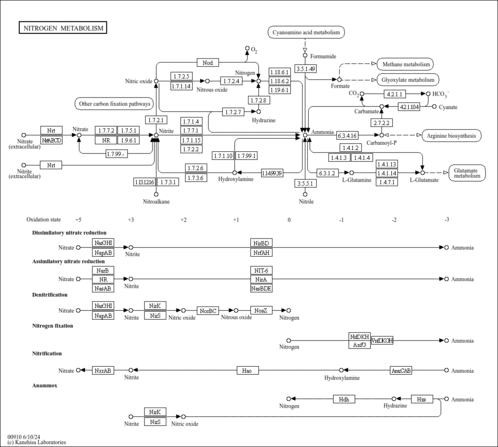
| Disease References | | Pellagra |
|---|
- Creeke PI, Dibari F, Cheung E, van den Briel T, Kyroussis E, Seal AJ: Whole blood NAD and NADP concentrations are not depressed in subjects with clinical pellagra. J Nutr. 2007 Sep;137(9):2013-7. [PubMed:17709435 ]
| | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Deficiency |
|---|
- Shi H, Enriquez A, Rapadas M, Martin EMMA, Wang R, Moreau J, Lim CK, Szot JO, Ip E, Hughes JN, Sugimoto K, Humphreys DT, McInerney-Leo AM, Leo PJ, Maghzal GJ, Halliday J, Smith J, Colley A, Mark PR, Collins F, Sillence DO, Winlaw DS, Ho JWK, Guillemin GJ, Brown MA, Kikuchi K, Thomas PQ, Stocker R, Giannoulatou E, Chapman G, Duncan EL, Sparrow DB, Dunwoodie SL: NAD Deficiency, Congenital Malformations, and Niacin Supplementation. N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 10;377(6):544-552. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1616361. [PubMed:28792876 ]
|
|
|---|
| General References | - Brautigam CA, Chuang JL, Tomchick DR, Machius M, Chuang DT: Crystal structure of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase: NAD+/NADH binding and the structural basis of disease-causing mutations. J Mol Biol. 2005 Jul 15;350(3):543-52. [PubMed:15946682 ]
- Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Nakayama Y, Kinoshita A, Tomita M: Dynamic simulation of red blood cell metabolism and its application to the analysis of a pathological condition. Theor Biol Med Model. 2005 May 9;2:18. [PubMed:15882454 ]
- Ying W: NAD+ and NADH in cellular functions and cell death. Front Biosci. 2006 Sep 1;11:3129-48. [PubMed:16720381 ]
- Hamza A, Cho H, Tai HH, Zhan CG: Understanding human 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase binding with NAD+ and PGE2 by homology modeling, docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005 Jul 15;13(14):4544-51. [PubMed:15908215 ]
- Begonja AJ, Gambaryan S, Geiger J, Aktas B, Pozgajova M, Nieswandt B, Walter U: Platelet NAD(P)H-oxidase-generated ROS production regulates alphaIIbbeta3-integrin activation independent of the NO/cGMP pathway. Blood. 2005 Oct 15;106(8):2757-60. Epub 2005 Jun 23. [PubMed:15976180 ]
- Bruzzone S, Moreschi I, Guida L, Usai C, Zocchi E, De Flora A: Extracellular NAD+ regulates intracellular calcium levels and induces activation of human granulocytes. Biochem J. 2006 Feb 1;393(Pt 3):697-704. [PubMed:16225456 ]
- Kim MY, Zhang T, Kraus WL: Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation by PARP-1: 'PAR-laying' NAD+ into a nuclear signal. Genes Dev. 2005 Sep 1;19(17):1951-67. [PubMed:16140981 ]
- Kunsman GW, Manno JE, Cockerham KR, Manno BR: A modification and validation of two urine ethanol procedures for use with the Monarch 2000 Chemistry System. J Anal Toxicol. 1991 May-Jun;15(3):130-5. [PubMed:1943056 ]
- Orczyk J, Morre DM, Morre DJ: Periodic fluctuations in oxygen consumption comparing HeLa (cancer) and CHO (non-cancer) cells and response to external NAD(P)+/NAD(P)H. Mol Cell Biochem. 2005 May;273(1-2):161-7. [PubMed:16013451 ]
- Krotz F, Sohn HY, Gloe T, Zahler S, Riexinger T, Schiele TM, Becker BF, Theisen K, Klauss V, Pohl U: NAD(P)H oxidase-dependent platelet superoxide anion release increases platelet recruitment. Blood. 2002 Aug 1;100(3):917-24. [PubMed:12130503 ]
- Elshenawy S, Pinney SE, Stuart T, Doulias PT, Zura G, Parry S, Elovitz MA, Bennett MJ, Bansal A, Strauss JF 3rd, Ischiropoulos H, Simmons RA: The Metabolomic Signature of the Placenta in Spontaneous Preterm Birth. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3). pii: ijms21031043. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031043. [PubMed:32033212 ]
| Show more...
|---|