| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-05-22 14:17:38 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:13 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0002152 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 11-cis-Retinaldehyde |
|---|
| Description | 11-cis-retinal is a retinal having 2E,4Z,6E,8E-double bond geometry. It has a role as a chromophore, a human metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a diterpene derived from the carotenoid vitamin A which functions as the active component of the visual cycle. It is the prosthetic group of rhodopsin. When stimulated by visible light, rhodopsin transforms this cis-isomer of retinal to the trans-isomer (11-trans-retinal). This transformation straightens-out the bend of the retinal molecule and causes a change in the shape of rhodopsin triggering the visual process. A series of energy-requiring enzyme-catalyzed reactions convert the 11-trans-retinal back to the cis-isomer. 11-cis-retinal functions in the retina in the transduction of light into the neural signals necessary for vision. 11-cis-retinal, while attached to opsin in rhodopsin is isomerized to all-trans-retinal by light. This is the event that triggers the nerve impulse to the brain which allows for the perception of light. All-trans-retinal is then released from opsin and reduced to all-trans-retinol. All-trans-retinol is isomerized to 11-cis-retinol in the dark, and then oxidized to 11-cis-retinal. 11-cis-retinal recombines with opsin to re-form rhodopsin. Night blindness or defective vision at low illumination results from a failure to resynthesize 11-cis retinal rapidly. |
|---|
| Structure | C/C(/C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C)=C\C=O InChI=1S/C20H28O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-13,15H,7,10,14H2,1-5H3/b9-6-,12-11+,16-8+,17-13+ |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (2E,4Z,6E,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal | ChEBI | | 11-cis-Retinene | ChEBI | | 11-cis-Vitamin a aldehyde | ChEBI | | 11-cis-Retinal | HMDB | | cis-11-Retinal | HMDB | | 11 cis Retinal | MeSH, HMDB | | Retinaldehyde | MeSH, HMDB | | Retinene | MeSH, HMDB | | Retinal | MeSH, HMDB | | Aldehyde, vitamin a | MeSH, HMDB | | Vitamin a aldehyde | MeSH, HMDB | | Axerophthal | MeSH, HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H28O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 284.4357 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 284.214015518 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2E,4Z,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 11-cis-retinal |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 564-87-4 |
|---|
| SMILES | C/C(/C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C)=C\C=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H28O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-13,15H,7,10,14H2,1-5H3/b9-6-,12-11+,16-8+,17-13+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | NCYCYZXNIZJOKI-IOUUIBBYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as retinoids. These are oxygenated derivatives of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene and derivatives thereof. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Retinoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Retinoids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Retinoid skeleton
- Diterpenoid
- Enal
- Alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehyde
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aldehyde
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 63.5 - 64.4 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized | Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-014i-2290000000-df9d2aa7545cc60a54f9 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-1490000000-97cddfba9819c3417386 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-001s-3920000000-0be8a19c3cba33e3b06b | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0kui-9720000000-a579102a9f5600032e3f | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0090000000-e7d5d678e91ec531c2ae | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a59-0090000000-8af2668c966a1c8a3cef | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00ku-3690000000-54506b9021b67caed041 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00n3-1960000000-43f8c66f164764c37361 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0609-3920000000-dbeab0a82b306761cf6a | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-052f-7900000000-d2bb7c1aeeb87d8833d2 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a59-0090000000-2ec2f8f314943441fa15 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-0190000000-312cebb17ccd0189ab4d | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 11-cis-Retinaldehyde 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-1590000000-b2551eac481c0c930a4d | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, CDCl3, experimental) | 2018-05-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Membrane
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
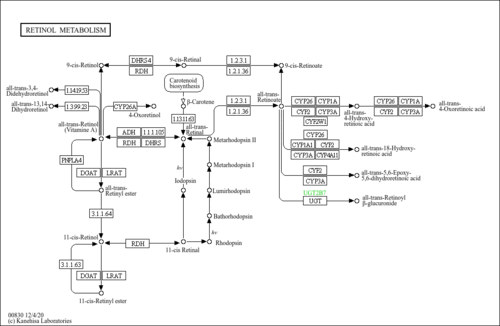
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | None |
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | None |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB022871 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 4444130 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C02110 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CPD-881 |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 2265510 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 6513 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 5280490 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 16066 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | RETINAL_11_CIS |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Ito, Masayoshi; Wada, Akimori. Preparation of 11-cis-Retinal and their intermediates. Jpn. Kokai Tokkyo Koho (1998), 12 pp. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Bankson DD, Russell RM, Sadowski JA: Determination of retinyl esters and retinol in serum or plasma by normal-phase liquid chromatography: method and applications. Clin Chem. 1986 Jan;32(1 Pt 1):35-40. [PubMed:3940733 ]
- Futterman S, Saari JC: Occurrence of 11-cis-retinal-binding protein restricted to the retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977 Aug;16(8):768-71. [PubMed:560359 ]
- Brunk E, Sahoo S, Zielinski DC, Altunkaya A, Drager A, Mih N, Gatto F, Nilsson A, Preciat Gonzalez GA, Aurich MK, Prlic A, Sastry A, Danielsdottir AD, Heinken A, Noronha A, Rose PW, Burley SK, Fleming RMT, Nielsen J, Thiele I, Palsson BO: Recon3D enables a three-dimensional view of gene variation in human metabolism. Nat Biotechnol. 2018 Mar;36(3):272-281. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4072. Epub 2018 Feb 19. [PubMed:29457794 ]
|
|---|