| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-05-22 14:17:49 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:15 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0002356 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0060125
- HMDB02356
- HMDB60125
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Hexacosanoic acid |
|---|
| Description | Hexacosanoic acid, or cerotic acid, is a 26-carbon long-chain saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)24COOH. It is most commonly found in beeswax and carnauba wax, and is a white crystalline solid. Cerotic acid is also a type of very long chain fatty acid that is often associated with the disease adrenoleukodystrophy, which involves the excessive saturation of unmetabolized fatty acid chains, including cerotic acid, in the peroxisome. Hexacosanoic acid, also known as C26:0 or N-hexacosanoate, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as very long-chain fatty acids. These are fatty acids with an aliphatic tail that contains at least 22 carbon atoms. Hexacosanoic acid is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble in water, and relatively neutral. Hexacosanoic acid is a potentially toxic compound. |
|---|
| Structure | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O InChI=1S/C26H52O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20-21-22-23-24-25-26(27)28/h2-25H2,1H3,(H,27,28) |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| C26:0 | ChEBI | | Ceratinic acid | ChEBI | | Ceric acid | ChEBI | | Cerinic acid | ChEBI | | Cerotic acid | ChEBI | | Cerotinic acid | ChEBI | | Cerylic acid | ChEBI | | CH3-[CH2]24-COOH | ChEBI | | Hexacosansaeure | ChEBI | | Hexacosoic acid | ChEBI | | Hexaeicosanoic acid | ChEBI | | N-C26:0 | ChEBI | | N-Hexacosanoic acid | ChEBI | | Ceratinate | Generator | | Cerate | Generator | | Cerinate | Generator | | Cerotate | Generator | | Cerotinate | Generator | | Cerylate | Generator | | Hexacosoate | Generator | | Hexaeicosanoate | Generator | | N-Hexacosanoate | Generator | | Hexacosanoate | Generator | | Hexacosanoate (N-C26:0) | HMDB | | Hexacosanoic acid | PhytoBank | | FA(26:0) | PhytoBank |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C26H52O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 396.6899 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 396.396730908 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | hexacosanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | hexacosanoic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 506-46-7 |
|---|
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C26H52O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20-21-22-23-24-25-26(27)28/h2-25H2,1H3,(H,27,28) |
|---|
| InChI Key | XMHIUKTWLZUKEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as very long-chain fatty acids. These are fatty acids with an aliphatic tail that contains at least 22 carbon atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acids and conjugates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Very long-chain fatty acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Very long-chain fatty acid
- Straight chain fatty acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 88.5 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized | Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid GC-MS (1 TMS) | splash10-0159-2900100000-dc0324482e5853e76290 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0159-2900100000-dc0324482e5853e76290 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0159-2900100000-dc0324482e5853e76290 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0159-1900000000-9d83fa08f63878dd9794 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-8890000000-a358b076f9e4d3b08976 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0fmr-9550000000-f90d4cc6a83ff8e16245 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0597-9201000000-41113a5b904c5db7332d | 2014-09-20 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0a4j-0109000000-bc2c74027165503fd92f | 2012-07-25 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0pb9-2193000000-cf0ac4a96f99022c7b3a | 2012-07-25 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0w30-6096000000-65025824de97c5fb5ff7 | 2012-07-25 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid n/a 27V, negative-QTOF | splash10-00lr-0009000000-998e2947790abd467bc7 | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-002b-0009000000-bd3c909a0431684b20e7 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0ug1-3439000000-ca5336c838aa14069626 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000f-6974000000-93ebd8f603ed3f48dd9d | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0009000000-50e9c7751bdac41b78c8 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0f6t-0009000000-fdc9aa019c323235312e | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4l-9113000000-af814ec2317a697df1a0 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0009000000-87ff11014d638fb7aedd | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-002b-1009000000-28b98f74e9fa6d052c38 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9003000000-9b4d6e9900769e9411a5 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-002b-2009000000-459e9bac675c0081de3d | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-056s-7039000000-16142145274003e6395d | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hexacosanoic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4l-9010000000-33f6f730f4cbdee5a975 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, CDCl3, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Membrane
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Adrenal Gland
- Fibroblasts
|
|---|
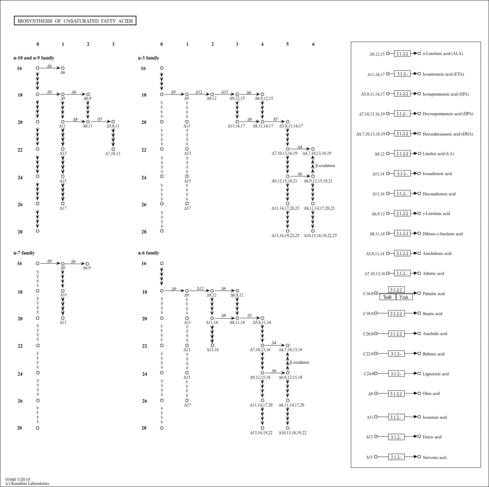
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.110 +/- 0.006 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | <0.9 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.832 +/- 0.454 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.832 +/- 0.454 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.45-1.32 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.83 +/- 0.45 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.781 (0.277-1.563) uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.790 (0.450-1.320) uM | Not Specified | Both | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.0-1.3 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | Mental retardation, enteropathy, deafness, peripheral neuropathy, ichthyosis, and keratoderma | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.993 (0.252-1.622) uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Adrenoleukodystrophy, neonatal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 6.806 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Male | Pseudo Zellweger->D-bifunctional protein deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 7.167 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Pseudoneonatal adrenoleukodystrophy | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.571-4.512 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.26 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 5.4 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | D-Bifunctional Protein Deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.21 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Male | Peroxisomal biogenesis disorder | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.33 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Female | Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 4.10 (2.42 - 6.43) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Adrenomyeloneuropathy | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 7.9 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Not Specified | Zellweger syndrome | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.300-2.370 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Peroxisomal biogenesis disorder | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.0167-2.0923 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | Peroxisomal disorders, new type, liver | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 4.710-6.700 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Female | Peroxisomal biogenesis disorder | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 7.200-18.400 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Not Specified | Neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 7.310 (4.185-11.218) uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Zellweger syndrome | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Adrenomyeloneuropathy |
|---|
- Sadeghi-Nejad A, Senior B: Adrenomyeloneuropathy presenting as Addison's disease in childhood. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 4;322(1):13-6. [PubMed:2294415 ]
| | Adrenoleukodystrophy, neonatal |
|---|
- G.Frauendienst-Egger, Friedrich K. Trefz (2017). MetaGene: Metabolic & Genetic Information Center (MIC: http://www.metagene.de). METAGENE consortium.
| | Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata |
|---|
- Baumgartner MR, Poll-The BT, Verhoeven NM, Jakobs C, Espeel M, Roels F, Rabier D, Levade T, Rolland MO, Martinez M, Wanders RJ, Saudubray JM: Clinical approach to inherited peroxisomal disorders: a series of 27 patients. Ann Neurol. 1998 Nov;44(5):720-30. [PubMed:9818927 ]
| | Peroxisomal biogenesis defect |
|---|
- Baumgartner MR, Poll-The BT, Verhoeven NM, Jakobs C, Espeel M, Roels F, Rabier D, Levade T, Rolland MO, Martinez M, Wanders RJ, Saudubray JM: Clinical approach to inherited peroxisomal disorders: a series of 27 patients. Ann Neurol. 1998 Nov;44(5):720-30. [PubMed:9818927 ]
- Mandel H, Espeel M, Roels F, Sofer N, Luder A, Iancu TC, Aizin A, Berant M, Wanders RJ, Schutgens RB: A new type of peroxisomal disorder with variable expression in liver and fibroblasts. J Pediatr. 1994 Oct;125(4):549-55. [PubMed:7931872 ]
| | Peroxisomal disorders, new type, liver |
|---|
- Mandel H, Espeel M, Roels F, Sofer N, Luder A, Iancu TC, Aizin A, Berant M, Wanders RJ, Schutgens RB: A new type of peroxisomal disorder with variable expression in liver and fibroblasts. J Pediatr. 1994 Oct;125(4):549-55. [PubMed:7931872 ]
- G.Frauendienst-Egger, Friedrich K. Trefz (2017). MetaGene: Metabolic & Genetic Information Center (MIC: http://www.metagene.de). METAGENE consortium.
| | Adrenoleukodystrophy |
|---|
- Steinberg SJ, Fensom AH, Dalton NR, Toseland PA, Kennedy CR, Mowat AP: Measurement of plasma very long-chain fatty acids as a preliminary screening procedure for the diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1994;17(3):323-6. [PubMed:7807943 ]
- ten Brink HJ, van den Heuvel CM, Poll-The BT, Wanders RJ, Jakobs C: Peroxisomal disorders: concentrations of metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid compared with plasma. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1993;16(3):587-90. [PubMed:7609459 ]
| | D-Bifunctional protein deficiency |
|---|
- Watkins PA, Chen WW, Harris CJ, Hoefler G, Hoefler S, Blake DC Jr, Balfe A, Kelley RI, Moser AB, Beard ME, et al.: Peroxisomal bifunctional enzyme deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):771-7. [PubMed:2921319 ]
- Rizzo C, Boenzi S, Wanders RJ, Duran M, Caruso U, Dionisi-Vici C: Characteristic acylcarnitine profiles in inherited defects of peroxisome biogenesis: a novel tool for screening diagnosis using tandem mass spectrometry. Pediatr Res. 2003 Jun;53(6):1013-8. doi: 10.1203/01.PDR.0000064902.59052.0F. Epub 2003 Mar 19. [PubMed:12646728 ]
| | Pseudoneonatal adrenoleukodystrophy |
|---|
- Poll-The BT, Roels F, Ogier H, Scotto J, Vamecq J, Schutgens RB, Wanders RJ, van Roermund CW, van Wijland MJ, Schram AW, et al.: A new peroxisomal disorder with enlarged peroxisomes and a specific deficiency of acyl-CoA oxidase (pseudo-neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy). Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;42(3):422-34. [PubMed:2894756 ]
| | Mental retardation, enteropathy, deafness, peripheral neuropathy, ichthyosis, and keratoderma |
|---|
- Martinelli D, Travaglini L, Drouin CA, Ceballos-Picot I, Rizza T, Bertini E, Carrozzo R, Petrini S, de Lonlay P, El Hachem M, Hubert L, Montpetit A, Torre G, Dionisi-Vici C: MEDNIK syndrome: a novel defect of copper metabolism treatable by zinc acetate therapy. Brain. 2013 Mar;136(Pt 3):872-81. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt012. Epub 2013 Feb 18. [PubMed:23423674 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 300100 (Adrenomyeloneuropathy)
- 215100 (Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata)
- 214100 (Peroxisomal biogenesis defect)
- 300100 (Adrenoleukodystrophy)
- 261515 (D-Bifunctional protein deficiency)
- 264470 (Pseudoneonatal adrenoleukodystrophy)
- 609313 (Mental retardation, enteropathy, deafness, peripheral neuropathy, ichthyosis, and keratoderma)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB004035 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00035114 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 10037 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 1459812 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Cerotic acid |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 6642 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 10469 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 31009 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | HEXC |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000391 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Tsuji S; Sano T; Ariga T; Miyatake T Increased synthesis of hexacosanoic acid (C23:0) by cultured skin fibroblasts from patients with adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) and adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN). Journal of biochemistry (1981), 90(4), 1233-6. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Dhaunsi GS, Kaur J, Alsaeid K, Turner RB, Bitar MS: Very long chain fatty acids activate NADPH oxidase in human dermal fibroblasts. Cell Biochem Funct. 2005 Jan-Feb;23(1):65-8. [PubMed:15565636 ]
- Moser HW, Moser AB, Powers JM, Nitowsky HM, Schaumburg HH, Norum RA, Migeon BR: The prenatal diagnosis of adrenoleukodystrophy. Demonstration of increased hexacosanoic acid levels in cultured amniocytes and fetal adrenal gland. Pediatr Res. 1982 Mar;16(3):172-5. [PubMed:7063272 ]
- Thiele I, Swainston N, Fleming RM, Hoppe A, Sahoo S, Aurich MK, Haraldsdottir H, Mo ML, Rolfsson O, Stobbe MD, Thorleifsson SG, Agren R, Bolling C, Bordel S, Chavali AK, Dobson P, Dunn WB, Endler L, Hala D, Hucka M, Hull D, Jameson D, Jamshidi N, Jonsson JJ, Juty N, Keating S, Nookaew I, Le Novere N, Malys N, Mazein A, Papin JA, Price ND, Selkov E Sr, Sigurdsson MI, Simeonidis E, Sonnenschein N, Smallbone K, Sorokin A, van Beek JH, Weichart D, Goryanin I, Nielsen J, Westerhoff HV, Kell DB, Mendes P, Palsson BO: A community-driven global reconstruction of human metabolism. Nat Biotechnol. 2013 May;31(5):419-25. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2488. Epub 2013 Mar 3. [PubMed:23455439 ]
- Deon M, Wajner M, Sirtori LR, Fitarelli D, Coelho DM, Sitta A, Barschak AG, Ferreira GC, Haeser A, Giugliani R, Vargas CR: The effect of Lorenzo's oil on oxidative stress in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 2006 Sep 25;247(2):157-64. Epub 2006 Jun 5. [PubMed:16750542 ]
- Brunk E, Sahoo S, Zielinski DC, Altunkaya A, Drager A, Mih N, Gatto F, Nilsson A, Preciat Gonzalez GA, Aurich MK, Prlic A, Sastry A, Danielsdottir AD, Heinken A, Noronha A, Rose PW, Burley SK, Fleming RMT, Nielsen J, Thiele I, Palsson BO: Recon3D enables a three-dimensional view of gene variation in human metabolism. Nat Biotechnol. 2018 Mar;36(3):272-281. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4072. Epub 2018 Feb 19. [PubMed:29457794 ]
|
|---|