| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-05-22 15:12:36 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2021-09-14 15:39:02 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0003141 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Retinoyl b-glucuronide |
|---|
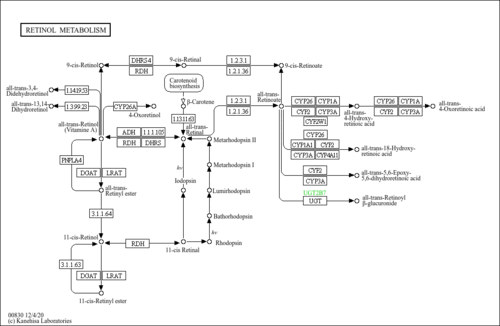
| Description | Retinoyl beta-glucuronide is a naturally occurring, biologically active metabolite of vitamin A. Although retinoyl beta-glucuronide is regarded as a detoxification product of retinoic acid, it plays several roles in the functions of vitamin A. It can serve as a source of retinoic acid, and it may be a vehicle for transport of retinoic acid to target tissues. Topically applied retinoyl beta-glucuronide is comparable in efficacy to retinoic acid in the treatment of acne in humans, without the same side effects. Retinoyl beta-glucuronide may or may not be teratogenic, depending on the mode of administration and the species in which it is used. It may be a valuable therapeutic compound for the treatment of skin disorders and certain types of cancers. |
|---|
| Structure | O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O[C@H](C(O)=O)[C@H]1O)OC(=O)\C=C(/C)\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C InChI=1S/C26H36O8/c1-15(11-12-18-17(3)10-7-13-26(18,4)5)8-6-9-16(2)14-19(27)33-25-22(30)20(28)21(29)23(34-25)24(31)32/h6,8-9,11-12,14,20-23,25,28-30H,7,10,13H2,1-5H3,(H,31,32)/b9-6+,12-11+,15-8+,16-14+/t20-,21-,22+,23-,25+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| all-trans-Retinoyl-beta-glucuronide | ChEBI | | Retinoyl glucuronide | ChEBI | | all-trans-Retinoyl-b-glucuronide | Generator | | all-trans-Retinoyl-β-glucuronide | Generator | | 13-cis-Retinoate | HMDB | | 13-cis-Retinoic acid | HMDB | | 13-cis-Retinoic acid acyl beta-D-glucuronide | HMDB | | 13-cis-Retinoic acid acyl beta-delta-glucuronide | HMDB | | 13-cis-Retinoyl glucuronide | HMDB | | 13-cis-Retinoyl-beta-D-glucuronide | HMDB | | 13-cis-Retinoyl-beta-delta-glucuronide | HMDB | | 13-cis-Retinoyl-beta-glucuronide | HMDB | | 9-cis-Retinoyl-beta-D-glucuronide | HMDB | | 9-cis-Retinoyl-beta-delta-glucuronide | HMDB | | all-trans-Retinoyl-beta-D-glucuronide | HMDB | | all-trans-Retinoyl-beta-delta-glucuronide | HMDB | | Glucuronide | HMDB | | Retinoate | HMDB | | Retinoic acid | HMDB | | Retinoic acid beta-D-glucuronide | HMDB | | Retinoic acid beta-delta-glucuronide | HMDB | | Retinoyl beta-glucuronide | HMDB | | Retinoyl-beta-glucuronide | HMDB | | trans-Retinoyl glucuronide | MeSH, HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C26H36O8 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 476.5592 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 476.241018128 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-{[(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoyl]oxy}-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | glucuronide |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 401-10-5 |
|---|
| SMILES | O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O[C@H](C(O)=O)[C@H]1O)OC(=O)\C=C(/C)\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C26H36O8/c1-15(11-12-18-17(3)10-7-13-26(18,4)5)8-6-9-16(2)14-19(27)33-25-22(30)20(28)21(29)23(34-25)24(31)32/h6,8-9,11-12,14,20-23,25,28-30H,7,10,13H2,1-5H3,(H,31,32)/b9-6+,12-11+,15-8+,16-14+/t20-,21-,22+,23-,25+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | MTGFYEHKPMOVNE-NEFMKCFNSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as diterpene glycosides. These are diterpenoids in which an isoprene unit is glycosylated. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Terpene glycosides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Diterpene glycosides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Diterpene glycoside
- Retinoid ester
- Diterpenoid
- Retinoid skeleton
- 1-o-glucuronide
- O-glucuronide
- Glucuronic acid or derivatives
- Hexose monosaccharide
- Beta-hydroxy acid
- Fatty acid ester
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Fatty acyl
- Hydroxy acid
- Monosaccharide
- Oxane
- Pyran
- Alpha,beta-unsaturated carboxylic ester
- Enoate ester
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Polyol
- Oxacycle
- Acetal
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Retinoyl b-glucuronide,1TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3755.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,1TMS,isomer #2 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3766.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,1TMS,isomer #3 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3728.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,1TMS,isomer #4 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3753.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3701.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TMS,isomer #2 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3700.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TMS,isomer #3 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3704.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TMS,isomer #4 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3702.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TMS,isomer #5 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3711.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TMS,isomer #6 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3701.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,3TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3666.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,3TMS,isomer #2 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3675.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,3TMS,isomer #3 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3691.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,3TMS,isomer #4 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3683.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,4TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3660.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3972.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3985.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3963.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,1TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 3971.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 4136.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 4131.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 4137.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 4139.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 4140.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,2TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 4139.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 4278.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 4291.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 4290.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Retinoyl b-glucuronide,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1 | 4313.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|
| General References | - Yamanaka H, Nakajima M, Katoh M, Kanoh A, Tamura O, Ishibashi H, Yokoi T: Trans-3'-hydroxycotinine O- and N-glucuronidations in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Jan;33(1):23-30. Epub 2004 Oct 6. [PubMed:15470160 ]
- Matsushima S, Maeda K, Kondo C, Hirano M, Sasaki M, Suzuki H, Sugiyama Y: Identification of the hepatic efflux transporters of organic anions using double-transfected Madin-Darby canine kidney II cells expressing human organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1)/multidrug resistance-associated protein 2, OATP1B1/multidrug resistance 1, and OATP1B1/breast cancer resistance protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Sep;314(3):1059-67. Epub 2005 May 18. [PubMed:15901800 ]
- Kosoglou T, Statkevich P, Johnson-Levonas AO, Paolini JF, Bergman AJ, Alton KB: Ezetimibe: a review of its metabolism, pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005;44(5):467-94. [PubMed:15871634 ]
- Kochansky CJ, Xia YQ, Wang S, Cato B, Creighton M, Vincent SH, Franklin RB, Reed JR: Species differences in the elimination of a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonist highlighted by oxidative metabolism of its acyl glucuronide. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Dec;33(12):1894-904. Epub 2005 Sep 23. [PubMed:16183782 ]
- Ghosal A, Yuan Y, Hapangama N, Su AD, Alvarez N, Chowdhury SK, Alton KB, Patrick JE, Zbaida S: Identification of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzyme(s) responsible for the glucuronidation of 3-hydroxydesloratadine. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2004 Sep;25(6):243-52. [PubMed:15334623 ]
- Brunelle FM, Verbeeck RK: Glucuronidation of diflunisal in liver and kidney microsomes of rat and man. Xenobiotica. 1996 Feb;26(2):123-31. [PubMed:8867997 ]
- Niles RM, Cook CP, Meadows GG, Fu YM, McLaughlin JL, Rankin GO: Resveratrol is rapidly metabolized in athymic (nu/nu) mice and does not inhibit human melanoma xenograft tumor growth. J Nutr. 2006 Oct;136(10):2542-6. [PubMed:16988123 ]
- Sass JO, Masgrau E, Saurat JH, Nau H: Metabolism of oral 9-cis-retinoic acid in the human. Identification of 9-cis-retinoyl-beta-glucuronide and 9-cis-4-oxo-retinoyl-beta-glucuronide as urinary metabolites. Drug Metab Dispos. 1995 Sep;23(9):887-91. [PubMed:8565776 ]
- Calabrese CR, Loadman PM, Lim LS, Bibby MC, Double JA, Brown JE, Lamb JH: In vivo metabolism of the antitumor imidazoacridinone C1311 in the mouse and in vitro comparison with humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 1999 Feb;27(2):240-5. [PubMed:9929509 ]
- Sperker B, Murdter TE, Schick M, Eckhardt K, Bosslet K, Kroemer HK: Interindividual variability in expression and activity of human beta-glucuronidase in liver and kidney: consequences for drug metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 May;281(2):914-20. [PubMed:9152401 ]
- Moss T, Howes D, Williams FM: Percutaneous penetration and dermal metabolism of triclosan (2,4, 4'-trichloro-2'-hydroxydiphenyl ether). Food Chem Toxicol. 2000 Apr;38(4):361-70. [PubMed:10722890 ]
- Cunha PD, Lord RS, Johnson ST, Wilker PR, Aster RH, Bougie DW: Immune hemolytic anemia caused by sensitivity to a metabolite of etodolac, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Transfusion. 2000 Jun;40(6):663-8. [PubMed:10864985 ]
- Nordin C, Bertilsson L: Active hydroxymetabolites of antidepressants. Emphasis on E-10-hydroxy-nortriptyline. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1995 Jan;28(1):26-40. [PubMed:7712660 ]
- Johnson AG, Rigby RJ, Taylor PJ, Jones CE, Allen J, Franzen K, Falk MC, Nicol D: The kinetics of mycophenolic acid and its glucuronide metabolite in adult kidney transplant recipients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Nov;66(5):492-500. [PubMed:10579476 ]
- Oswald S, Haenisch S, Fricke C, Sudhop T, Remmler C, Giessmann T, Jedlitschky G, Adam U, Dazert E, Warzok R, Wacke W, Cascorbi I, Kroemer HK, Weitschies W, von Bergmann K, Siegmund W: Intestinal expression of P-glycoprotein (ABCB1), multidrug resistance associated protein 2 (ABCC2), and uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 predicts the disposition and modulates the effects of the cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Mar;79(3):206-17. Epub 2006 Feb 7. [PubMed:16513445 ]
- Kenny JR, Maggs JL, Tettey JN, Harrell AW, Parker SG, Clarke SE, Park BK: Formation and protein binding of the acyl glucuronide of a leukotriene B4 antagonist (SB-209247): relation to species differences in hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Feb;33(2):271-81. Epub 2004 Nov 2. [PubMed:15523047 ]
- Qiao GL, Williams PL, Riviere JE: Percutaneous absorption, biotransformation, and systemic disposition of parathion in vivo in swine. I. Comprehensive pharmacokinetic model. Drug Metab Dispos. 1994 May-Jun;22(3):459-71. [PubMed:8070325 ]
- Ethell BT, Riedel J, Englert H, Jantz H, Oekonomopulos R, Burchell B: Glucuronidation of HMR1098 in human microsomes: evidence for the involvement of UGT1A1 in the formation of S-glucuronides. Drug Metab Dispos. 2003 Aug;31(8):1027-34. [PubMed:12867491 ]
- Andersen A: Final report on the safety assessment of sodium p-chloro-m-cresol, p-chloro-m-cresol, chlorothymol, mixed cresols, m-cresol, o-cresol, p-cresol, isopropyl cresols, thymol, o-cymen-5-ol, and carvacrol. Int J Toxicol. 2006;25 Suppl 1:29-127. [PubMed:16835130 ]
- Sallustio BC, Sabordo L, Evans AM, Nation RL: Hepatic disposition of electrophilic acyl glucuronide conjugates. Curr Drug Metab. 2000 Sep;1(2):163-80. [PubMed:11465081 ]
|
|---|