| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-05-22 15:12:43 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-07-12 23:05:07 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0003235 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0005100
- HMDB03235
- HMDB05100
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Prostaglandin G2 |
|---|
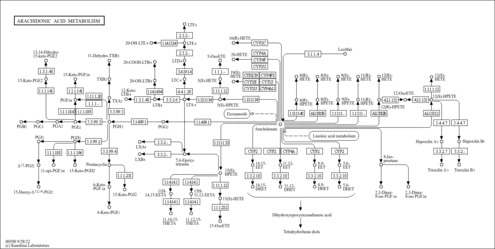
| Description | Prostaglandin G2 (PGG2) is synthesized from arachidonic acid on a cyclooxygenase (COX) metabolic pathway as a primary step; the COX biosynthesis of prostaglandin (PG) begins with the highly specific oxygenation of arachidonic acid in the 11R configuration and ends with a 15S oxygenation to form PGG2. The COX site activity that catalyzes the conversion of arachidonic acid to PGG2 is the target for nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The peroxidase site activity catalyzes the two-electron reduction of the hydroperoxide bond of PGG2 to yield the corresponding alcohol prostaglandin H2 (PGH2). The formation of a phenoxyl radical on Tyr385 couples the activities of the two sites. The Tyr385 radical is produced via oxidation by compound I, an oxoferryl porphyrin -cation radical, which is generated by reaction of the hemin resting state with PGG2 or other hydroperoxides. The tyrosyl radical homolytically abstracts the 13proS hydrogen atom of arachidonic acid which initiates a radical cascade that ends with the stereoselective formation of PGG2. PGG2 then migrates from the cyclooxygenase (COX) site to the peroxidase (POX) site where it reacts with the hemin group to generate PGH2 and compound I. The heterolytic oxygen-oxygen bond cleavage is assisted by the conserved distal residues His207 and Gln203, mutation of which has been shown to severely impair enzyme activity. Compound I, upon reaction with Tyr385, gives compound II, which in turn is reduced to the hemin resting state by one-electron oxidation of reducing cosubstrates or undergoes reactions that result in enzyme self-inactivation. Prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase (PGHS) 1 is a bifunctional membrane enzyme of the endoplasmic reticulum that converts arachidonic acid into prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), the precursor of all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and prostacyclins. These lipid mediators are intricately involved in normal physiology, namely, in mitogenesis, fever generation, pain response, lymphocyte chemotaxis, fertility, and contradictory stimuli such as vasoconstriction and vasodilatation, as well as platelet aggregation and quiescence. PGHS is implicated in numerous pathologies, including inflammation, cancers of the colon, lung, and breast, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and numerous cardiovascular diseases including atherosclerosis, thrombosis, myocardial infarction, and stroke. (PMID: 14594816 , 16552393 , 16411757 ). Prostaglandins are eicosanoids. The eicosanoids consist of the prostaglandins (PGs), thromboxanes (TXs), leukotrienes (LTs), and lipoxins (LXs). The PGs and TXs are collectively identified as prostanoids. Prostaglandins were originally shown to be synthesized in the prostate gland, thromboxanes from platelets (thrombocytes), and leukotrienes from leukocytes, hence the derivation of their names. All mammalian cells except erythrocytes synthesize eicosanoids. These molecules are extremely potent, able to cause profound physiological effects at very dilute concentrations. All eicosanoids function locally at the site of synthesis, through receptor-mediated G-protein linked signalling pathways. |
|---|
| Structure | [H][C@@](CCCCC)(OO)\C=C\[C@@]1([H])[C@@]2([H])C[C@]([H])(OO2)[C@]1([H])C\C=C/CCCC(O)=O InChI=1S/C20H32O6/c1-2-3-6-9-15(24-23)12-13-17-16(18-14-19(17)26-25-18)10-7-4-5-8-11-20(21)22/h4,7,12-13,15-19,23H,2-3,5-6,8-11,14H2,1H3,(H,21,22)/b7-4-,13-12+/t15-,16+,17+,18-,19+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| PGG2 | ChEBI | | (5Z)-7-{(1R,4S,5R,6R)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroperoxyoct-1-en-1-yl]-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-yl}hept-5-enoate | HMDB | | (5Z)-7-{(1R,4S,5R,6R)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroperoxyoct-1-en-1-yl]-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-yl}hept-5-enoic acid | HMDB | | 9,11-Epidioxy-15-hydroperoxy-prosta-5,13-dien-1-Oate | HMDB | | 9,11-Epidioxy-15-hydroperoxy-prosta-5,13-dien-1-Oic acid | HMDB | | 9S,11R-Epidioxy-15S-hydroperoxy-5Z,13E-prostadienoate | HMDB | | 9S,11R-Epidioxy-15S-hydroperoxy-5Z,13E-prostadienoic acid | HMDB | | Endoperoxide g2 | HMDB | | PGG(2) | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H32O6 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 368.4645 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 368.219888756 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (5Z)-7-[(1R,4S,5R,6R)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroperoxyoct-1-en-1-yl]-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-5-yl]hept-5-enoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | prostaglandin G2 |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 51982-36-6 |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@](CCCCC)(OO)\C=C\[C@@]1([H])[C@@]2([H])C[C@]([H])(OO2)[C@]1([H])C\C=C/CCCC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H32O6/c1-2-3-6-9-15(24-23)12-13-17-16(18-14-19(17)26-25-18)10-7-4-5-8-11-20(21)22/h4,7,12-13,15-19,23H,2-3,5-6,8-11,14H2,1H3,(H,21,22)/b7-4-,13-12+/t15-,16+,17+,18-,19+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | SGUKUZOVHSFKPH-YNNPMVKQSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as prostaglandins and related compounds. These are unsaturated carboxylic acids consisting of a 20 carbon skeleton that also contains a five member ring, and are based upon the fatty acid arachidonic acid. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Eicosanoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Prostaglandins and related compounds |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Prostaglandin skeleton
- Long-chain fatty acid
- Hydroperoxy fatty acid
- Heterocyclic fatty acid
- Ortho-dioxane
- Fatty acid
- Unsaturated fatty acid
- Allylic hydroperoxide
- Ortho-dioxolane
- Dialkyl peroxide
- Hydroperoxide
- Alkyl hydroperoxide
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Oxacycle
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Peroxol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-006x-5293000000-4f6f219630c974fad684 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00gr-9142200000-12079cbb99c54d74b4e4 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0119000000-06893304af83e030a39b | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0zmr-3369000000-b1d0f67eea930b11ae4c | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-1003-9400000000-7fbd48d8b1a086fc44d2 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-0019000000-4a1c6a9bb1b35fe201ef | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00r2-2149000000-16bc14c91731cdc79586 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9162000000-ad0929ccdcab78d69a99 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0gb9-0009000000-7bd756fb66d8a2f4e9dd | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014r-2069000000-0067297ea99f20c4e4ca | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-06ec-7920000000-d773a60db405a4944865 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00lr-0009000000-a2da7230358a405653f8 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00li-0029000000-c33c17a6864e28828b80 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin G2 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-014j-3096000000-14b691a730b064b98583 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| General References | - Agnoli GC, Borgatti R, Cacciari M, Dorigoni S, Garutti C, Ikonomu E, Marinelli M: [Urinary excretion of prostanoids in the course of changes in diuresis over short and long terms respectively]. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1987 Apr 30;63(4):357-63. [PubMed:3447615 ]
- Burdan F, Chalas A, Szumilo J: [Cyclooxygenase and prostanoids--biological implications]. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006;60:129-41. [PubMed:16552393 ]
- Schneider C, Boeglin WE, Brash AR: Identification of two cyclooxygenase active site residues, Leucine 384 and Glycine 526, that control carbon ring cyclization in prostaglandin biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 6;279(6):4404-14. Epub 2003 Oct 31. [PubMed:14594816 ]
- Chubb AJ, Fitzgerald DJ, Nolan KB, Moman E: The productive conformation of prostaglandin G2 at the peroxidase site of prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase: docking, molecular dynamics, and site-directed mutagenesis studies. Biochemistry. 2006 Jan 24;45(3):811-20. [PubMed:16411757 ]
|
|---|