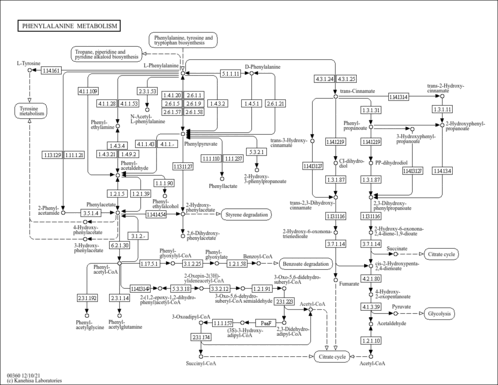
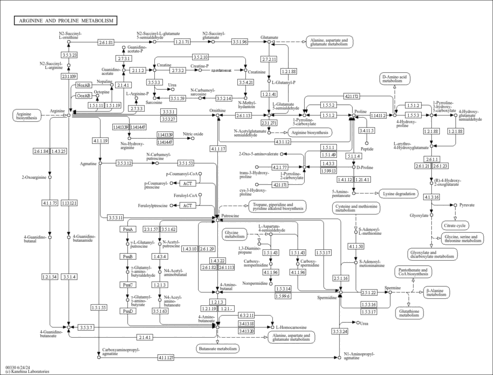
| Disease References | | Short bowel syndrome |
|---|
- Pita AM, Wakabayashi Y, Fernandez-Bustos MA, Virgili N, Riudor E, Soler J, Farriol M: Plasma urea-cycle-related amino acids, ammonium levels, and urinary orotic acid excretion in short-bowel patients managed with an oral diet. Clin Nutr. 2003 Feb;22(1):93-8. [PubMed:12553956 ]
| | 3-Methyl-crotonyl-glycinuria |
|---|
- G.Frauendienst-Egger, Friedrich K. Trefz (2017). MetaGene: Metabolic & Genetic Information Center (MIC: http://www.metagene.de). METAGENE consortium.
| | Argininosuccinic aciduria |
|---|
- Kleijer WJ, Garritsen VH, Linnebank M, Mooyer P, Huijmans JG, Mustonen A, Simola KO, Arslan-Kirchner M, Battini R, Briones P, Cardo E, Mandel H, Tschiedel E, Wanders RJ, Koch HG: Clinical, enzymatic, and molecular genetic characterization of a biochemical variant type of argininosuccinic aciduria: prenatal and postnatal diagnosis in five unrelated families. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2002 Sep;25(5):399-410. [PubMed:12408190 ]
- G.Frauendienst-Egger, Friedrich K. Trefz (2017). MetaGene: Metabolic & Genetic Information Center (MIC: http://www.metagene.de). METAGENE consortium.
| | Sulfite oxidase deficiency, ISOLATED |
|---|
- Choong T. et al. (2010). Clinical and Laboratory Barriers to the Timely Diagnosis of Sulphite Oxidase Deficiency. Proceedings of Singapore Healthcare, 19(2), 94-100.. Proceedings of Singapore Healthcare.
| | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency |
|---|
- Muroi J, Yorifuji T, Uematsu A, Shigematsu Y, Onigata K, Maruyama H, Nobutoki T, Kitamura A, Nakahata T: Molecular and clinical analysis of Japanese patients with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA lyase (HL) deficiency. Hum Genet. 2000 Oct;107(4):320-6. [PubMed:11129331 ]
- Grunert SC, Schlatter SM, Schmitt RN, Gemperle-Britschgi C, Mrazova L, Balci MC, Bischof F, Coker M, Das AM, Demirkol M, de Vries M, Gokcay G, Haberle J, Ucar SK, Lotz-Havla AS, Lucke T, Roland D, Rutsch F, Santer R, Schlune A, Staufner C, Schwab KO, Mitchell GA, Sass JO: 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A lyase deficiency: Clinical presentation and outcome in a series of 37 patients. Mol Genet Metab. 2017 Jul;121(3):206-215. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2017.05.014. Epub 2017 May 22. [PubMed:28583327 ]
- Ozand PT, al Aqeel A, Gascon G, Brismar J, Thomas E, Gleispach H: 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) lyase deficiency in Saudi Arabia. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1991;14(2):174-88. [PubMed:1886403 ]
- Santarelli F, Cassanello M, Enea A, Poma F, D'Onofrio V, Guala G, Garrone G, Puccinelli P, Caruso U, Porta F, Spada M: A neonatal case of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric-coenzyme A lyase deficiency. Ital J Pediatr. 2013 May 24;39:33. doi: 10.1186/1824-7288-39-33. [PubMed:23705938 ]
| | Fumarase deficiency |
|---|
- Bastug O, Kardas F, Ozturk MA, Halis H, Memur S, Korkmaz L, Tag Z, Gunes T: A rare cause of opistotonus; fumaric aciduria: The first case presentation in Turkey. Turk Pediatri Ars. 2014 Mar 1;49(1):74-6. doi: 10.5152/tpa.2014.442. eCollection 2014 Mar. [PubMed:26078636 ]
| | N-acetylglutamate synthetase deficiency |
|---|
- Schubiger G, Bachmann C, Barben P, Colombo JP, Tonz O, Schupbach D: N-acetylglutamate synthetase deficiency: diagnosis, management and follow-up of a rare disorder of ammonia detoxication. Eur J Pediatr. 1991 Mar;150(5):353-6. [PubMed:2044610 ]
| | Citrullinemia type I |
|---|
- Kose E, Unal O, Bulbul S, Gunduz M, Haberle J, Arslan N: Identification of three novel mutations in fourteen patients with citrullinemia type 1. Clin Biochem. 2017 Aug;50(12):686-689. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.01.011. Epub 2017 Jan 27. [PubMed:28132756 ]
| | Citrullinemia type II, adult-onset |
|---|
- Yajima Y, Hirasawa T, Saheki T: Diurnal fluctuation of blood ammonia levels in adult-type citrullinemia. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1982 Jun;137(2):213-20. [PubMed:7202267 ]
- Komatsu M, Yazaki M, Tanaka N, Sano K, Hashimoto E, Takei Y, Song YZ, Tanaka E, Kiyosawa K, Saheki T, Aoyama T, Kobayashi K: Citrin deficiency as a cause of chronic liver disorder mimicking non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2008 Nov;49(5):810-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.05.016. Epub 2008 Jun 10. [PubMed:18620775 ]
| | 3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
|---|
- Hsu BY, Kelly A, Thornton PS, Greenberg CR, Dilling LA, Stanley CA: Protein-sensitive and fasting hypoglycemia in children with the hyperinsulinism/hyperammonemia syndrome. J Pediatr. 2001 Mar;138(3):383-9. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2001.111818. [PubMed:11241047 ]
- Popa FI, Perlini S, Teofoli F, Degani D, Funghini S, La Marca G, Rinaldo P, Vincenzi M, Antoniazzi F, Boner A, Camilot M: 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme a dehydrogenase deficiency: identification of a new mutation causing hyperinsulinemic hypoketotic hypoglycemia, altered organic acids and acylcarnitines concentrations. JIMD Rep. 2012;2:71-7. doi: 10.1007/8904_2011_50. Epub 2011 Sep 6. [PubMed:23430856 ]
| | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency due to ACAD9 deficiency |
|---|
- He M, Rutledge SL, Kelly DR, Palmer CA, Murdoch G, Majumder N, Nicholls RD, Pei Z, Watkins PA, Vockley J: A new genetic disorder in mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation: ACAD9 deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 2007 Jul;81(1):87-103. Epub 2007 Jun 4. [PubMed:17564966 ]
| | Hyperdibasic aminoaciduria I |
|---|
- Whelan DT, Scriver CR: Hyperdibasicaminoaciduria: an inherited disorder of amino acid transport. Pediatr Res. 1968 Nov;2(6):525-34. [PubMed:5727921 ]
| | Pearson Syndrome |
|---|
- Crippa BL, Leon E, Calhoun A, Lowichik A, Pasquali M, Longo N: Biochemical abnormalities in Pearson syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2015 Mar;167A(3):621-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36939. [PubMed:25691415 ]
| | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type IIIA |
|---|
- Baumgartner MR, Hu CA, Almashanu S, Steel G, Obie C, Aral B, Rabier D, Kamoun P, Saudubray JM, Valle D: Hyperammonemia with reduced ornithine, citrulline, arginine and proline: a new inborn error caused by a mutation in the gene encoding delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase. Hum Mol Genet. 2000 Nov 22;9(19):2853-8. [PubMed:11092761 ]
| | Metabolic encephalomyopathic crises, recurrent, with rhabdomyolysis, cardiac arrhythmias, and neurodegeneration |
|---|
- Lalani SR, Liu P, Rosenfeld JA, Watkin LB, Chiang T, Leduc MS, Zhu W, Ding Y, Pan S, Vetrini F, Miyake CY, Shinawi M, Gambin T, Eldomery MK, Akdemir ZH, Emrick L, Wilnai Y, Schelley S, Koenig MK, Memon N, Farach LS, Coe BP, Azamian M, Hernandez P, Zapata G, Jhangiani SN, Muzny DM, Lotze T, Clark G, Wilfong A, Northrup H, Adesina A, Bacino CA, Scaglia F, Bonnen PE, Crosson J, Duis J, Maegawa GH, Coman D, Inwood A, McGill J, Boerwinkle E, Graham B, Beaudet A, Eng CM, Hanchard NA, Xia F, Orange JS, Gibbs RA, Lupski JR, Yang Y: Recurrent Muscle Weakness with Rhabdomyolysis, Metabolic Crises, and Cardiac Arrhythmia Due to Bi-allelic TANGO2 Mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Feb 4;98(2):347-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.12.008. Epub 2016 Jan 21. [PubMed:26805781 ]
| | Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency |
|---|
- den Boer ME, Dionisi-Vici C, Chakrapani A, van Thuijl AO, Wanders RJ, Wijburg FA: Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency: a severe fatty acid oxidation disorder with cardiac and neurologic involvement. J Pediatr. 2003 Jun;142(6):684-9. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2003.231. [PubMed:12838198 ]
| | Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency |
|---|
- Habarou F, Brassier A, Rio M, Chretien D, Monnot S, Barbier V, Barouki R, Bonnefont JP, Boddaert N, Chadefaux-Vekemans B, Le Moyec L, Bastin J, Ottolenghi C, de Lonlay P: Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency: An underestimated cause of lactic acidosis. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2014 Nov 28;2:25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2014.11.001. eCollection 2015 Mar. [PubMed:28649521 ]
| | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency |
|---|
- Olpin SE, Allen J, Bonham JR, Clark S, Clayton PT, Calvin J, Downing M, Ives K, Jones S, Manning NJ, Pollitt RJ, Standing SJ, Tanner MS: Features of carnitine palmitoyltransferase type I deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2001 Feb;24(1):35-42. [PubMed:11286380 ]
| | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 2 |
|---|
- Schulze A, Hess T, Wevers R, Mayatepek E, Bachert P, Marescau B, Knopp MV, De Deyn PP, Bremer HJ, Rating D: Creatine deficiency syndrome caused by guanidinoacetate methyltransferase deficiency: diagnostic tools for a new inborn error of metabolism. J Pediatr. 1997 Oct;131(4):626-31. [PubMed:9386672 ]
| | Infantile Liver Failure Syndrome 2 |
|---|
- Staufner C, Haack TB, Kopke MG, Straub BK, Kolker S, Thiel C, Freisinger P, Baric I, McKiernan PJ, Dikow N, Harting I, Beisse F, Burgard P, Kotzaeridou U, Lenz D, Kuhr J, Himbert U, Taylor RW, Distelmaier F, Vockley J, Ghaloul-Gonzalez L, Ozolek JA, Zschocke J, Kuster A, Dick A, Das AM, Wieland T, Terrile C, Strom TM, Meitinger T, Prokisch H, Hoffmann GF: Recurrent acute liver failure due to NBAS deficiency: phenotypic spectrum, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic concepts. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2016 Jan;39(1):3-16. doi: 10.1007/s10545-015-9896-7. Epub 2015 Nov 5. [PubMed:26541327 ]
| | Long-chain Fatty Acids, Defect in Transport of |
|---|
- Treem WR, Stanley CA, Finegold DN, Hale DE, Coates PM: Primary carnitine deficiency due to a failure of carnitine transport in kidney, muscle, and fibroblasts. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 17;319(20):1331-6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811173192006. [PubMed:3185635 ]
| | Myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia 1 |
|---|
- Parfait B, de Lonlay P, von Kleist-Retzow JC, Cormier-Daire V, Chretien D, Rotig A, Rabier D, Saudubray JM, Rustin P, Munnich A: The neurogenic weakness, ataxia and retinitis pigmentosa (NARP) syndrome mtDNA mutation (T8993G) triggers muscle ATPase deficiency and hypocitrullinaemia. Eur J Pediatr. 1999 Jan;158(1):55-8. [PubMed:9950309 ]
| | Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase Deficiency 1, Cytosolic |
|---|
- Vieira P, Cameron J, Rahikkala E, Keski-Filppula R, Zhang LH, Santra S, Matthews A, Myllynen P, Nuutinen M, Moilanen JS, Rodenburg RJ, Rolfs A, Uusimaa J, van Karnebeek CDM: Novel homozygous PCK1 mutation causing cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase deficiency presenting as childhood hypoglycemia, an abnormal pattern of urine metabolites and liver dysfunction. Mol Genet Metab. 2017 Apr;120(4):337-341. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Feb 6. [PubMed:28216384 ]
- Santra S, Cameron JM, Shyr C, Zhang L, Drogemoller B, Ross CJ, Wasserman WW, Wevers RA, Rodenburg RJ, Gupte G, Preece MA, van Karnebeek CD: Cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase deficiency presenting with acute liver failure following gastroenteritis. Mol Genet Metab. 2016 May;118(1):21-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 4. [PubMed:26971250 ]
|
|
|---|
| General References | - Yoshida Y, Higashi T, Nouso K, Nakatsukasa H, Nakamura SI, Watanabe A, Tsuji T: Effects of zinc deficiency/zinc supplementation on ammonia metabolism in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. Acta Med Okayama. 2001 Dec;55(6):349-55. [PubMed:11779097 ]
- Huizenga JR, Teelken AW, Tangerman A, de Jager AE, Gips CH, Jansen PL: Determination of ammonia in cerebrospinal fluid using the indophenol direct method. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1998 Jun-Aug;34(2-3):169-77. [PubMed:10327416 ]
- Cohen BI: The significance of ammonia/gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ratio for normality and liver disorders. Med Hypotheses. 2002 Dec;59(6):757-8. [PubMed:12445521 ]
- Kochar DK, Agarwal P, Kochar SK, Jain R, Rawat N, Pokharna RK, Kachhawa S, Srivastava T: Hepatocyte dysfunction and hepatic encephalopathy in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. QJM. 2003 Jul;96(7):505-12. [PubMed:12881593 ]
- Zupke C, Sinskey AJ, Stephanopoulos G: Intracellular flux analysis applied to the effect of dissolved oxygen on hybridomas. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1995 Dec;44(1-2):27-36. [PubMed:8579834 ]
- Cooper AJ: Role of glutamine in cerebral nitrogen metabolism and ammonia neurotoxicity. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2001;7(4):280-6. [PubMed:11754523 ]
- Remer T: Influence of nutrition on acid-base balance--metabolic aspects. Eur J Nutr. 2001 Oct;40(5):214-20. [PubMed:11842946 ]
- Kaiho T, Tanaka T, Tsuchiya S, Yanagisawa S, Takeuchi O, Miura M, Saigusa N, Miyazaki M: Effect of the herbal medicine Dai-kenchu-to for serum ammonia in hepatectomized patients. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005 Jan-Feb;52(61):161-5. [PubMed:15783019 ]
- Nybo L, Dalsgaard MK, Steensberg A, Moller K, Secher NH: Cerebral ammonia uptake and accumulation during prolonged exercise in humans. J Physiol. 2005 Feb 15;563(Pt 1):285-90. Epub 2004 Dec 20. [PubMed:15611036 ]
- Huizenga JR, Vissink A, Kuipers EJ, Gips CH: Helicobacter pylori and ammonia concentrations of whole, parotid and submandibular/sublingual saliva. Clin Oral Investig. 1999 Jun;3(2):84-7. [PubMed:10803116 ]
- Satoh M, Yokoya S, Hachiya Y, Hachiya M, Fujisawa T, Hoshino K, Saji T: Two hyperandrogenic adolescent girls with congenital portosystemic shunt. Eur J Pediatr. 2001 May;160(5):307-11. [PubMed:11388600 ]
- Suarez I, Bodega G, Fernandez B: Glutamine synthetase in brain: effect of ammonia. Neurochem Int. 2002 Aug-Sep;41(2-3):123-42. [PubMed:12020613 ]
- Helewski K, Kowalczyk-Ziomek G, Konecki J: [Ammonia and GABA-ergic neurotransmission in pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy]. Wiad Lek. 2003;56(11-12):560-3. [PubMed:15058165 ]
- Grasten SM, Juntunen KS, Poutanen KS, Gylling HK, Miettinen TA, Mykkanen HM: Rye bread improves bowel function and decreases the concentrations of some compounds that are putative colon cancer risk markers in middle-aged women and men. J Nutr. 2000 Sep;130(9):2215-21. [PubMed:10958815 ]
- Pita AM, Wakabayashi Y, Fernandez-Bustos MA, Virgili N, Riudor E, Soler J, Farriol M: Plasma urea-cycle-related amino acids, ammonium levels, and urinary orotic acid excretion in short-bowel patients managed with an oral diet. Clin Nutr. 2003 Feb;22(1):93-8. [PubMed:12553956 ]
- Geier M, Bosch OJ, Boeckh J: Ammonia as an attractive component of host odour for the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Chem Senses. 1999 Dec;24(6):647-53. [PubMed:10587497 ]
- Iwata H, Ueda Y: Pharmacokinetic considerations in development of a bioartificial liver. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2004;43(4):211-25. [PubMed:15005636 ]
- Ohmoto K, Miyake I, Tsuduki M, Ohno S, Yamamoto S: Control of solitary gastric fundal varices and portosystemic encephalopathy accompanying liver cirrhosis by balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration (B-RTO): a case report. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999 Mar-Apr;46(26):1249-52. [PubMed:10370701 ]
- Verrotti A, Greco R, Morgese G, Chiarelli F: Carnitine deficiency and hyperammonemia in children receiving valproic acid with and without other anticonvulsant drugs. Int J Clin Lab Res. 1999;29(1):36-40. [PubMed:10356662 ]
- Hussein HS, Flickinger EA, Fahey GC Jr: Petfood applications of inulin and oligofructose. J Nutr. 1999 Jul;129(7 Suppl):1454S-6S. [PubMed:10395620 ]
- Shawcross DL, Olde Damink SW, Butterworth RF, Jalan R: Ammonia and hepatic encephalopathy: the more things change, the more they remain the same. Metab Brain Dis. 2005 Sep;20(3):169-79. [PubMed:16167195 ]
- Albrecht J, Norenberg MD: Glutamine: a Trojan horse in ammonia neurotoxicity. Hepatology. 2006 Oct;44(4):788-94. [PubMed:17006913 ]
- Norenberg MD, Rama Rao KV, Jayakumar AR: Ammonia neurotoxicity and the mitochondrial permeability transition. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004 Aug;36(4):303-7. [PubMed:15377862 ]
- Brautbar N, Wu MP, Richter ED: Chronic ammonia inhalation and interstitial pulmonary fibrosis: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Environ Health. 2003 Sep;58(9):592-6. [PubMed:15369278 ]
- Seiler N: Ammonia and Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Int. 2002 Aug-Sep;41(2-3):189-207. [PubMed:12020619 ]
- Monfort P, Kosenko E, Erceg S, Canales JJ, Felipo V: Molecular mechanism of acute ammonia toxicity: role of NMDA receptors. Neurochem Int. 2002 Aug-Sep;41(2-3):95-102. [PubMed:12020609 ]
| Show more...
|---|