| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2021-09-14 15:48:16 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000085 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Deoxyguanosine |
|---|
| Description | Deoxyguanosine, also known as dG, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides. Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides are compounds consisting of a purine linked to a ribose which lacks a hydroxyl group at position 2’. Deoxyguanosine is a nucleoside consisting of the base guanine and the sugar deoxyribose. Deoxyguanosine is one of the four deoxyribonucleosides that make up DNA. Deoxyguanosine exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to plants to humans. Deoxyguanosine participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, deoxyguanosine can be biosynthesized from 2'-deoxyguanosine 5'-monophosphate through the enzyme known as cytosolic purine 5'-nucleotidase. In addition, deoxyguanosine can be converted into 2'-deoxyguanosine 5'-monophosphate (dGMP); which is mediated by the enzyme deoxyguanosine kinase. Deoxyguanosine is involved in the rare, inherited metabolic disorder called the purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency (PNP deficiency). In particular PNP deficiency is characterized by elevated levels of dGTP (deoxyguanosine triphosphate). PNP accounts for approximately 4% of patients with severe combined immunodeficiency (PMID: 1931007 ). PNP-deficient patients suffer from recurrent infections, usually beginning in the first year of life. Two thirds of patients have evidence of neurologic disorders with spasticity, developmental delay and mental retardation. Deoxyguanosine can be converted to 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) due to hydroxyl radical attack at the C8 of guanine. 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanosine is a sensitive marker of the DNA damage This damage, if left unrepaired, has been proposed to contribute to mutagenicity and cancer promotion. |
|---|
| Structure | NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1 InChI=1S/C10H13N5O4/c11-10-13-8-7(9(18)14-10)12-3-15(8)6-1-4(17)5(2-16)19-6/h3-6,16-17H,1-2H2,(H3,11,13,14,18)/t4-,5+,6+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 2-Amino-9-(2-deoxy-9-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-9H-purin-6-ol | ChEBI | | 9-(2-Deoxy-beta-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)-guanine | ChEBI | | dG | ChEBI | | Guanine deoxy nucleoside | ChEBI | | 2'-Deoxyguanosine | Kegg | | 2-Amino-9-(2-deoxy-9-b-D-ribofuranosyl)-9H-purin-6-ol | Generator | | 2-Amino-9-(2-deoxy-9-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-9H-purin-6-ol | Generator | | 9-(2-Deoxy-b-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)-guanine | Generator | | 9-(2-Deoxy-β-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)-guanine | Generator | | 2'-Deoxy-guanosine | HMDB | | 2-Deoxyguanosine | HMDB | | 9-(2-Deoxy-b-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)guanine | HMDB | | 9-(2-Deoxy-beta-delta-erythro-pentofuranosyl)-guanine | HMDB | | 9-(2-Deoxy-beta-delta-erythro-pentofuranosyl)guanine | HMDB | | Desoxyguanosine | HMDB | | Guanine deoxyriboside | HMDB | | Deoxyguanosine | ChEBI |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C10H13N5O4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 267.2413 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 267.096753929 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-amino-9-[(2R,4S,5R)-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-6,9-dihydro-1H-purin-6-one |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 2-deoxyguanosine |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 961-07-9 |
|---|
| SMILES | NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C10H13N5O4/c11-10-13-8-7(9(18)14-10)12-3-15(8)6-1-4(17)5(2-16)19-6/h3-6,16-17H,1-2H2,(H3,11,13,14,18)/t4-,5+,6+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | YKBGVTZYEHREMT-KVQBGUIXSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides. Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides are compounds consisting of a purine linked to a ribose which lacks a hydroxyl group at position 2. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues |
|---|
| Class | Purine nucleosides |
|---|
| Sub Class | Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleoside
- 6-oxopurine
- Hypoxanthine
- Purinone
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Aminopyrimidine
- Pyrimidone
- N-substituted imidazole
- Pyrimidine
- Azole
- Imidazole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Vinylogous amide
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Secondary alcohol
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Amine
- Primary amine
- Primary alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Alcohol
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 300 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | -1.30 | BALZARINI,JM ET AL. (1989) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Deoxyguanosine,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)[NH]C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2679.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 2650.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 2711.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,1TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C(N)=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C1=O | 2758.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2607.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 2623.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2694.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 2603.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 2672.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)[NH]1)[Si](C)(C)C | 2616.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C | 2705.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 2593.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 2884.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 3957.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2641.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2812.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4091.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2623.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2954.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3801.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C | 2691.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C | 2875.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C | 3857.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 2612.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 2981.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 3821.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C | 2672.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C | 2907.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C | 3879.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2735.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2990.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3798.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2650.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2974.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3513.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C | 2687.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C | 2897.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C | 3566.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2758.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3013.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3447.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 2726.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 3035.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 3478.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2773.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3022.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3225.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)[NH]C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 2900.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 2890.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 2914.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,1TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C(N)=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C1=O | 2930.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3032.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 3036.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3108.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 3050.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 3106.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)[NH]1)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3040.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,2TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3126.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 3233.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 3562.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)[NH]1 | 3957.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3303.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3512.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4056.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3205.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3638.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3795.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3302.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3578.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3827.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 3205.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 3650.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 3834.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3311.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3592.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3866.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3305.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3677.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3769.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3403.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3824.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[NH]C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3689.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3494.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3774.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@H]2C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O2)C(=O)N1[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3724.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3492.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3852.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C[C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)O[C@@H]1CO | 3627.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 3495.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 3876.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O | 3666.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3671.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3968.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxyguanosine,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C3=O)C[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3553.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-001j-0891000000-3d776d25cb03b01b9339 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (4 TMS) | splash10-0f8a-2960000000-dfb317b7b1eb025d909e | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (5 TMS) | splash10-0udi-2913000000-1b2f5de9c93a151947ec | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-001j-0891000000-3d776d25cb03b01b9339 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0f8a-2960000000-dfb317b7b1eb025d909e | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0udi-2913000000-1b2f5de9c93a151947ec | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-052p-9580000000-831d1b4a56d55342e5d9 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (2 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-8009000000-43fe5e369133cc5b35c0 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TMS_2_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TMS_2_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TMS_2_6) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TMS_2_7) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TBDMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TBDMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TBDMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine GC-MS (TBDMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0udi-0900000000-1ff2faf768c32875ae94 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0udi-0900000000-6ecd3556539c87465829 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0f89-2900000000-3c7a46a8b1ebc3478b0e | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-0090000000-d7b5f1fd49de4c188c2b | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-066r-1290000000-f1789943f3a3aa93bf11 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-1960000000-cae86b9369b467a619ac | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-2930000000-59733590e9e1f1f9e3ab | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a59-3900000000-63f2d871818a0f9ea2c4 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0490000000-a0d35f9580527e157997 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0940000000-501ccdb19ac1399ea47d | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-2900000000-3c8141b790d1e751030c | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0k96-6900000000-218b8cf773fa785dd6fc | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9700000000-16fac3cb96899ba7c58c | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-IT (LC/MSD Trap XCT, Agilent Technologies) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0900000000-c020044f3d53ad944e38 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-IT (LC/MSD Trap XCT, Agilent Technologies) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0900000000-09d1a1821d4e622a1f9a | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-0090000000-d7b5f1fd49de4c188c2b | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-066r-1290000000-cf5beb73c1ce61ceb87b | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-1960000000-cae86b9369b467a619ac | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-2930000000-08d635c63c26f8baa811 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0920000000-d7d80ec246617036e55e | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0900000000-c5bd180b555397bc1ae5 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0900000000-c54d0a1dec8712b2b8f7 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-0290000000-393ce4bbd1a38882e581 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0910000000-7bc10bc144a1a343b08f | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxyguanosine 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0pbc-4900000000-c3082fcc9288ad93f897 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
- Lysosome
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
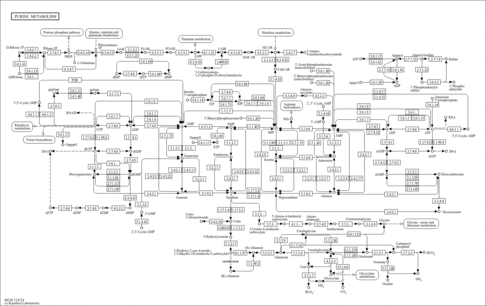
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0 uM | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.00 (0.00-2.00) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0-5 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <1.0 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <0.1 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 11.0 (2.0-20.0) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) deficiency | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal Cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal Cancer | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 177.0-322.0 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) deficiency | | details |
|
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ: Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 25;11(3):e0152126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27015276 ]
- Brown DG, Rao S, Weir TL, O'Malia J, Bazan M, Brown RJ, Ryan EP: Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016 Jun 6;4:11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0151-y. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27275383 ]
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Ahn J, Shi J, Sinha R: Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2089-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131. Epub 2014 Jul 18. [PubMed:25037050 ]
| | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency |
|---|
- Wevers RA, Engelke UF, Moolenaar SH, Brautigam C, de Jong JG, Duran R, de Abreu RA, van Gennip AH: 1H-NMR spectroscopy of body fluids: inborn errors of purine and pyrimidine metabolism. Clin Chem. 1999 Apr;45(4):539-48. [PubMed:10102915 ]
- Gandhi V, Kilpatrick JM, Plunkett W, Ayres M, Harman L, Du M, Bantia S, Davisson J, Wierda WG, Faderl S, Kantarjian H, Thomas D: A proof-of-principle pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and clinical study with purine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibitor immucillin-H (BCX-1777, forodesine). Blood. 2005 Dec 15;106(13):4253-60. Epub 2005 Aug 30. [PubMed:16131572 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 114500 (Colorectal cancer)
- 164050 (Purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency )
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB012064 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 163230 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00330 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | DEOXYGUANOSINE |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 34637 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Deoxyguanosine |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 3395 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 187790 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 17172 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | DGSN |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000044 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Noguchi, Toshitada; Hamamoto, Tomoki; Okuyama, Kiyoshi; Shibuya, Susumu. Process for producing 2'-deoxyguanosine. PCT Int. Appl. (2003), 31 pp. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Gao K, Henning SM, Niu Y, Youssefian AA, Seeram NP, Xu A, Heber D: The citrus flavonoid naringenin stimulates DNA repair in prostate cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem. 2006 Feb;17(2):89-95. Epub 2005 Jun 20. [PubMed:16111881 ]
- Podmore K, Farmer PB, Herbert KE, Jones GD, Martin EA: 32P-postlabelling approaches for the detection of 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine-3'-monophosphate in DNA. Mutat Res. 1997 Aug 1;378(1-2):139-49. [PubMed:9288892 ]
- Shibata T, Iio K, Kawai Y, Shibata N, Kawaguchi M, Toi S, Kobayashi M, Kobayashi M, Yamamoto K, Uchida K: Identification of a lipid peroxidation product as a potential trigger of the p53 pathway. J Biol Chem. 2006 Jan 13;281(2):1196-204. Epub 2005 Oct 26. [PubMed:16251187 ]
- Gackowski D, Ciecierski M, Jawien A, Olinski R: Background level of 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine in lymphocyte DNA does not correlate with the concentration of antioxidant vitamins in blood plasma. Acta Biochim Pol. 2001;48(2):535-9. [PubMed:11732622 ]
- Takamura-Enya T, Watanabe M, Totsuka Y, Kanazawa T, Matsushima-Hibiya Y, Koyama K, Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K: Mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation of 2'-deoxyguanosine residue in DNA by an apoptosis-inducing protein, pierisin-1, from cabbage butterfly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Oct 23;98(22):12414-9. Epub 2001 Oct 9. [PubMed:11592983 ]
- Palozza P, Serini S, Di Nicuolo F, Boninsegna A, Torsello A, Maggiano N, Ranelletti FO, Wolf FI, Calviello G, Cittadini A: beta-Carotene exacerbates DNA oxidative damage and modifies p53-related pathways of cell proliferation and apoptosis in cultured cells exposed to tobacco smoke condensate. Carcinogenesis. 2004 Aug;25(8):1315-25. Epub 2004 Apr 8. [PubMed:15073048 ]
- Zaidi SN, Laidlaw I, Howell A, Potten CS, Cooper DP, O'Connor PJ: Normal human breast xenografts activate N-nitrosodimethylamine: identification of potential target cells for an environmental nitrosamine. Br J Cancer. 1992 Jul;66(1):79-83. [PubMed:1637681 ]
- Gackowski D, Banaszkiewicz Z, Rozalski R, Jawien A, Olinski R: Persistent oxidative stress in colorectal carcinoma patients. Int J Cancer. 2002 Oct 1;101(4):395-7. [PubMed:12209966 ]
- Araki S, Hayashi M, Tamagawa K, Saito M, Kato S, Komori T, Sakakihara Y, Mizutani T, Oda M: Neuropathological analysis in spinal muscular atrophy type II. Acta Neuropathol. 2003 Nov;106(5):441-8. Epub 2003 Jul 25. [PubMed:12898156 ]
- Kato I, Ren J, Heilbrun LK, Djuric Z: Intra- and inter-individual variability in measurements of biomarkers for oxidative damage in vivo: Nutrition and Breast Health Study. Biomarkers. 2006 Mar-Apr;11(2):143-52. [PubMed:16766390 ]
- Izzedine H, Launay-Vacher V, Aymard G, Legrand M, Deray G: Pharmacokinetics of abacavir in HIV-1-infected patients with impaired renal function. Nephron. 2001 Sep;89(1):62-7. [PubMed:11528234 ]
- Wevers RA, Engelke UF, Moolenaar SH, Brautigam C, de Jong JG, Duran R, de Abreu RA, van Gennip AH: 1H-NMR spectroscopy of body fluids: inborn errors of purine and pyrimidine metabolism. Clin Chem. 1999 Apr;45(4):539-48. [PubMed:10102915 ]
- Bowen P, Chen L, Stacewicz-Sapuntzakis M, Duncan C, Sharifi R, Ghosh L, Kim HS, Christov-Tzelkov K, van Breemen R: Tomato sauce supplementation and prostate cancer: lycopene accumulation and modulation of biomarkers of carcinogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2002 Nov;227(10):886-93. [PubMed:12424330 ]
- Staal GE, Stoop JW, Zegers BJ, Siegenbeek van Heukelom LH, van der Vlist MJ, Wadman SK, Martin DW: Erythrocyte metabolism in purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency after enzyme replacement therapy by infusion of erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):103-8. [PubMed:6765955 ]
- Blair IA: Lipid hydroperoxide-mediated DNA damage. Exp Gerontol. 2001 Sep;36(9):1473-81. [PubMed:11525870 ]
- Schramm VL: Development of transition state analogues of purine nucleoside phosphorylase as anti-T-cell agents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jul 18;1587(2-3):107-17. [PubMed:12084452 ]
- Schilderman PA, Rhijnsburger E, Zwingmann I, Kleinjans JC: Induction of oxidative DNA damages and enhancement of cell proliferation in human lymphocytes in vitro by butylated hydroxyanisole. Carcinogenesis. 1995 Mar;16(3):507-12. [PubMed:7697806 ]
- Kaneko T, Tahara S: Formation of 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine in the DNA of human diploid fibroblasts by treatment with linoleic acid hydroperoxide and ferric ion. Lipids. 2000 Sep;35(9):961-5. [PubMed:11026616 ]
- Hou SM, Nori P, Fang JL, Vaca CE: Methylglyoxal induces hprt mutation and DNA adducts in human T-lymphocytes in vitro. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1995;26(4):286-91. [PubMed:8575417 ]
- Bialkowski K, Kowara R, Windorbska W, Olinski R: 8-Oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine level in lymphocytes DNA of cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy. Cancer Lett. 1996 Jan 19;99(1):93-7. [PubMed:8564935 ]
- Markert ML: Purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. Immunodefic Rev. 1991;3(1):45-81. [PubMed:1931007 ]
| Show more...
|---|