| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:04 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000626 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Deoxycholic acid |
|---|
| Description | Deoxycholic acid is a secondary bile acid produced in the liver and is usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion. Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals. The distinction between different bile acids is minute, and depends only on the presence or absence of hydroxyl groups on positions 3, 7, and 12. Bile acids are physiological detergents that facilitate excretion, absorption, and transport of fats and sterols in the intestine and liver. Bile acids are also steroidal amphipathic molecules derived from the catabolism of cholesterol. They modulate bile flow and lipid secretion, are essential for the absorption of dietary fats and vitamins, and have been implicated in the regulation of all the key enzymes involved in cholesterol homeostasis. Bile acids recirculate through the liver, bile ducts, small intestine, and portal vein to form an enterohepatic circuit. They exist as anions at physiological pH, and consequently require a carrier for transport across the membranes of the enterohepatic tissues. The unique detergent properties of bile acids are essential for the digestion and intestinal absorption of hydrophobic nutrients. Bile acids have potent toxic properties (e.g. membrane disruption) and there are a plethora of mechanisms to limit their accumulation in blood and tissues (PMID: 11316487 , 16037564 , 12576301 , 11907135 ). When present in sufficiently high levels, deoxycholic acid can act as a hepatotoxin, a metabotoxin, and an oncometabolite. A hepatotoxin causes damage to the liver or liver cells. A metabotoxin is an endogenously produced metabolite that causes adverse health effects at chronically high levels. An oncometabolite is a compound, when present at chronically high levels, that promotes tumour growth and survival. Among the primary bile acids, cholic acid is considered to be the least hepatotoxic while deoxycholic acid is the most hepatoxic (PMID: 1641875 ). The liver toxicity of bile acids appears to be due to their ability to peroxidate lipids and to lyse liver cells. High bile acid levels lead to the generation of reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species, disruption of the cell membrane and mitochondria, induction of DNA damage, mutation and apoptosis, and the development of reduced apoptosis capability upon chronic exposure (PMID: 24884764 ). Chronically high levels of deoxycholic acid are associated with familial hypercholanemia. In hypercholanemia, bile acids, including deoxycholic acid, are elevated in the blood. This disease causes liver damage, extensive itching, poor fat absorption, and can lead to rickets due to lack of calcium in bones. The deficiency of normal bile acids in the intestines results in a deficiency of vitamin K, which also adversely affects clotting of the blood. The bile acid ursodiol (ursodeoxycholic acid) can improve symptoms associated with familial hypercholanemia. Chronically high levels of deoxycholic acid are also associated with several forms of cancer including colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, esophageal cancer, and many other GI cancers. | Read more...
|---|
| Structure | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])CC[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])C[C@H](O)[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O InChI=1S/C24H40O4/c1-14(4-9-22(27)28)18-7-8-19-17-6-5-15-12-16(25)10-11-23(15,2)20(17)13-21(26)24(18,19)3/h14-21,25-26H,4-13H2,1-3H3,(H,27,28)/t14-,15-,16-,17+,18-,19+,20+,21+,23+,24-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (3ALPHA,5ALPHA,12ALPHA)-3,12-DIHYDROXYCHOLAN-24-OIC ACID | ChEBI | | (3alpha,5beta,12alpha)-3,12-Dihydroxycholan-24-Oic acid | ChEBI | | 3alpha,12alpha-Dihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid | ChEBI | | 7alpha-Deoxycholic acid | ChEBI | | Desoxycholic acid | ChEBI | | Desoxycholsaeure | ChEBI | | Deoxycholate | Kegg | | 3alpha,12alpha-Dihydroxy-5beta-cholanate | Kegg | | (3a,5a,12a)-3,12-DIHYDROXYCHOLAN-24-Oate | Generator | | (3a,5a,12a)-3,12-DIHYDROXYCHOLAN-24-Oic acid | Generator | | (3alpha,5alpha,12alpha)-3,12-DIHYDROXYCHOLAN-24-Oate | Generator | | (3Α,5α,12α)-3,12-dihydroxycholan-24-Oate | Generator | | (3Α,5α,12α)-3,12-dihydroxycholan-24-Oic acid | Generator | | (3a,5b,12a)-3,12-Dihydroxycholan-24-Oate | Generator | | (3a,5b,12a)-3,12-Dihydroxycholan-24-Oic acid | Generator | | (3alpha,5beta,12alpha)-3,12-Dihydroxycholan-24-Oate | Generator | | (3Α,5β,12α)-3,12-dihydroxycholan-24-Oate | Generator | | (3Α,5β,12α)-3,12-dihydroxycholan-24-Oic acid | Generator | | 3a,12a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholanate | Generator | | 3a,12a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholanic acid | Generator | | 3Α,12α-dihydroxy-5β-cholanate | Generator | | 3Α,12α-dihydroxy-5β-cholanic acid | Generator | | 7a-Deoxycholate | Generator | | 7a-Deoxycholic acid | Generator | | 7alpha-Deoxycholate | Generator | | 7Α-deoxycholate | Generator | | 7Α-deoxycholic acid | Generator | | Desoxycholate | Generator | | 5b-Cholanic acid-3a,12a-diol | HMDB | | 5b-Deoxycholate | HMDB | | 5b-Deoxycholic acid | HMDB | | 7-Deoxycholate | HMDB | | 7-Deoxycholic acid | HMDB | | Cholerebic | HMDB | | Cholorebic | HMDB | | Degalol | HMDB | | Deoxy-cholate | HMDB | | Deoxy-cholic acid | HMDB | | Deoxycholatate | HMDB | | Deoxycholatic acid | HMDB | | Acid, lagodeoxycholic | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, 5alpha isomer | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, sodium salt, 12beta-isomer | HMDB | | Lagodeoxycholic acid | HMDB | | Acid, choleic | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, 12beta isomer | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, 3beta-isomer | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, monoammonium salt | HMDB | | 12beta-Isomer deoxycholic acid | HMDB | | 3beta-Isomer deoxycholic acid | HMDB | | Acid, 5alpha-isomer deoxycholic | HMDB | | Acid, deoxycholic | HMDB | | Acid, desoxycholic | HMDB | | Deoxycholate, sodium | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, 12beta-isomer | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, 5alpha-isomer | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, monopotassium salt | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, monosodium salt | HMDB | | 5alpha-Isomer deoxycholic acid | HMDB | | Acid, dihydroxycholanoic | HMDB | | Choleic acid | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, 3beta isomer | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, disodium salt | HMDB | | Deoxycholic acid, magnesium (2:1) salt | HMDB | | Dihydroxycholanoic acid | HMDB | | Sodium deoxycholate | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C24H40O4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 392.572 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 392.292659768 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (4R)-4-[(1S,2S,5R,7R,10R,11S,14R,15R,16S)-5,16-dihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadecan-14-yl]pentanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (4R)-4-[(1S,2S,5R,7R,10R,11S,14R,15R,16S)-5,16-dihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadecan-14-yl]pentanoic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 83-44-3 |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])CC[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])C[C@H](O)[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C24H40O4/c1-14(4-9-22(27)28)18-7-8-19-17-6-5-15-12-16(25)10-11-23(15,2)20(17)13-21(26)24(18,19)3/h14-21,25-26H,4-13H2,1-3H3,(H,27,28)/t14-,15-,16-,17+,18-,19+,20+,21+,23+,24-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | KXGVEGMKQFWNSR-LLQZFEROSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as dihydroxy bile acids, alcohols and derivatives. Dihydroxy bile acids, alcohols and derivatives are compounds containing or derived from a bile acid or alcohol, and which bears exactly two carboxylic acid groups. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Steroids and steroid derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Bile acids, alcohols and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Dihydroxy bile acids, alcohols and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Dihydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- 3-hydroxysteroid
- 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid
- 12-hydroxysteroid
- Hydroxysteroid
- Cyclic alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic homopolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homopolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 171 - 174 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 0.044 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | 3.50 | RODA,A ET AL. (1990) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Deoxycholic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C | 3376.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C | 3366.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C | 3290.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C | 3307.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C | 3308.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C | 3285.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C | 3270.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C | 3592.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C | 3585.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C | 3553.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C | 3785.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C | 3758.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C | 3775.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Deoxycholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C | 3984.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00os-0119000000-ff101495d4bc6a37fc83 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-1110390000-cc7d539ad02f4039ec09 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_3_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid Quattro_QQQ 10V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0006-0009000000-8b9c4803e9cb1d194c2e | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid Quattro_QQQ 25V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0006-0009000000-cccabd9d13ac783b6e31 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid Quattro_QQQ 40V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0007-2009000000-d7c20760d2074c07af22 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-0009000000-269a5d1ed75b71c78ecb | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) 30V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0007-0009000000-72f1acf9f31f344daaa1 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid LC-ESI-ITTOF (LCMS-IT-TOF) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-000x-0008000900-ebb0e6a61bd8f06a21f7 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid LC-ESI-IT , negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0009000000-8078ef73008efc65c713 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid LC-ESI-QTOF , negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-0009000000-269a5d1ed75b71c78ecb | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid LC-ESI-QTOF , negative-QTOF | splash10-0007-0009000000-827a9ce119d7f2f1cb5c | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-0009000000-ade8ee412cabab0a5cdd | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 30V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0007-0009000000-827a9ce119d7f2f1cb5c | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-0009000000-46347f9ccba012a193b3 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0007-0009000000-7de3b9549dc580acb2af | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 30V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0007-0009000000-72f1acf9f31f344daaa1 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0007-0009000000-fa7c4f74eaf1bb2e1f57 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-0009000000-737c78b82fef7180b7ac | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-0009000000-eb86d43bab0334d7cfe4 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-056r-0009000000-db8bf3905980e8620f12 | 2017-07-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-056r-0009000000-6a632f1c8fbb19a314cb | 2017-07-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-4219000000-29a9a2c5d3d148fca202 | 2017-07-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-0009000000-ab9ac299290313e78fe4 | 2017-07-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-006x-1009000000-6444232cac6b7a24dd96 | 2017-07-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4l-9006000000-b2f4c82d34550211259c | 2017-07-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-054o-0019000000-a4dfbb4ad2f96e8ee6db | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Deoxycholic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0adl-4298000000-b6171657518bf9639cbe | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Erythrocyte
- Fibroblasts
- Intestine
|
|---|
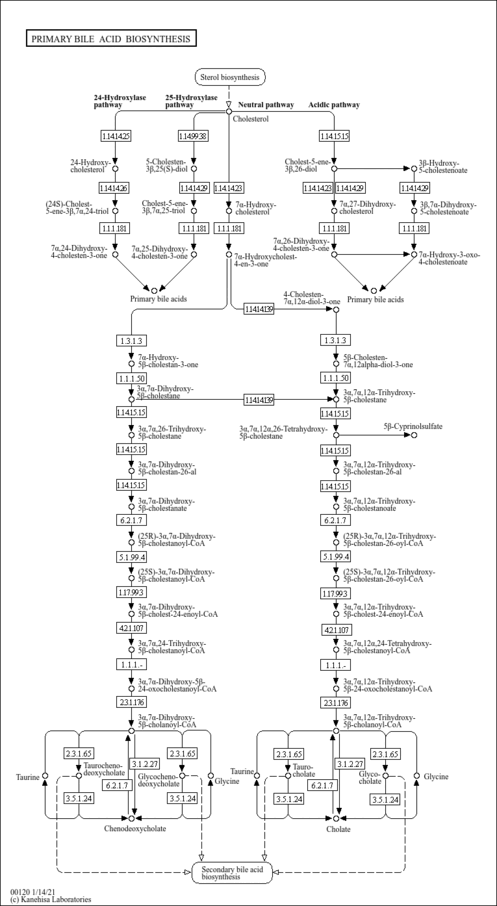
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Bile | Detected and Quantified | 11720 (11570-11860) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.57 +/- 0.35 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.33 +/- 0.06 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected and Quantified | 1920.10 +/- 1390.50 nmol/g dry feces | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.055 (0.05-0.060) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.43 +/- 0.09 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Cystic fibrosis | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.76 +/- 0.26 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Cystic fibrosis | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Irritable bowel syndrome | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Ulcerative colitis | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal Cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Not Specified | Recurrent Clostridium difficile infection | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Clostridium difficile infection | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Not Specified | Premature neonates | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.5 (0.1-1.3) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Biliary cirrhosis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.3 (0.06-0.87) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Biliary cirrhosis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.509 (0.113 - 1.324) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Primary biliary cirrhosis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.328 (0.0679 - 0.871) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Primary biliary cirrhosis | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Cystic fibrosis |
|---|
- Smith JL, Lewindon PJ, Hoskins AC, Pereira TN, Setchell KD, O'Connell NC, Shepherd RW, Ramm GA: Endogenous ursodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid in liver disease due to cystic fibrosis. Hepatology. 2004 Jun;39(6):1673-82. [PubMed:15185309 ]
| | Irritable bowel syndrome |
|---|
- Le Gall G, Noor SO, Ridgway K, Scovell L, Jamieson C, Johnson IT, Colquhoun IJ, Kemsley EK, Narbad A: Metabolomics of fecal extracts detects altered metabolic activity of gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. J Proteome Res. 2011 Sep 2;10(9):4208-18. doi: 10.1021/pr2003598. Epub 2011 Aug 8. [PubMed:21761941 ]
| | Ulcerative colitis |
|---|
- Le Gall G, Noor SO, Ridgway K, Scovell L, Jamieson C, Johnson IT, Colquhoun IJ, Kemsley EK, Narbad A: Metabolomics of fecal extracts detects altered metabolic activity of gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. J Proteome Res. 2011 Sep 2;10(9):4208-18. doi: 10.1021/pr2003598. Epub 2011 Aug 8. [PubMed:21761941 ]
| | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Brown DG, Rao S, Weir TL, O'Malia J, Bazan M, Brown RJ, Ryan EP: Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016 Jun 6;4:11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0151-y. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27275383 ]
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ: Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 25;11(3):e0152126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27015276 ]
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Ahn J, Shi J, Sinha R: Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2089-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131. Epub 2014 Jul 18. [PubMed:25037050 ]
| | Primary biliary cirrhosis |
|---|
- Batta AK, Arora R, Salen G, Tint GS, Eskreis D, Katz S: Characterization of serum and urinary bile acids in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis by gas-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: effect of ursodeoxycholic acid treatment. J Lipid Res. 1989 Dec;30(12):1953-62. [PubMed:2621422 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB03619 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB012780 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00030117 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 193196 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C04483 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Deoxycholic acid |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 265 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 222528 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 28834 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | DCHAC |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | He, Zhiquan. in-situ generation of deoxycholic acid by poultry for Chinese medicine. Faming Zhuanli Shenqing Gongkai Shuomingshu (1993), 3 pp. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Tadano T, Kanoh M, Matsumoto M, Sakamoto K, Kamano T: Studies of serum and feces bile acids determination by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Rinsho Byori. 2006 Feb;54(2):103-10. [PubMed:16548228 ]
- Salen G, Tint GS, Eliav B, Deering N, Mosbach EH: Increased formation of ursodeoxycholic acid in patients treated with chenodeoxycholic acid. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):612-21. [PubMed:11344576 ]
- Berr F, Stellaard F, Pratschke E, Paumgartner G: Effects of cholecystectomy on the kinetics of primary and secondary bile acids. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1541-50. [PubMed:2708522 ]
- Yamaga N, Adachi K, Shimizu K, Miyake S, Sumi F, Miyagawa I, Goto H: Bile acids of patients with renal failure receiving chronic hemodialysis. Steroids. 1986 Nov-Dec;48(5-6):427-38. [PubMed:3445292 ]
- Stellaard F, Paumgartner G, van Berge Henegouwen GP, van der Werf SD: Determination of deoxycholic acid pool size and input rate using [24-13C]deoxycholic acid and serum sampling. J Lipid Res. 1986 Nov;27(11):1222-5. [PubMed:3559388 ]
- Andersen RB, Bruusgaard A: Effect of the common bile acids on the fibrin/fibrinogen fragments in rheumatoid synovial fluid. A possible clue to the ameliorating effect of jaundice in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1975;4(3):158-64. [PubMed:52191 ]
- Deleze G, Paumgartner G, Karlaganis G, Giger W, Reinhard M, Sidiropoulos D: Bile acid pattern in human amniotic fluid. Eur J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;8(1):41-5. [PubMed:417931 ]
- Beher WT, Gabbard A, Norum RA, Stradnieks S: Effect of blood high density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration on fecal steroid excretion in humans. Life Sci. 1983 Jun 27;32(26):2933-7. [PubMed:6865641 ]
- Nobuoka A, Takayama T, Miyanishi K, Sato T, Takanashi K, Hayashi T, Kukitsu T, Sato Y, Takahashi M, Okamoto T, Matsunaga T, Kato J, Oda M, Azuma T, Niitsu Y: Glutathione-S-transferase P1-1 protects aberrant crypt foci from apoptosis induced by deoxycholic acid. Gastroenterology. 2004 Aug;127(2):428-43. [PubMed:15300575 ]
- Rudi J, Schonig T, Stremmel W: -Therapy with ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cirrhosis in pregnancy-. Z Gastroenterol. 1996 Mar;34(3):188-91. [PubMed:8650973 ]
- Heikkinen J, Maentausta O, Tuimala R, Ylostalo P, Janne O: Amniotic fluid bile acids in normal and pathologic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Jul;56(1):60-4. [PubMed:7383489 ]
- Duret G, Delcour AH: Deoxycholic acid blocks vibrio cholerae OmpT but not OmpU porin. J Biol Chem. 2006 Jul 21;281(29):19899-905. Epub 2006 May 2. [PubMed:16670088 ]
- Costarelli V, Sanders TA: Plasma deoxycholic acid concentration is elevated in postmenopausal women with newly diagnosed breast cancer. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2002 Sep;56(9):925-7. [PubMed:12209383 ]
- Stadler J, Yeung KS, Furrer R, Marcon N, Himal HS, Bruce WR: Proliferative activity of rectal mucosa and soluble fecal bile acids in patients with normal colons and in patients with colonic polyps or cancer. Cancer Lett. 1988 Jan;38(3):315-20. [PubMed:3349450 ]
- St-Pierre MV, Kullak-Ublick GA, Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ: Transport of bile acids in hepatic and non-hepatic tissues. J Exp Biol. 2001 May;204(Pt 10):1673-86. [PubMed:11316487 ]
- Claudel T, Staels B, Kuipers F: The Farnesoid X receptor: a molecular link between bile acid and lipid and glucose metabolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 Oct;25(10):2020-30. Epub 2005 Jul 21. [PubMed:16037564 ]
- Chiang JY: Bile acid regulation of hepatic physiology: III. Bile acids and nuclear receptors. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Mar;284(3):G349-56. [PubMed:12576301 ]
- Davis RA, Miyake JH, Hui TY, Spann NJ: Regulation of cholesterol-7alpha-hydroxylase: BAREly missing a SHP. J Lipid Res. 2002 Apr;43(4):533-43. [PubMed:11907135 ]
- Delzenne NM, Calderon PB, Taper HS, Roberfroid MB: Comparative hepatotoxicity of cholic acid, deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid in the rat: in vivo and in vitro studies. Toxicol Lett. 1992 Jul;61(2-3):291-304. [PubMed:1641875 ]
- Ajouz H, Mukherji D, Shamseddine A: Secondary bile acids: an underrecognized cause of colon cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 2014 May 24;12:164. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-164. [PubMed:24884764 ]
| Show more...
|---|