| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:09 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0001335 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Prostaglandin I2 |
|---|
| Description | Prostaglandin I2 or prostacyclin (or PGI2) is a member of the family of lipid molecules known as eicosanoids. It is produced in endothelial cells from prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) by the action of the enzyme prostacyclin synthase. It is a powerful vasodilator and inhibits platelet aggregation. Prostaglandin I2 is the main prostaglandin synthesized by the blood vessel wall. This suggests that it may play an important role in limiting platelet-mediated thrombosis. In particular, prostacyclin (PGI2) chiefly prevents formation of the platelet plug involved in primary hemostasis (a part of blood clot formation). The sodium salt (known as epoprostenol) has been used to treat primary pulmonary hypertension. Prostacyclin (PGI2) is released by healthy endothelial cells and performs its function through a paracrine signaling cascade that involves G protein-coupled receptors on nearby platelets and endothelial cells. The platelet Gs protein-coupled receptor (prostacyclin receptor) is activated when it binds to PGI2. This activation, in turn, signals adenylyl cyclase to produce cAMP. cAMP goes on to inhibit any undue platelet activation (in order to promote circulation) and also counteracts any increase in cytosolic calcium levels which would result from thromboxane A2 (TXA2) binding (leading to platelet activation and subsequent coagulation). PGI2 also binds to endothelial prostacyclin receptors and in the same manner raise cAMP levels in the cytosol. This cAMP then goes on to activate protein kinase A (PKA). PKA then continues the cascade by inhibiting myosin light-chain kinase which leads to smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation. Notably, PGI2 and TXA2 work as antagonists. PGI2 is stable in basic buffers (pH=8), but it is rapidly hydrolyzed to 6-keto PGF1alpha in neutral or acidic solutions. The half-life is short both in vivo and in vitro, ranging from 30 seconds to a few minutes. PGI2 is administered by continuous infusion in humans for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary hypertension.Prostaglandins are eicosanoids. The eicosanoids consist of the prostaglandins (PGs), thromboxanes (TXs), leukotrienes (LTs), and lipoxins (LXs). The PGs and TXs are collectively identified as prostanoids. Prostaglandins were originally shown to be synthesized in the prostate gland, thromboxanes from platelets (thrombocytes), and leukotrienes from leukocytes, hence the derivation of their names. All mammalian cells except erythrocytes synthesize eicosanoids. These molecules are extremely potent, able to cause profound physiological effects at very dilute concentrations. All eicosanoids function locally at the site of synthesis, through receptor-mediated G-protein linked signalling pathways. | Read more...
|---|
| Structure | CCCCC[C@H](O)\C=C\[C@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@H]2OC(C[C@H]12)=CCCCC(O)=O InChI=1S/C20H32O5/c1-2-3-4-7-14(21)10-11-16-17-12-15(8-5-6-9-20(23)24)25-19(17)13-18(16)22/h8,10-11,14,16-19,21-22H,2-7,9,12-13H2,1H3,(H,23,24)/b11-10+,15-8-/t14-,16+,17+,18+,19-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9alpha-Epoxy-11alpha,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate | ChEBI | | (5Z,9alpha,11alpha,13E,15S)-6,9-Epoxy-11,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-Oic acid | ChEBI | | Epoprostenol | ChEBI | | Flolan | ChEBI | | PGI2 | ChEBI | | PGX | ChEBI | | Prostacyclin | ChEBI | | Prostaglandin X | ChEBI | | Vasocyclin | ChEBI | | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9a-Epoxy-11a,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate | Generator | | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9a-Epoxy-11a,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoic acid | Generator | | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9alpha-Epoxy-11alpha,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoic acid | Generator | | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9Α-epoxy-11α,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate | Generator | | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9Α-epoxy-11α,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoic acid | Generator | | (5Z,9a,11a,13E,15S)-6,9-Epoxy-11,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-Oate | Generator | | (5Z,9a,11a,13E,15S)-6,9-Epoxy-11,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-Oic acid | Generator | | (5Z,9alpha,11alpha,13E,15S)-6,9-Epoxy-11,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-Oate | Generator | | (5Z,9Α,11α,13E,15S)-6,9-epoxy-11,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-Oate | Generator | | (5Z,9Α,11α,13E,15S)-6,9-epoxy-11,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-Oic acid | Generator | | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9-alpha-Epoxy-11-alpha,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate | HMDB | | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9-alpha-Epoxy-11-alpha,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoic acid | HMDB | | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9-Epoxy-11,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate | HMDB | | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9-Epoxy-11,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoic acid | HMDB | | (5Z,13E,15S)-6,9a-Epoxy-11a,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate | HMDB | | (5Z,13E,15S)-6,9a-Epoxy-11a,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoic acid | HMDB | | Prostacycline | HMDB | | Epoprostanol | HMDB | | Epoprostenol sodium | HMDB | | Epoprostenol sodium salt, (5Z,9alpha,11alpha,13E,15S)-isomer | HMDB | | Prostaglandin I(2) | HMDB | | Veletri | MeSH |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H32O5 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 352.4651 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 352.224974134 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 5-[(3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-hydroxy-4-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-en-1-yl]-hexahydro-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-ylidene]pentanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | epoprostenol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 35121-78-9 |
|---|
| SMILES | CCCCC[C@H](O)\C=C\[C@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@H]2OC(C[C@H]12)=CCCCC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H32O5/c1-2-3-4-7-14(21)10-11-16-17-12-15(8-5-6-9-20(23)24)25-19(17)13-18(16)22/h8,10-11,14,16-19,21-22H,2-7,9,12-13H2,1H3,(H,23,24)/b11-10+,15-8-/t14-,16+,17+,18+,19-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | KAQKFAOMNZTLHT-OZUDYXHBSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as prostaglandins and related compounds. These are unsaturated carboxylic acids consisting of a 20 carbon skeleton that also contains a five member ring, and are based upon the fatty acid arachidonic acid. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Eicosanoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Prostaglandins and related compounds |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Prostaglandin skeleton
- Fatty alcohol
- Medium-chain hydroxy acid
- Medium-chain fatty acid
- Heterocyclic fatty acid
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Cyclic alcohol
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Secondary alcohol
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Oxacycle
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Not Available | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Prostaglandin I2,1TMS,isomer #1 | CCCCC[C@@H](/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O)C[C@@H]21)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2836.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,1TMS,isomer #2 | CCCCC[C@H](O)/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O)C[C@@H]21 | 2827.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,1TMS,isomer #3 | CCCCC[C@H](O)/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@@H]21 | 2790.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,2TMS,isomer #1 | CCCCC[C@@H](/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O)C[C@@H]21)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2842.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,2TMS,isomer #2 | CCCCC[C@@H](/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@@H]21)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2854.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,2TMS,isomer #3 | CCCCC[C@H](O)/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@@H]21 | 2810.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,3TMS,isomer #1 | CCCCC[C@@H](/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@@H]21)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2816.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CCCCC[C@@H](/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O)C[C@@H]21)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3051.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CCCCC[C@H](O)/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O)C[C@@H]21 | 3046.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CCCCC[C@H](O)/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@@H]21 | 3018.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CCCCC[C@@H](/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O)C[C@@H]21)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3294.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CCCCC[C@@H](/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@@H]21)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3299.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CCCCC[C@H](O)/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@@H]21 | 3262.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Prostaglandin I2,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CCCCC[C@@H](/C=C/[C@H]1[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@@H]2OC(=CCCCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@@H]21)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3541.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0159-5693000000-d4cdd32893c86bb9479a | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0ug0-9253570000-9f0d8bdb642b0c32f40b | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00kr-0029000000-6c6186798558c5d1611f | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00y0-1093000000-eacafc8768142dba71da | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00du-9450000000-e3b550dcd32e28648707 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0009000000-34a4a3eaa1abb59e8245 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0f89-2139000000-efe90037816a750cfeee | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a59-9871000000-f961005fef0ef2363ce4 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0009000000-39b83b5b9b932bb2f6a1 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0ue9-0089000000-7141693b6303cf4e2e29 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-003s-2391000000-22e55e30c5e2afce8cc2 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014r-0009000000-fcc9a31a4c60d564196f | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-6359000000-d638f048af6abdb45cbf | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Prostaglandin I2 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-05tf-9610000000-8baf1f1acd84f0ed7ba8 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Extracellular
- Membrane (predicted from logP)
- Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Adipose Tissue
- Bladder
- Blood
- Brain
- Fibroblasts
- Kidney
- Liver
- Neuron
- Placenta
- Platelet
|
|---|
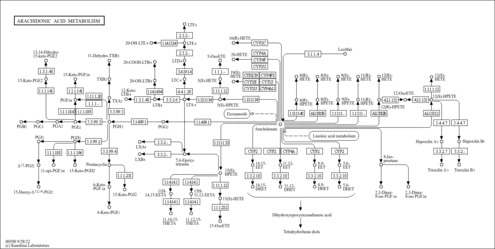
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | None |
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | None |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB022560 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 4445566 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C01312 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 37333 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Prostacyclin |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 778 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 5282411 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 15552 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | PROSTGI2 |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Walsh SW, Wang Y, Killian A: AA-2414, an antioxidant and thromboxane receptor blocker, completely inhibits peroxide-induced vasoconstriction in the human placenta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Jul;290(1):220-6. [PubMed:10381779 ]
- Brinkmann A, Seeling W, Wolf CF, Kneitinger E, Junger S, Rockemann M, Oettinger W, Georgieff M: [The effect of thoracic epidural anesthesia on the pathophysiology of the eventration syndrome]. Anaesthesist. 1994 Apr;43(4):235-44. [PubMed:8179173 ]
- Kearney D, Byrne A, Crean P, Cox D, Fitzgerald DJ: Optimal suppression of thromboxane A(2) formation by aspirin during percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty: no additional effect of a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004 Feb 18;43(4):526-31. [PubMed:14975458 ]
- De La Cruz JP, Arrebola MM, Villalobos MA, Pinacho A, Guerrero A, Gonzalez-Correa JA, Sanchez de la Cuesta F: Influence of glucose concentration on the effects of aspirin, ticlopidine and clopidogrel on platelet function and platelet-subendothelium interaction. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Jan 19;484(1):19-27. [PubMed:14729378 ]
- Cruz-Gervis R, Stecenko AA, Dworski R, Lane KB, Loyd JE, Pierson R, King G, Brigham KL: Altered prostanoid production by fibroblasts cultured from the lungs of human subjects with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 2002;3:17. Epub 2002 Feb 23. [PubMed:11980586 ]
- den Dekker E, Gorter G, Heemskerk JW, Akkerman JW: Development of platelet inhibition by cAMP during megakaryocytopoiesis. J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 9;277(32):29321-9. Epub 2002 May 7. [PubMed:11997386 ]
- McAdam BF, Byrne D, Morrow JD, Oates JA: Contribution of cyclooxygenase-2 to elevated biosynthesis of thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin in cigarette smokers. Circulation. 2005 Aug 16;112(7):1024-9. Epub 2005 Aug 8. [PubMed:16087791 ]
- Hei ZQ, Huang HQ, Luo CF, Li SR, Luo GJ: Changes of nitric oxide and endothelin, thromboxane A2 and prostaglandin in cirrhotic patients undergoing liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jul 7;12(25):4049-51. [PubMed:16810757 ]
- Nadar S, Lip GY: Platelet activation in the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2004 May;13(5):523-9. [PubMed:15155127 ]
- Fruzzetti F, Giannessi D, Ricci C, Bernini W, Puntoni R, Genazzani AR, De Caterina R: Platelet-vessel wall interactions with third-generation oral contraceptives: no evidence of detrimental effects. Thromb Haemost. 1999 Sep;82(3):1164-70. [PubMed:10494782 ]
- Cheng Y, Austin SC, Rocca B, Koller BH, Coffman TM, Grosser T, Lawson JA, FitzGerald GA: Role of prostacyclin in the cardiovascular response to thromboxane A2. Science. 2002 Apr 19;296(5567):539-41. [PubMed:11964481 ]
- Okamoto M, Abe T, Shouno M, Kitabata Y, Narukawa N, Kobata H, Akizawa T: A case of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura refractory to plasma exchange. Ther Apher. 2001 Feb;5(1):49-53. [PubMed:11258611 ]
- Li J, Dai G, Feng Z, Wang C, Yang Y, Wei W, Zhou B: Effect of low HDL combined with hypertriglyceridemia in coronary artery disease patients on PGI2 biological activity in relation to lipid regulating treatment. J Tongji Med Univ. 1998;18(2):87-9, 93. [PubMed:10806831 ]
- Vassaux G, Gaillard D, Darimont C, Ailhaud G, Negrel R: Differential response of preadipocytes and adipocytes to prostacyclin and prostaglandin E2: physiological implications. Endocrinology. 1992 Nov;131(5):2393-8. [PubMed:1330499 ]
- Haraldsson A, Kieler-Jensen N, Wadenvik H, Ricksten SE: Inhaled prostacyclin and platelet function after cardiac surgery and cardiopulmonary bypass. Intensive Care Med. 2000 Feb;26(2):188-94. [PubMed:10784307 ]
- Axelrod L: Insulin, prostaglandins, and the pathogenesis of hypertension. Diabetes. 1991 Oct;40(10):1223-7. [PubMed:1936584 ]
- Lehmann C, Taymoorian K, Wauer H, Krausch D, Birnbaum J, Kox WJ: Effects of the stable prostacyclin analogue iloprost on the plasma disappearance rate of indocyanine green in human septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2000 Oct;26(10):1557-60. [PubMed:11126272 ]
- Dickinson JE, Meyer BA, Brath PC, Chmielowiec S, Walsh SW, Parisi VM, Palmer SM: Placental thromboxane and prostacyclin production in an ovine diabetic model. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Dec;163(6 Pt 1):1831-5. [PubMed:2147814 ]
- Watanabe T, Kishi Y, Numano F, Isobe M: Enhanced platelet sensitivity to prostacyclin in patients in an active stage of Takayasu arteritis. Thromb Res. 2001 Oct 15;104(2):77-83. [PubMed:11672751 ]
- Harada N, Okajima K, Yuksel M, Isobe H: Contribution of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons to antithrombin-induced reduction of ischemia/reperfusion-induced liver injury in rats. Thromb Haemost. 2005 Jan;93(1):48-56. [PubMed:15630490 ]
| Show more...
|---|