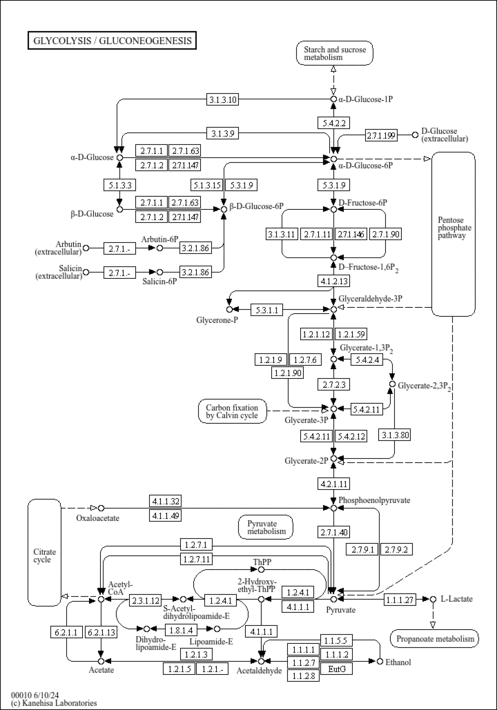
| Glucose 6-phosphate,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2152.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)O)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2115.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@H]1O | 2129.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,1TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2157.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,1TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2267.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2113.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2261.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2268.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2113.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2134.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2242.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@@H]1COP(=O)(O)O | 2126.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)O)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2081.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2205.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@H]1O | 2127.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2225.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2118.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2153.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2179.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2198.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #13 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2185.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #14 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2219.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2115.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2167.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2127.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2182.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2180.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2177.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2137.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@@H]1COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2200.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2149.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2211.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2253.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2203.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2211.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2203.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2215.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2230.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2185.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2237.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@@H]1COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2258.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2236.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2242.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2583.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2255.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2270.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2487.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2274.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2293.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2538.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2268.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2268.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2499.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2277.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2267.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2462.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,6TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2288.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,6TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2293.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,6TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2407.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2395.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)O)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2398.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@H]1O | 2412.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,1TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2432.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,1TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2523.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2530.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2703.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2740.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2533.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2535.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2662.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@@H]1COP(=O)(O)O | 2570.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)O)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2536.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2662.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@H]1O | 2569.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2673.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2742.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2817.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2845.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2848.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2848.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2883.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2733.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2795.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2753.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2799.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2798.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2831.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2790.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@@H]1COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2844.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2982.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3023.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3066.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2989.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3000.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O | 2999.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3013.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3011.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3017.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3054.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,4TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@@H]1COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3070.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3237.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3137.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3009.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3214.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3130.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 2948.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3228.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3159.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2972.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3232.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3123.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2957.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3275.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3139.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate,5TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(O)O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2929.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 |