| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2021-09-14 14:59:39 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0001413 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Citicoline |
|---|
| Description | Citicoline is an essential intermediate in the biosynthetic pathway of structural phospholipids in cell membranes, particularly phosphatidylcholine. Once absorbed, citicoline is widely distributed throughout the body, crosses the blood-brain barrier and reaches the central nervous system (CNS), where it is incorporated into the membrane and microsomal phospholipid fraction. Citicoline activates biosynthesis of structural phospholipids of neuronal membranes, increases brain metabolism, and acts upon the levels of different neurotransmitters. Thus, citicoline has been experimentally shown to increase norepinephrine and dopamine levels in the CNS. Owing to these pharmacological mechanisms, citicoline has a neuroprotective effect in hypoxic and ischemic conditions, decreasing the volume of ischemic lesion, and also improves learning and memory performance in animal models of brain aging. In addition, citicoline has been shown to restore the activity of mitochondrial ATPase and membrane Na+/K+ATPase, to inhibit activation of certain phospholipases, and to accelerate reabsorption of cerebral edema in various experimental models. Citicoline has also been shown to be able to inhibit mechanisms of apoptosis associated to cerebral ischemia and in certain neurodegeneration models, and to potentiate neuroplasticity mechanisms. Citicoline is a safe drug, as shown by the toxicological tests conducted, that has no significant systemic cholinergic effects and is a well tolerated product. (PMID:17171187 ). |
|---|
| Structure | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N1C=CC(N)=NC1=O InChI=1S/C14H26N4O11P2/c1-18(2,3)6-7-26-30(22,23)29-31(24,25)27-8-9-11(19)12(20)13(28-9)17-5-4-10(15)16-14(17)21/h4-5,9,11-13,19-20H,6-8H2,1-3H3,(H3-,15,16,21,22,23,24,25)/p+1/t9-,11-,12-,13-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| Cytidine 5'-(trihydrogen diphosphate), mono(2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl) ester | ChEBI | | Cytidine 5'-(trihydrogen diphosphoric acid), mono(2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl) ester | Generator | | Cidifos | MeSH | | Diphosphate choline, cytidine | MeSH | | 5'-Diphosphocholine, cytidine | MeSH | | Choline, cytidine diphosphate | MeSH | | Citicholine | MeSH | | Choline, CDP | MeSH | | Citicoline | MeSH | | Cyticholine | MeSH | | Cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine | MeSH | | Cytidine diphosphate choline | MeSH | | CDP Choline | MeSH | | Cytidine 5' diphosphocholine | MeSH | | CDP-choline | HMDB | | Choline 5'-cytidine diphosphate | HMDB | | Choline 5’-cytidine diphosphate | HMDB | | Choline cytidine diphosphate | HMDB | | Cytidine 5'-(choline diphosphate) | HMDB | | Cytidine 5'-(cholinyl pyrophosphate) | HMDB | | Cytidine 5'-diphosphate choline | HMDB | | Cytidine 5’-(choline diphosphate) | HMDB | | Cytidine 5’-(cholinyl pyrophosphate) | HMDB | | Cytidine 5’-diphosphate choline | HMDB | | Cytidine 5’-diphosphocholine | HMDB | | Cytidine choline diphosphate | HMDB | | Cytidine diphosphate choline ester | HMDB | | Cytidine diphosphocholine | HMDB | | Cytidine diphosphorylcholine | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C14H27N4O11P2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 489.3319 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 489.11515575 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | {[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}({hydroxy[2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethoxy]phosphoryl}oxy)phosphinic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | cdp-choline(1+) |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 987-78-0 |
|---|
| SMILES | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N1C=CC(N)=NC1=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C14H26N4O11P2/c1-18(2,3)6-7-26-30(22,23)29-31(24,25)27-8-9-11(19)12(20)13(28-9)17-5-4-10(15)16-14(17)21/h4-5,9,11-13,19-20H,6-8H2,1-3H3,(H3-,15,16,21,22,23,24,25)/p+1/t9-,11-,12-,13-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | RZZPDXZPRHQOCG-OJAKKHQRSA-O |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pterins and derivatives. These are polycyclic aromatic compounds containing a pterin moiety, which consist of a pteridine ring bearing a ketone and an amine group to form 2-aminopteridin-4(3H)-one. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Pteridines and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Pterins and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Pterins and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Pterin
- Aminobenzoic acid
- Aminobenzoic acid or derivatives
- Benzoic acid or derivatives
- Benzoic acid
- Benzoyl
- Aniline or substituted anilines
- Phenylalkylamine
- Hydroxypyrimidine
- Secondary aliphatic/aromatic amine
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Pyrimidine
- Benzenoid
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Amino acid
- Ketimine
- Azacycle
- Secondary amine
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Imine
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Amine
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
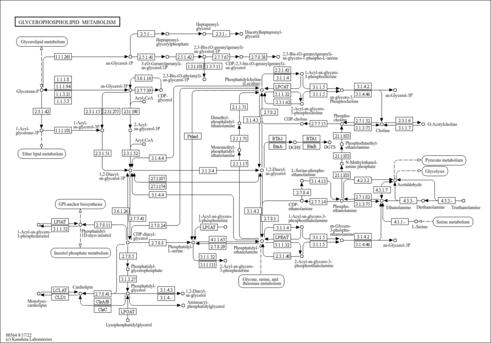
| Process | Naturally occurring processBiological processBiochemical pathwayMetabolic pathway- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0014212)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014219)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014221)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014250)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014258)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014278)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014280)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014307)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014316)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014338)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014366)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014367)
- Phospholipid Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0063652)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0063808)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063822)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063831)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063834)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063835)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0063836)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063844)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0063846)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063849)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063866)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063867)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0063870)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063884)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063888)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069980)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069983)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069986)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069987)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069996)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070008)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0070011)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070015)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070018)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070022)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070023)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070024)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070043)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070046)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070058)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070065)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070072)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070073)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070078)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070088)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070089)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070090)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070102)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070110)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070123)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070132)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070133)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070136)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070139)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070140)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070143)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070146)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070148)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070150)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070153)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070157)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070160)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070170)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070175)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070178)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070192)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070196)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070204)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070207)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070214)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070217)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070225)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070235)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070237)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070239)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070243)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070244)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070253)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070255)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070256)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070266)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070270)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070285)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070286)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070292)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070294)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070299)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070300)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070311)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070312)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070314)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070316)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070317)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070318)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070319)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070336)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070337)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070339)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070340)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070343)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070347)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070350)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070355)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070358)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070360)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070365)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070366)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070381)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070382)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070384)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070389)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070390)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070392)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070396)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070397)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070398)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070399)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070402)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070406)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070409)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070411)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070412)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070415)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080443)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080446)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080449)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080450)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080451)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080452)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080453)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080457)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080467)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080469)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080479)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080485)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0080490)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080493)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080498)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080511)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080525)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080528)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080529)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080530)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080533)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080549)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080552)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080554)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080562)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080563)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080568)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080573)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080577)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080579)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080585)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080589)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080592)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080595)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080599)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080609)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080615)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080616)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080627)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080632)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080634)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080636)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080639)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080643)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080645)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080657)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080659)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080667)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080668)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080672)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080674)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080690)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080695)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080697)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080699)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080706)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080713)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080716)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080721)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080723)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080726)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080727)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080729)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080731)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080737)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080745)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080750)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080751)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080752)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080755)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080756)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080758)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080771)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080775)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080776)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080777)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080780)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080782)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080783)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080790)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080799)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080820)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080821)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080826)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080833)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080834)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080843)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080849)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080853)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080854)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080866)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086740)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086742)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0086743)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086745)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086756)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086765)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086767)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086777)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086782)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0086798)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086800)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086803)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086805)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086823)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086828)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086835)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086836)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086847)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086854)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086858)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086882)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0086918)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086922)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086934)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086941)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086946)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086948)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086963)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0086966)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086967)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0086979)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086995)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087002)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087015)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087020)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087022)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087024)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0087025)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087030)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087032)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087052)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087066)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087083)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087107)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087110)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087115)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087118)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087123)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0087124)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087125)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087129)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087131)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087135)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087137)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087144)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087148)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087170)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087188)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0100277)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/14:0) | PE(14:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0100278)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/16:0) | PE(14:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0100281)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(14:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100286)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:1(11Z)) | PE(16:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100314)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(16:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100318)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:0) | PE(18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0100320)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:1(9Z)) | PE(18:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100321)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) | PE(18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100335)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:1(11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100339)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100346)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100353)
- Phospholipid Biosynthesis (HMDB: HMDB0001413)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014222)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014249)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014277)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014308)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014309)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014337)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014339)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014344)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063820)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063842)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063875)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063880)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069989)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069994)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070004)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070006)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070009)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0070010)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070047)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070054)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070084)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070111)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070127)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070135)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070149)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070159)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070171)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070212)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070215)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070223)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070240)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070248)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070252)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070277)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070280)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070282)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070298)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070309)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070313)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070324)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070338)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070341)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070371)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070400)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070413)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0080430)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080448)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080477)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080483)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080484)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080486)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0080487)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080500)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080506)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080508)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080523)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080546)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080547)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080561)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080590)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080600)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080604)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080606)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080611)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080620)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080637)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080638)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080641)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080642)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080648)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080649)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080651)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080661)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080670)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080677)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080680)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080681)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080698)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080710)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080738)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080743)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080754)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080769)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080796)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080800)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080804)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080807)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080817)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080825)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080842)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080857)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0086733)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086776)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0086779)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086795)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086802)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0086806)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086840)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086845)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086856)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086860)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086863)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086880)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086886)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086892)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086899)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086935)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086943)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086982)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087006)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087045)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087048)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087081)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087087)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087106)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087122)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100315)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:1(11Z)) | PE(18:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100322)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(18:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100323)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(18:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100324)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100330)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100331)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100333)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(18:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100336)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(18:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100337)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100348)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014257)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063858)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063877)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070060)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070083)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070116)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070126)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070154)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070181)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070208)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070216)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070231)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070236)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070246)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070260)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070267)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070274)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070301)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070325)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070330)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070353)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070380)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070388)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070407)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080512)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080556)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080705)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080724)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080744)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080763)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080792)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080823)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080864)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086781)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086811)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086937)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086989)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087054)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087092)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087094)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087128)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087140)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087152)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:0) | PE(14:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0100282)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(14:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100285)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(14:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100288)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/16:0) | PE(16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0100311)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:1(9Z)) | PE(16:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100313)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(16:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100316)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100328)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100341)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063827)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070032)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070183)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:1(9Z)) | PE(14:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100283)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:1(11Z)) | PE(14:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100284)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:0) | PE(16:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0100312)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100326)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100329)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100342)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100344)
- Ether lipid metabolism (PathBank: SMP0121068)
- Plasmalogen Synthesis (HMDB: HMDB0001413)
- Choline Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0002393)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER (PathBank: SMP0002425)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(10:0/10:0) (PathBank: SMP0002512)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(14:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002513)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002514)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002515)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(16:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002516)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002517)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002518)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(18:2(9Z,11Z)/18:2(9Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002519)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002520)
- Choline Biosynthesis II (PathBank: SMP0012027)
- Glycine Betaine Biosynthesis II (PathBank: SMP0012048)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014245)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014274)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014275)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014303)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014304)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014305)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014332)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014333)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014334)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014335)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014361)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014362)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014363)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014364)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014365)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014390)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014391)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014392)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014393)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014394)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014395)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014419)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014420)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014421)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014422)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014423)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014424)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014447)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014448)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014449)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014450)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014451)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014452)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014453)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014454)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014476)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014477)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014478)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014479)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014480)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014481)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014482)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014483)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014484)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014505)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014506)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014507)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014508)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014509)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014510)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014511)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014512)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014513)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014514)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014534)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014535)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014536)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014537)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014538)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014539)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014540)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014541)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014542)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014543)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014544)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014563)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014564)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014565)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014566)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014567)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014568)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014569)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014570)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014571)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014572)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014573)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014574)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014592)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014593)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014594)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014595)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014596)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014597)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014598)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014599)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014600)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014601)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014602)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014603)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014604)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014621)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014622)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014623)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014624)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014625)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014626)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014627)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014628)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014629)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014630)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014631)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014632)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014633)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014634)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014650)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014651)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014652)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014653)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014654)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014655)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014656)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014657)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014658)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014659)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014660)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014661)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014662)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014663)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014664)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014679)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014680)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014681)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014682)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014683)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014684)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014685)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014686)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014687)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014688)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014689)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014690)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014691)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014692)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014693)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014694)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014708)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014709)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014710)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014711)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014712)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014713)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014714)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014715)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014716)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014717)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014718)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014719)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014720)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014721)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014722)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014723)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014724)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014737)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014738)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014739)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014740)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014741)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014742)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014743)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014744)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014745)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014746)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014747)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014748)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014749)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014750)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014751)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014752)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014753)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014754)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014766)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014767)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014768)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014769)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014770)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014771)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014772)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014773)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014774)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014775)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014776)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014777)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014778)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014779)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014780)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014781)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014782)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014783)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014784)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014795)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014796)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014797)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014798)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014799)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014800)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014801)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014802)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014803)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014804)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014805)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014806)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014807)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014808)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014809)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014810)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014811)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014812)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014813)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014814)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014824)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014825)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014826)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014827)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014828)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014829)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014830)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014831)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014832)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014833)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014834)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014835)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014836)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014837)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014838)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014839)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014840)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014842)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014843)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014844)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014853)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014854)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014855)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014856)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014857)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014858)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014859)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014860)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014861)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014862)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014863)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014864)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014865)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014866)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014867)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014868)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014869)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014870)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014871)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014872)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014873)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014874)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014882)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014883)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014884)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014885)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014886)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014887)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014888)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014889)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014890)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014891)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014892)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014893)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014894)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014895)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014896)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014897)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014898)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014899)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014900)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014901)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014902)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014903)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014904)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014911)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014912)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014913)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014914)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014915)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014916)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014917)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014918)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014919)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014920)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014921)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014922)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014923)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014924)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014925)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014926)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014927)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014928)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014929)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014930)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014931)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014932)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014933)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014934)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014940)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014941)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014942)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014943)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014944)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014945)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014946)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014947)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014948)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014949)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014950)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014951)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014952)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014953)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014954)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014955)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014956)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014957)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014958)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014959)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014960)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014961)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014962)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014963)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014964)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014969)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014970)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014971)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014972)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014973)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014974)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014975)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014976)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014977)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014978)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014979)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014980)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014981)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014982)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014983)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014984)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014985)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014986)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014987)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014988)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014989)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014990)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014991)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014992)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014993)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014994)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014998)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014999)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0015000)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0015001)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015002)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0015003)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015004)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015005)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015006)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015007)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015008)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015009)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0015010)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015011)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015012)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015013)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015014)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015015)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015016)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015017)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0015018)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015019)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015020)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015021)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015022)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015023)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015024)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0015027)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015028)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0015029)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0015030)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015031)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0015032)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015033)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015034)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015035)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015036)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015037)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015038)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0015039)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015040)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015041)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015042)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015043)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015044)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015045)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015046)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0015047)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015048)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015049)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015050)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015051)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015052)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015053)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0015054)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030241)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030242)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030243)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030244)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030245)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030246)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030247)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030248)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030249)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030250)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030251)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030252)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030253)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030254)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030255)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030256)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030257)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030258)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030259)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030260)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030261)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030262)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030263)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030264)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030265)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030266)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030267)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030268)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030269)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030270)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030271)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030272)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030273)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030274)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030275)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030276)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030277)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030278)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030279)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030280)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030281)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030282)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030283)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030284)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030285)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030286)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030287)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030288)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030289)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030290)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030291)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030292)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030293)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030294)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030295)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030296)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030297)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030298)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030299)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030300)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030301)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030302)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030303)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030304)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030305)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030306)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030307)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030308)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030309)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030310)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030311)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030312)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030313)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030314)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030315)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030316)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030317)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030318)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030319)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030320)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030321)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063838)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063848)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063857)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063865)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063872)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063878)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063883)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063887)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(13Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063890)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(13Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063891)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063892)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/i-15:0) | PE(14:0/i-15:0) (PathBank: SMP0100123)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/16:1(9Z)) | PE(14:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100125)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/i-17:0) | PE(14:0/i-17:0) (PathBank: SMP0100126)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | PE(14:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100131)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:0) | PE(14:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100133)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(14:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100134)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(14:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100135)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(14:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100137)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(14:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100138)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/i-15:0) | PE(i-15:0/i-15:0) (PathBank: SMP0100139)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/16:0) | PE(i-15:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0100140)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/16:1(9Z)) | PE(i-15:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100141)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/i-17:0) | PE(i-15:0/i-17:0) (PathBank: SMP0100142)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/18:0) | PE(i-15:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0100143)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/18:1(9Z)) | PE(i-15:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100144)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/18:1(11Z)) | PE(i-15:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100145)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(i-15:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100146)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | PE(i-15:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100147)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(i-15:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100148)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/20:0) | PE(i-15:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100149)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(i-15:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100150)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(i-15:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100151)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(i-15:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100152)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(i-15:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100153)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-15:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(i-15:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100154)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/16:1(9Z)) | PE(16:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100156)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/i-17:0) | PE(16:0/i-17:0) (PathBank: SMP0100157)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | PE(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100162)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:0) | PE(16:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100164)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(16:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100165)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(16:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100166)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(16:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100168)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(16:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100169)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100170)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/i-17:0) | PE(16:1(9Z)/i-17:0) (PathBank: SMP0100171)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:0) | PE(16:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0100172)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100173)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100174)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100175)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100176)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100177)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:0) | PE(16:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100178)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100179)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100180)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100181)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100182)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(16:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100183)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/i-17:0) | PE(i-17:0/i-17:0) (PathBank: SMP0100184)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/18:0) | PE(i-17:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0100185)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/18:1(9Z)) | PE(i-17:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100186)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/18:1(11Z)) | PE(i-17:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100187)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(i-17:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100188)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | PE(i-17:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100189)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(i-17:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100190)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/20:0) | PE(i-17:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100191)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(i-17:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100192)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(i-17:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100193)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(i-17:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100194)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(i-17:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100195)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(i-17:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(i-17:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100196)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | PE(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100201)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:0) | PE(18:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100203)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(18:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100204)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100205)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100207)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100208)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100212)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:0) | PE(18:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100214)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100215)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100216)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100218)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100219)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | PE(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100222)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:0) | PE(18:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100224)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(18:1(11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100225)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:1(11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100226)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:1(11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100228)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:1(11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100229)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100231)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:0) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100233)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100234)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100235)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100237)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100238)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100239)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100240)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) | PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100241)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100242)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100243)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100244)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100245)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100246)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0) | PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100248)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100249)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100250)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100252)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100253)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:0) | PE(20:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0100254)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(20:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100255)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(20:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100256)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(20:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100257)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100258)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100259)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) | PE(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100260)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100261)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100262)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100263)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100264)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100265)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100266)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100267)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100268)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100270)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100271)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100272)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100273)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | PE(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100274)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/14:1(9Z)) | PE(14:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100279)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/15:0) | PE(14:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0100280)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:1(11Z)) | PE(14:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100287)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:0) | PE(14:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100289)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) | PE(14:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100290)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/15:0) | PE(14:1(9Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0100291)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/16:0) | PE(14:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0100292)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:0) | PE(14:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0100293)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) | PE(14:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100294)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) | PE(14:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100295)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(14:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100296)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(14:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100297)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) | PE(14:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100298)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(14:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100299)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:0) | PE(14:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100300)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/15:0) | PE(15:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0100301)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/16:0) | PE(15:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0100302)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:0) | PE(15:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0100303)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:1(9Z)) | PE(15:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100304)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:1(11Z)) | PE(15:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100305)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | PE(15:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100306)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | PE(15:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100307)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:1(11Z)) | PE(15:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100308)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(15:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100309)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:0) | PE(15:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100310)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:1(11Z)) | PE(16:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100317)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:0) | PE(16:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100319)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:1(11Z)) | PE(18:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100325)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:0) | PE(18:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100327)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) | PE(18:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100332)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:0) | PE(18:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100334)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) | PE(18:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100338)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:0) | PE(18:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100340)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100343)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:0) | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100345)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)) | PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100347)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0) | PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100349)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) | PE(20:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100350)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | PE(20:1(11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0100351)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:0) | PE(20:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100352)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:0) | PE(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100354)
- Phosphatidylcholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:0) | PE(22:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0100355)
|
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross Sections| Predictor | Adduct Type | CCS Value (Å2) | Reference |
|---|
| DeepCCS | [M+H]+ | 180.261 | 30932474 | | DeepCCS | [M-H]- | 178.179 | 30932474 | | DeepCCS | [M-2H]- | 211.417 | 30932474 | | DeepCCS | [M+Na]+ | 186.169 | 30932474 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Citicoline,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3566.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3570.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3616.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,1TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3613.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,1TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3661.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3476.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #10 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3627.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #11 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3585.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3506.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3506.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3573.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3515.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #6 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3516.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #7 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3573.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #8 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3541.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TMS,isomer #9 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3626.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3440.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3319.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5262.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #10 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3556.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #10 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3401.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #10 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4953.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #11 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3496.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #11 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3428.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #11 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5133.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #12 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3587.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #12 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3457.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #12 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4756.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #13 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3546.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #13 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3467.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #13 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4920.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #14 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3548.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #14 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3462.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #14 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4923.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3442.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3313.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 5267.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3515.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3398.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5232.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3452.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3360.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 5046.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3552.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3429.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4975.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3556.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3425.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4977.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3497.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3446.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 5149.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #8 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3460.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #8 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3337.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #8 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 5027.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #9 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3552.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #9 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3408.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TMS,isomer #9 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4959.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3408.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3276.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4858.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3510.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3375.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4571.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3538.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3422.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4377.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3504.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3368.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4694.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3509.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3361.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4684.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3469.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3379.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4842.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3533.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3392.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4459.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3502.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3401.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4599.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3507.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3395.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4599.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3535.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3365.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4428.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3504.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3382.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4579.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3504.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3339.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4213.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3481.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3345.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4354.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3488.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3340.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4342.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3510.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3359.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4134.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3519.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3340.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4103.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=CC(N)=NC1=O | 3794.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O | 3796.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3827.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,1TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C | 3825.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,1TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 3922.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3907.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 4072.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)C=C1)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3992.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=CC(N)=NC1=O | 3930.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=CC(N)=NC1=O | 3933.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C1 | 4038.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O | 3935.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O | 3935.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 4036.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3952.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,2TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 4074.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4057.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3778.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5289.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 4185.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 3874.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 4964.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O | 4113.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O | 3945.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O | 5081.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 4200.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 3884.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 4781.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4144.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3947.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4901.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C | 4144.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C | 3945.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OP(=O)(OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C | 4901.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4055.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3780.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5289.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C1 | 4150.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C1 | 3902.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C1 | 5198.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=CC(N)=NC1=O | 4053.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=CC(N)=NC1=O | 3784.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=CC(N)=NC1=O | 5087.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C1 | 4184.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C1 | 3900.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C1 | 4982.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C1 | 4184.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C1 | 3901.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C1 | 4983.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC1=O | 4112.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC1=O | 3966.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=CC(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=NC1=O | 5096.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O | 4055.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O | 3755.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)[C@@H]1O | 5064.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 4187.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 3871.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Citicoline,3TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC(=O)N([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)OP(=O)(O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]2O)C=C1 | 4956.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|