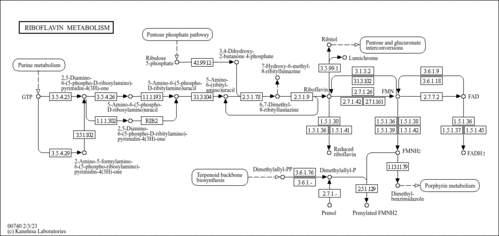
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Quinone EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0zgi-9500000000-c8bfbbc465fad7929f87 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Quinone GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00xr-1900000000-9b99afb0e9c6350434a4 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Quinone EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0zgi-9500000000-c8bfbbc465fad7929f87 | 2018-05-18 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Quinone GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00xr-1900000000-9b99afb0e9c6350434a4 | 2018-05-18 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Quinone GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9500000000-6664b553a87d4fc15f94 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Quinone GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0zgi-9200000000-8777cde0dbcbb2157cdd | 2014-09-20 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0a4i-7900000000-fca2433f986ba378f8c9 | 2012-07-25 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-00or-9000000000-6897ef153b4119e50ceb | 2012-07-25 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-014u-9000000000-9bddbff45c6d0d3e0cf1 | 2012-07-25 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone EI-B (JEOL JMS-D-3000) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0zgi-9500000000-c8bfbbc465fad7929f87 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone ESI-QFT 7V, negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-1900000000-6d13549d8c534563dc9b | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone ESI-QFT 9V, negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-1900000000-af62dc0334e009fe3e5b | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone ESI-QFT 14V, negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-3900000000-1167cf77177c0761168e | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-d886efcfed5b0135bcd5 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-1900000000-7f5c75e048ee2f454e33 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a6r-9100000000-db1ffa9cf092dd5e4551 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-648d78080240a1294e4c | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-648d78080240a1294e4c | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-5900000000-0f04c7bee6397237ee21 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-2c6cb60a5040c6239920 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-4900000000-f1f9c8ded0fe97bb684d | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-9000000000-3c2c54b9382bddbdf0df | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-62ea0dd9303aae554ccd | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-2900000000-7966cc06756dd3b8c736 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quinone 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-9000000000-28217a7272677bec662a | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, 5%_DMSO, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| General References | - Kwasnicka-Crawford DA, Vincent SR: Role of a novel dual flavin reductase (NR1) and an associated histidine triad protein (DCS-1) in menadione-induced cytotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Oct 21;336(2):565-71. [PubMed:16140270 ]
- Fabiani R, De Bartolomeo A, Morozzi G: Involvement of oxygen free radicals in the serum-mediated increase of benzoquinone genotoxicity. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2005 Oct;46(3):156-63. [PubMed:15920754 ]
- Gaskell M, McLuckie KI, Farmer PB: Comparison of the repair of DNA damage induced by the benzene metabolites hydroquinone and p-benzoquinone: a role for hydroquinone in benzene genotoxicity. Carcinogenesis. 2005 Mar;26(3):673-80. Epub 2004 Dec 23. [PubMed:15618234 ]
- Bello RI, Gomez-Diaz C, Navarro F, Alcain FJ, Villalba JM: Expression of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 in HeLa cells: role of hydrogen peroxide and growth phase. J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 30;276(48):44379-84. Epub 2001 Sep 20. [PubMed:11567026 ]
- Park S, Geddes TJ, Javitch JA, Kuhn DM: Dopamine prevents nitration of tyrosine hydroxylase by peroxynitrite and nitrogen dioxide: is nitrotyrosine formation an early step in dopamine neuronal damage? J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 1;278(31):28736-42. Epub 2003 May 27. [PubMed:12771134 ]
- Siegel D, Ryder J, Ross D: NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 expression in human bone marrow endothelial cells. Toxicol Lett. 2001 Dec 15;125(1-3):93-8. [PubMed:11701227 ]
- Roberg K, Johansson U, Ollinger K: Lysosomal release of cathepsin D precedes relocation of cytochrome c and loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential during apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999 Dec;27(11-12):1228-37. [PubMed:10641715 ]
- Yamazaki H, Shibata A, Suzuki M, Nakajima M, Shimada N, Guengerich FP, Yokoi T: Oxidation of troglitazone to a quinone-type metabolite catalyzed by cytochrome P-450 2C8 and P-450 3A4 in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 1999 Nov;27(11):1260-6. [PubMed:10534310 ]
- He K, Woolf TF, Kindt EK, Fielder AE, Talaat RE: Troglitazone quinone formation catalyzed by human and rat CYP3A: an atypical CYP oxidation reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 2001 Jul 15;62(2):191-8. [PubMed:11389877 ]
- Soucek P: Cytochrome P450 destruction by quinones: comparison of effects in rat and human liver microsomes. Chem Biol Interact. 1999 Aug 1;121(3):223-36. [PubMed:10462055 ]
- Xu L, Eiseman JL, Egorin MJ, D'Argenio DZ: Physiologically-based pharmacokinetics and molecular pharmacodynamics of 17-(allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin and its active metabolite in tumor-bearing mice. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2003 Jun;30(3):185-219. [PubMed:14571691 ]
- He K, Talaat RE, Woolf TF: Incorporation of an oxygen from water into troglitazone quinone by cytochrome P450 and myeloperoxidase. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004 Apr;32(4):442-6. [PubMed:15039298 ]
- Toyota T, Ueno Y: [Clinical effect and side effect of troglitazone]. Nihon Rinsho. 2000 Feb;58(2):376-82. [PubMed:10707561 ]
- Smith MT: The mechanism of benzene-induced leukemia: a hypothesis and speculations on the causes of leukemia. Environ Health Perspect. 1996 Dec;104 Suppl 6:1219-25. [PubMed:9118896 ]
- Terman A, Neuzil J, Kagedal K, Ollinger K, Brunk UT: Decreased apoptotic response of inclusion-cell disease fibroblasts: a consequence of lysosomal enzyme missorting? Exp Cell Res. 2002 Mar 10;274(1):9-15. [PubMed:11855852 ]
- Mu D, Medzihradszky KF, Adams GW, Mayer P, Hines WM, Burlingame AL, Smith AJ, Cai D, Klinman JP: Primary structures for a mammalian cellular and serum copper amine oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9926-32. [PubMed:8144587 ]
- Hasegawa T, Matsuzaki M, Takeda A, Kikuchi A, Furukawa K, Shibahara S, Itoyama Y: Increased dopamine and its metabolites in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells that express tyrosinase. J Neurochem. 2003 Oct;87(2):470-5. [PubMed:14511124 ]
| Show more...
|---|