| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-01-29 15:47:32 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:51:12 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0011618 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol |
|---|
| Description | All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol, also known as 13,14-dihydro-all-trans-retinol, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as retinoids. These are oxygenated derivatives of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene and derivatives thereof. Thus, all-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol is considered to be an isoprenoid lipid molecule. All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble (in water), and relatively neutral. |
|---|
| Structure | CC(CCO)\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C InChI=1S/C20H32O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-12,17,21H,7,10,13-15H2,1-5H3/b9-6+,12-11+,16-8+ |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 13,14-Dihydroretinol | ChEBI | | 13,14-Dihydro-all-trans-retinol | HMDB | | 13,14-Dihydro-retinol | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H32O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 288.4675 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 288.245315646 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-4,6,8-trien-1-ol |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 13,14-dihydroretinol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 115797-14-3 |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(CCO)\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H32O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-12,17,21H,7,10,13-15H2,1-5H3/b9-6+,12-11+,16-8+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | OVBOQVAIYMSUDT-HRYGCDPOSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as retinoids. These are oxygenated derivatives of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene and derivatives thereof. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Retinoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Retinoids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Retinoid skeleton
- Diterpenoid
- Fatty alcohol
- Fatty acyl
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized | Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00di-3290000000-50a2d27c4e5b3092828a | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0002-7259000000-c043fe3a5e5f48c88c48 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0079-1590000000-305f5c3efcc6bbc100d7 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00s9-4920000000-6a12f345df3ddb86a595 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-067r-9710000000-f39cf90bb1534db3c158 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-0090000000-f8ae4eefdd8e0d6c6a3c | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4r-0090000000-fa8cc05c3e7e51ea73cb | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-006x-4690000000-a18e2c16a607dab729c0 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-0090000000-3ebe1a43ea8596a21475 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4r-0190000000-d4dde516c54806fe814d | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0gbc-2950000000-74b22df066dc0c5110ae | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00dr-1950000000-b7be8f013d56482c890c | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0079-2910000000-343b05ba0dc7811743a1 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - All-trans-13,14-dihydroretinol 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-01bc-7900000000-5cefb7639e63f6cfeb5a | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
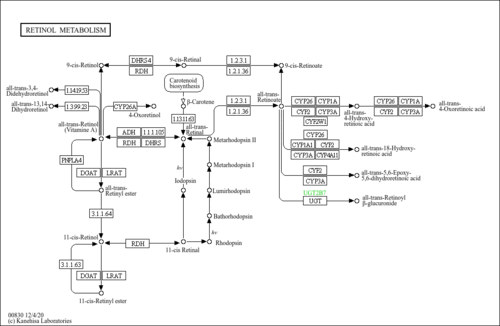
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | None |
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | None |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB028323 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 394057 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C15492 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CPD-7247 |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 446798 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 52075 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | Not Available |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Simons K, Toomre D: Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;1(1):31-9. [PubMed:11413487 ]
- Watson AD: Thematic review series: systems biology approaches to metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. Lipidomics: a global approach to lipid analysis in biological systems. J Lipid Res. 2006 Oct;47(10):2101-11. Epub 2006 Aug 10. [PubMed:16902246 ]
- Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig AJ: Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue function and plasticity orchestrate nutritional adaptation. J Lipid Res. 2007 Jun;48(6):1253-62. Epub 2007 Mar 20. [PubMed:17374880 ]
- Lingwood D, Simons K: Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science. 2010 Jan 1;327(5961):46-50. doi: 10.1126/science.1174621. [PubMed:20044567 ]
- Gunstone, Frank D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra (2007). The lipid handbook with CD-ROM. CRC Press.
|
|---|