| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:48:59 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000138 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB00138
- HMDB0032596
- HMDB31818
- HMDB32596
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Glycocholic acid |
|---|
| Description | Glycocholic acid is an acyl glycine and a bile acid-glycine conjugate. It is a secondary bile acid produced by the action of enzymes existing in the microbial flora of the colonic environment. Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, Clostridium and Lactobacillus are involved in bile acid metabolism and produce glycocholic acid (PMID: 6265737 ; 10629797). In hepatocytes, both primary and secondary bile acids undergo amino acid conjugation at the C-24 carboxylic acid on the side chain, and almost all bile acids in the bile duct therefore exist in a glycine conjugated form (PMID: 16949895 ). More specifically, glycocholic acid or cholylglycine, is a crystalline bile acid involved in the emulsification of fats. It occurs as a sodium salt in the bile of mammals. Its anion is called glycocholate. As the glycine conjugate of cholic acid, this compound acts as a detergent to solubilize fats for absorption and is itself absorbed (PubChem). Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in bile of mammals. The distinction between different bile acids is minute, depends only on presence or absence of hydroxyl groups on positions 3, 7, and 12. Bile acids are physiological detergents that facilitate excretion, absorption, and transport of fats and sterols in the intestine and liver. Bile acids are also steroidal amphipathic molecules derived from the catabolism of cholesterol. They modulate bile flow and lipid secretion, are essential for the absorption of dietary fats and vitamins, and have been implicated in the regulation of all the key enzymes involved in cholesterol homeostasis. Bile acids recirculate through the liver, bile ducts, small intestine and portal vein to form an enterohepatic circuit. They exist as anions at physiological pH and, consequently, require a carrier for transport across the membranes of the enterohepatic tissues. The unique detergent properties of bile acids are essential for the digestion and intestinal absorption of hydrophobic nutrients. Bile acids have potent toxic properties (e.g., membrane disruption) and there are a plethora of mechanisms to limit their accumulation in blood and tissues (PMID: 11316487 , 16037564 , 12576301 , 11907135 ). Glycocholic acid is found to be associated with alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, which is an inborn error of metabolism. |
|---|
| Structure | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(O)=O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3[C@H](O)C[C@@H]4C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O)[C@]12C InChI=1S/C26H43NO6/c1-14(4-7-22(31)27-13-23(32)33)17-5-6-18-24-19(12-21(30)26(17,18)3)25(2)9-8-16(28)10-15(25)11-20(24)29/h14-21,24,28-30H,4-13H2,1-3H3,(H,27,31)(H,32,33)/t14-,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20-,21+,24+,25+,26-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-Trihydroxy-5beta-cholan-24-oylglycine | ChEBI | | N-[(3alpha,5beta,7alpha,12alpha)-3,7,12-Trihydroxy-24-oxocholan-24-yl]glycine | ChEBI | | N-Choloylglycine | ChEBI | | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholan-24-oylglycine | Generator | | 3Α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oylglycine | Generator | | N-[(3a,5b,7a,12a)-3,7,12-Trihydroxy-24-oxocholan-24-yl]glycine | Generator | | N-[(3Α,5β,7α,12α)-3,7,12-trihydroxy-24-oxocholan-24-yl]glycine | Generator | | Glycocholate | Generator | | Glycine cholate | HMDB | | Glycocholic acid, sodium salt | HMDB | | Cholylglycine | HMDB | | Glycocholate sodium | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-Trihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid-24-glycine | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-Trihydroxy-N-(carboxymethyl)-5beta-cholan-24-amide | HMDB | | 3Α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholanic acid-24-glycine | HMDB | | 3Α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-N-(carboxymethyl)-5β-cholan-24-amide | HMDB | | Glycoreductodehydrocholic acid | HMDB | | Glycylcholate | HMDB | | Glycylcholic acid | HMDB | | N-(Carboxymethyl)-3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-trihydroxy-5beta-cholan-24-amide | HMDB | | N-(Carboxymethyl)-3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amide | HMDB | | N-Choloyl-glycine | HMDB | | Glycocholic acid | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C26H43NO6 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 465.6227 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 465.309038113 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-[(4R)-4-[(1S,2S,5R,7S,9R,10R,11S,14R,15R,16S)-5,9,16-trihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadecan-14-yl]pentanamido]acetic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | [(4R)-4-[(1S,2S,5R,7S,9R,10R,11S,14R,15R,16S)-5,9,16-trihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadecan-14-yl]pentanamido]acetic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 475-31-0 |
|---|
| SMILES | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(O)=O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3[C@H](O)C[C@@H]4C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O)[C@]12C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C26H43NO6/c1-14(4-7-22(31)27-13-23(32)33)17-5-6-18-24-19(12-21(30)26(17,18)3)25(2)9-8-16(28)10-15(25)11-20(24)29/h14-21,24,28-30H,4-13H2,1-3H3,(H,27,31)(H,32,33)/t14-,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20-,21+,24+,25+,26-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | RFDAIACWWDREDC-FRVQLJSFSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as glycinated bile acids and derivatives. Glycinated bile acids and derivatives are compounds with a structure characterized by the presence of a glycine linked to a bile acid skeleton. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Steroids and steroid derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Bile acids, alcohols and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Glycinated bile acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Glycinated bile acid
- Trihydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- Hydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- 3-hydroxysteroid
- 12-hydroxysteroid
- Hydroxysteroid
- 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid
- 7-hydroxysteroid
- N-acyl-alpha-amino acid
- N-acyl-alpha amino acid or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Cyclic alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Polyol
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Carboximidic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboximidic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Organonitrogen compound
- Aliphatic homopolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homopolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 170 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 0.0033 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | 1.65 | RODA,A ET AL. (1990) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Glycocholic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3929.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3846.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3737.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,1TMS,isomer #4 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3862.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,1TMS,isomer #5 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3813.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3844.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #10 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3750.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3824.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3864.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3752.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #5 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3778.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #6 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3813.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #7 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3699.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #8 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3689.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #9 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3705.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3770.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #10 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3673.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3782.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3704.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3751.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3717.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3725.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3726.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #8 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3692.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #9 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3696.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3709.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3698.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3699.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3694.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3701.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3681.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4125.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4087.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3948.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4070.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #5 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4019.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4265.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #10 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4173.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4234.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4281.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4153.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4222.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #6 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4259.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #7 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4133.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #8 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4126.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #9 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4140.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4376.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #10 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4324.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4404.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4296.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4374.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4326.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | C[C@H](CCC(=NCC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4330.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 4367.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #8 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4321.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #9 | C[C@H](CCC(O)=NCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4313.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_6) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_7) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_8) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_9) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_10) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_6) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_7) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_8) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid Quattro_QQQ 10V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-03di-0000900000-52e93813a9681b93b67c | 2019-05-16 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid Quattro_QQQ 25V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-03k9-4000900000-79dfcaf6e620e89a8f51 | 2019-05-16 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid Quattro_QQQ 40V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-00di-9000000000-0153bf31bdc096136252 | 2019-05-16 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000400000-e797c46f8e20c716b24c | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000200000-478282fdac3fd2f1d8a5 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0000900000-ea860edeae64135340d1 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000300000-9a12b83610eacbe64ab6 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0000900000-54d1a3d9fa6179530909 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0000900000-e81f9c948a937824aad7 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0000900000-7872961e706b0ce2acef | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03e9-0000900000-d2c234df86de685accab | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a6r-3950000000-5e1c0bb11352c04bf6ab | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-1245900000-820e9f5a57e1ee8bcc05 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03dr-0125900000-2a2d378bef3e5d7d7ef3 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 35V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03g0-2896300000-3561f6267f9465ea26a7 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 35V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-092i-2896300000-a9ffe90b7ae4ed58097b | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-06vi-2950000000-acdd4501d3673c8d4f18 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03e9-0000900000-6e1ef68f12bc3fcd4183 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-01q9-0000900000-5010fdb018700f1ff637 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00ea-5001900000-32dcdb2995334e0be0c9 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-9001200000-efaede61ec6ea62b8f4b | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-9001000000-4a63863012ce5e7f9e89 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03dj-0000900000-e906f3d7308d2f341edc | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0h2b-2001900000-b325ccc2ef8a18eae690 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycocholic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00dl-9101100000-9cd953b22c5f0740b0bb | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2019-05-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2019-05-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Fibroblasts
- Liver
- Placenta
- Prostate
|
|---|
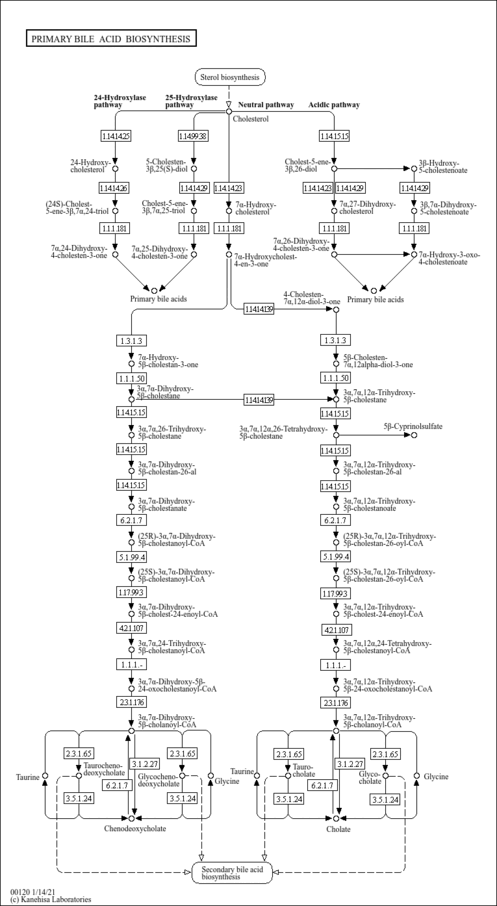
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.06 +/- 0.04 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.6(0.4-1.9) uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.88 +/- 0.26 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected and Quantified | 10.15 +/- 7.51 nmol/g dry feces | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.42 +/- 0.36 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.7 +/- 0.13 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Celiac Disease | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 22 +/- 6 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | GI disorder | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 16 +/- 5 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | GI disorder | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 3.2 +/- 0.6 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | GI disorder | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.4 +/- 0.4 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | GI disorder | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 44.0 +/- 29.1 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Extrahepatic biliary atresia (EHBA) | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 14.8(5.2-25.3) uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Severe acute malnutrition | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 8.4 +/- 8.7 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Cholecohal cyst | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 91.8 +/- 54.9 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Intrahepatic biliary hypoplasia | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.8 +/- 3.1 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Idiopathic neonatal hepatitis | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 25.9 +/- 24.0 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 9.8 +/- 14.7 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Cystic fibrosis | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.9 +/- 2.4 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Galactosemia | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 14.5 +/- 16.1 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Chronic active hepatitis | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 8.6 +/- 7.9 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Glycogen storage disease | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.5 +/- 1.2 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Fulminant hepatic failure | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 10.5 +/- 13.1 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Portal vein obstruction | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 5.1 +/- 6.9 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Wilson's disease | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 43.6 +/- 11.8 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Hepatobiliary Disease | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal Cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | CCD | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Crohns disease | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Ulcerative colitis | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Unclassified IBD | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Ileal Crohn's disease | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal Cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Not Specified | Recurrent Clostridium difficile infection | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Not Specified | Recurrent Clostridium difficile infection | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Clostridium difficile infection | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Hepatobiliary diseases |
|---|
- Rifai K, Ockenga J, Manns MP, Bischoff SC: Repeated administration of a vitamin preparation containing glycocholic acid in patients with hepatobiliary disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006 May 1;23(9):1337-45. [PubMed:16629939 ]
| | Celiac disease |
|---|
- Spiller RC, Frost PF, Stewart JS, Bloom SR, Silk DB: Delayed postprandial plasma bile acid response in coeliac patients with slow mouth-caecum transit. Clin Sci (Lond). 1987 Feb;72(2):217-23. [PubMed:3816078 ]
| | Biliary atresia |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Choledochal cysts |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Intrahepatic biliary hypoplasia |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Neonatal hepatitis |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Cystic fibrosis |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Galactosemia type 1 |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Chronic active hepatitis |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Glycogen storage disease |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Acute liver failure |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Portal vein obstruction |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Wilson's disease |
|---|
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
| | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ: Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 25;11(3):e0152126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27015276 ]
- Brown DG, Rao S, Weir TL, O'Malia J, Bazan M, Brown RJ, Ryan EP: Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016 Jun 6;4:11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0151-y. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27275383 ]
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Ahn J, Shi J, Sinha R: Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2089-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131. Epub 2014 Jul 18. [PubMed:25037050 ]
| | Crohn's disease |
|---|
- Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V: Faecal and Serum Metabolomics in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017 Mar 1;11(3):321-334. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw158. [PubMed:27609529 ]
| | Ulcerative colitis |
|---|
- Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V: Faecal and Serum Metabolomics in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017 Mar 1;11(3):321-334. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw158. [PubMed:27609529 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB012346 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00030410 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 9734 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C01921 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | GLYCOCHOLIC_ACID |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Glycocholic_acid |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 10140 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 17687 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | GCHOLA |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000066 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Cortese, Frank; Bauman, Louis. A synthesis of conjugated bile acids. I. Glycocholic acid. Journal of the American Chemical Society (1935), 57 1393-5. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Rius M, Nies AT, Hummel-Eisenbeiss J, Jedlitschky G, Keppler D: Cotransport of reduced glutathione with bile salts by MRP4 (ABCC4) localized to the basolateral hepatocyte membrane. Hepatology. 2003 Aug;38(2):374-84. [PubMed:12883481 ]
- Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Spiller RC, Frost PF, Stewart JS, Bloom SR, Silk DB: Delayed postprandial plasma bile acid response in coeliac patients with slow mouth-caecum transit. Clin Sci (Lond). 1987 Feb;72(2):217-23. [PubMed:3816078 ]
- Matsui A, Psacharopoulos HT, Mowat AP, Portmann B, Murphy GM: Radioimmunoassay of serum glycocholic acid, standard laboratory tests of liver function and liver biopsy findings: comparative study of children with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):1011-7. [PubMed:7119120 ]
- Marigold JH, Gilmore IT, Thompson RP: Effects of a meal on plasma clearance of [14C]glycocholic acid and indocyanine green in man. Clin Sci (Lond). 1981 Sep;61(3):325-30. [PubMed:7261553 ]
- Xia S, Chen Z, Li L: [Relationship of vascular endothelial growth factor with bile acid in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy]. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2002 Nov;37(11):669-71. [PubMed:12487922 ]
- Li GY, Wang T, Huggins EM Jr, Shams NK, Davis JF, Calkins JH, Hornung CA, Altekruse JM, Sigel MM: Cholylglycine measured in serum by RIA and interleukin-1 beta determined by ELISA in differentiating viral hepatitis from chemical liver injury. J Occup Med. 1992 Sep;34(9):930-3. [PubMed:1447600 ]
- de Franchis R, Vecchi M, Primignani M, Bonato C, Parravicini A, Cambieri R, Ciaci D, Annoni G: Diagnostic value of serum cholylglycine radioimmunoassay in chronic asymptomatic HBsAg carriers. Ric Clin Lab. 1983 Jul-Sep;13(3):301-5. [PubMed:6648236 ]
- Xuan B, McClellan DA, Moore R, Chiou GC: Alternative delivery of insulin via eye drops. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2005 Oct;7(5):695-8. [PubMed:16241870 ]
- Liss GM, Greenberg RA, Tamburro CH: Use of serum bile acids in the identification of vinyl chloride hepatotoxicity. Am J Med. 1985 Jan;78(1):68-76. [PubMed:3966491 ]
- Rifai K, Ockenga J, Manns MP, Bischoff SC: Repeated administration of a vitamin preparation containing glycocholic acid in patients with hepatobiliary disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006 May 1;23(9):1337-45. [PubMed:16629939 ]
- Klapdor R: On the kinetics of glycocholate uptake and excretion by the normal and diseased liver in man. Hepatogastroenterology. 1981 Aug;28(4):189-91. [PubMed:7274980 ]
- Friman S, Radberg G, Bosaeus I, Svanvik J: Hepatobiliary compensation for the loss of gallbladder function after cholecystectomy. An experimental study in the cat. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1990 Mar;25(3):307-14. [PubMed:2108486 ]
- Bocharova LV, Tsodikov GV, Chernyshova NN, Kataev SS, Burkov SG: [Clinical value of determining serum levels of glycocholic acid in alcoholic lesions of the liver]. Klin Med (Mosk). 1992 Jul-Aug;70(7-8):41-4. [PubMed:1460824 ]
- Murphy JL, Badaloo AV, Chambers B, Forrester TE, Wootton SA, Jackson AA: Maldigestion and malabsorption of dietary lipid during severe childhood malnutrition. Arch Dis Child. 2002 Dec;87(6):522-5. [PubMed:12456554 ]
- Bremmelgaard A, Ranek L, Bahnsen M, Andreasen PB, Christensen E: Cholic acid conjugation test and quantitative liver function in acute liver failure. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Sep;18(6):797-802. [PubMed:6669944 ]
- Hepner GW, Demers LM: Dynamics of the enterohepatic circulation of the glycine conjugates of cholic, chenodeoxycholic, deoxycholic, and sulfolithocholic acid in man. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):499-501. [PubMed:832799 ]
- Kasatkin IuN, Vidiukov VI, Mironov SP, Chernyshova NN, Bocharova LV, Kataev SS: [Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis based on scintigraphic data and the level of cholylglycine in the blood serum]. Med Radiol (Mosk). 1989 Sep;34(9):8-12. [PubMed:2796646 ]
- Collazos J, Mendarte U, De Miguel J: Clinical value of the determination of fasting glycocholic acid serum levels in patients with liver diseases. A comparison with standard liver tests. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1993;17(2):79-82. [PubMed:8500713 ]
- Nittono H, Obinata K, Nakatsu N, Watanabe T, Niijima S, Sasaki H, Arisaka O, Kato H, Yabuta K, Miyano T: Sulfated and nonsulfated bile acids in urine of patients with biliary atresia: analysis of bile acids by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1986 Jan;5(1):23-9. [PubMed:3944741 ]
- Goto T, Myint KT, Sato K, Wada O, Kakiyama G, Iida T, Hishinuma T, Mano N, Goto J: LC/ESI-tandem mass spectrometric determination of bile acid 3-sulfates in human urine 3beta-Sulfooxy-12alpha-hydroxy-5beta-cholanoic acid is an abundant nonamidated sulfate. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007 Feb 1;846(1-2):69-77. Epub 2006 Sep 1. [PubMed:16949895 ]
- St-Pierre MV, Kullak-Ublick GA, Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ: Transport of bile acids in hepatic and non-hepatic tissues. J Exp Biol. 2001 May;204(Pt 10):1673-86. [PubMed:11316487 ]
- Claudel T, Staels B, Kuipers F: The Farnesoid X receptor: a molecular link between bile acid and lipid and glucose metabolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 Oct;25(10):2020-30. Epub 2005 Jul 21. [PubMed:16037564 ]
- Chiang JY: Bile acid regulation of hepatic physiology: III. Bile acids and nuclear receptors. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Mar;284(3):G349-56. [PubMed:12576301 ]
- Davis RA, Miyake JH, Hui TY, Spann NJ: Regulation of cholesterol-7alpha-hydroxylase: BAREly missing a SHP. J Lipid Res. 2002 Apr;43(4):533-43. [PubMed:11907135 ]
- Simons K, Toomre D: Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;1(1):31-9. [PubMed:11413487 ]
- Watson AD: Thematic review series: systems biology approaches to metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. Lipidomics: a global approach to lipid analysis in biological systems. J Lipid Res. 2006 Oct;47(10):2101-11. Epub 2006 Aug 10. [PubMed:16902246 ]
- Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig AJ: Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue function and plasticity orchestrate nutritional adaptation. J Lipid Res. 2007 Jun;48(6):1253-62. Epub 2007 Mar 20. [PubMed:17374880 ]
- Lingwood D, Simons K: Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science. 2010 Jan 1;327(5961):46-50. doi: 10.1126/science.1174621. [PubMed:20044567 ]
- Masuda N: Deconjugation of bile salts by Bacteroids and Clostridium. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(1):1-11. [PubMed:6265737 ]
- Elshenawy S, Pinney SE, Stuart T, Doulias PT, Zura G, Parry S, Elovitz MA, Bennett MJ, Bansal A, Strauss JF 3rd, Ischiropoulos H, Simmons RA: The Metabolomic Signature of the Placenta in Spontaneous Preterm Birth. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3). pii: ijms21031043. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031043. [PubMed:32033212 ]
- (). Yannai, Shmuel. (2004) Dictionary of food compounds with CD-ROM: Additives, flavors, and ingredients. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC.. .
- Gunstone, Frank D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra (2007). The lipid handbook with CD-ROM. CRC Press.
| Show more...
|---|