| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2007-05-22 17:52:59 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-09-22 18:34:19 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0006218 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 9-cis-Retinal |
|---|
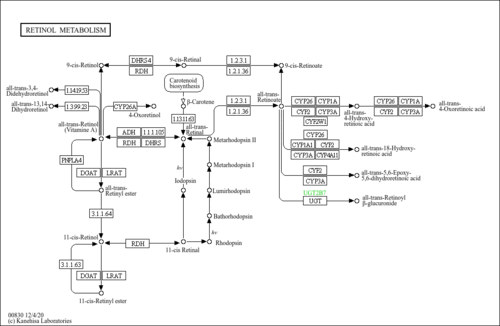
| Description | In vivo, 9-cis-retinal is formed through oxidation of 9-cis-retinol by cis-retinol dehydrogenase (cRDH). (PMID:15572038 ). The generation of retinoic acid from retinol is a two-step reaction, with the rate-limiting step being the oxidation of retinol into the intermediate retinaldehyde. Two classes of. unrelated enzymes have been implicated in the oxidation of retinol, the classical cytosolic medium chain alcohol dehydrogenases and recently identified microsomal members of the short chain alcohol dehydrogenase reductase (SDR) superfamily. Further oxidation of the retinaldehyde to the retinoic acid is believed to be catalyzed by several cytosolic aldehyde dehydrogenases. Retinoids are micronutrients required to maintain and promote health of vertebrates. They act physiologically by participating in the visual cycle, in regulating cell differentiation, in embryonic development (PMID:10893430 ), in maintaining normal reproduction, and in the immune response (PMID:8882153 ). In non-ocular tissues, the effects of retinoids within the body are mediated through retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and retinoid X receptors (RXRs), which act to regulate gene expression as ligand-dependent transcription factors. The naturally occurring ligands for these nuclear receptors are thought to be all-trans-retinoic acid for RARs and 9-cis-retinoic acid for RXRs (PMID:10322133 ). While many details of the molecular actions of the RARs and RXRs in regulating gene transcription are understood (PMID:10418975 ), tissue-specific synthetic pathway(s) of their ligands has not been adequately defined. Nevertheless, the therapeutic efficacy of retinoids, including 9-cis-retinoic acid, is well established in both tissue culture and animal models of breast cancer (PMID:8825126 , PMID:12743994 ). |
|---|
| Structure | C/C(/C=C/C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C)=C\C=O InChI=1S/C20H28O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-13,15H,7,10,14H2,1-5H3/b9-6+,12-11+,16-8-,17-13+ |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (2E,4E,6Z,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal | ChEBI | | (9cis)-Retinal | ChEBI | | 9-C-Retinal | ChEBI | | 9-cis-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenal | ChEBI | | 9-cis-7,11,13-trans-Retinal | ChEBI | | 9-cis-Retinaldehyde | ChEBI | | 9-cis-Vitamin a aldehyde | ChEBI | | Isoretinene a | ChEBI | | cis-9-Retinal | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H28O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 284.4357 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 284.214015518 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2E,4E,6Z,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 9-cis-retinal |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 514-85-2 |
|---|
| SMILES | C/C(/C=C/C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C)=C\C=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H28O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-13,15H,7,10,14H2,1-5H3/b9-6+,12-11+,16-8-,17-13+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | NCYCYZXNIZJOKI-MKOSUFFBSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as retinoids. These are oxygenated derivatives of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene and derivatives thereof. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Retinoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Retinoids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Retinoid skeleton
- Diterpenoid
- Enal
- Alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehyde
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aldehyde
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-014i-2290000000-df9d2aa7545cc60a54f9 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-1490000000-97cddfba9819c3417386 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-001s-3920000000-0be8a19c3cba33e3b06b | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0kui-9720000000-a579102a9f5600032e3f | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0090000000-e7d5d678e91ec531c2ae | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a59-0090000000-8af2668c966a1c8a3cef | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00ku-3690000000-54506b9021b67caed041 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00n3-1960000000-43f8c66f164764c37361 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0609-3920000000-dbeab0a82b306761cf6a | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-052f-7900000000-d2bb7c1aeeb87d8833d2 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a59-0090000000-2ec2f8f314943441fa15 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-0190000000-312cebb17ccd0189ab4d | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinal 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-1590000000-b2551eac481c0c930a4d | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, CDCl3, experimental) | 2018-05-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| General References | - Paik J, Blaner WS, Swisshelm K: Cis-retinol dehydrogenase: 9-cis-retinol metabolism and its effect on proliferation of human MCF7 breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Feb 1;303(1):183-96. [PubMed:15572038 ]
- Ross SA, McCaffery PJ, Drager UC, De Luca LM: Retinoids in embryonal development. Physiol Rev. 2000 Jul;80(3):1021-54. [PubMed:10893430 ]
- Glass CK: Some new twists in the regulation of gene expression by thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. J Endocrinol. 1996 Sep;150(3):349-57. [PubMed:8882153 ]
- Xu L, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG: Coactivator and corepressor complexes in nuclear receptor function. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999 Apr;9(2):140-7. [PubMed:10322133 ]
- McKenna NJ, Xu J, Nawaz Z, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW: Nuclear receptor coactivators: multiple enzymes, multiple complexes, multiple functions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1999 Apr-Jun;69(1-6):3-12. [PubMed:10418975 ]
- Gottardis MM, Lamph WW, Shalinsky DR, Wellstein A, Heyman RA: The efficacy of 9-cis retinoic acid in experimental models of cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996;38(1):85-96. [PubMed:8825126 ]
- Paik J, Blaner WS, Sommer KM, Moe R, Swisshlem K: Retinoids, retinoic acid receptors, and breast cancer. Cancer Invest. 2003 Apr;21(2):304-12. [PubMed:12743994 ]
|
|---|