| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:15:17 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000898 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0000976
- HMDB00898
- HMDB00976
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 1-Methylhistamine |
|---|
| Description | 1-Methylhistamine, also known as H137, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 2-arylethylamines. These are primary amines that have the general formula RCCNH2, where R is an organic group. 1-Methylhistamine exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans. Within humans, 1-methylhistamine participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, S-adenosylhomocysteine and 1-methylhistamine can be biosynthesized from S-adenosylmethionine and histamine; which is mediated by the enzyme histamine N-methyltransferase. In addition, 1-methylhistamine can be converted into methylimidazole acetaldehyde through its interaction with the enzyme amine oxidase [flavin-containing] a. In humans, 1-methylhistamine is involved in histidine metabolism. 1-Methylhistamine is a potentially toxic compound. |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C6H11N3/c1-9-4-6(2-3-7)8-5-9/h4-5H,2-3,7H2,1H3 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 1-Methyl-1H-imidazole-4-ethanamine | ChEBI | | 1-Methyl-4-(2-aminoethyl)imidazole | ChEBI | | 3-Methylhistamine | ChEBI | | 4-(1-Aminoethyl)-1-methyl-1H-imidazole | ChEBI | | Methylhistamine | ChEBI | | N-Methylhistamine | ChEBI | | N(1)-Methylhistamine | ChEBI | | Ntau-methylhistamine | ChEBI | | tele-Methylhistamine | ChEBI | | tele-Methylhistamine dihydrochloride | HMDB | | 1-Methyl-4-(beta-aminoethyl)imidazole | HMDB | | 1,4-Methylhistamine | HMDB | | N-tele Methylhistamine | HMDB | | 1-Methyl-4-(b-aminoethyl)imidazole | HMDB | | 1-Methyl-4-histamine | HMDB | | 2-(1-Methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)ethanamine | HMDB | | 2-(1-Methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)ethylamine | HMDB | | 4-(2-Aminoethyl)-1-methyl-imidazole | HMDB | | 4-(2-Aminoethyl)-1-methylimidazole | HMDB | | H137 | HMDB | | N( 1)-Methylhistamine | HMDB | | N(T)-Methylhistamine | HMDB | | N-tele-Methylhistamine | HMDB | | N-Telle-methylhistamine | HMDB | | N1-Methylhistamine | HMDB | | NT-Methylhistamine | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H11N3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 125.1716 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 125.095297367 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)ethan-1-amine |
|---|
| Traditional Name | methylhistamine |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 501-75-7 |
|---|
| SMILES | CN1C=NC(CCN)=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H11N3/c1-9-4-6(2-3-7)8-5-9/h4-5H,2-3,7H2,1H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | FHQDWPCFSJMNCT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 2-arylethylamines. These are primary amines that have the general formula RCCNH2, where R is an organic group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic nitrogen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organonitrogen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amines |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 2-arylethylamines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 2-arylethylamine
- Aralkylamine
- N-substituted imidazole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Imidazole
- Azole
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| 1-Methylhistamine,1TMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN[Si](C)(C)C)=C1 | 1513.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,1TMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN[Si](C)(C)C)=C1 | 1559.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,1TMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN[Si](C)(C)C)=C1 | 1930.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,2TMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=C1 | 1793.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,2TMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=C1 | 1764.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,2TMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=C1 | 1892.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=C1 | 1743.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=C1 | 1791.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=C1 | 2045.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=C1 | 2147.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=C1 | 2184.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | 1-Methylhistamine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CN1C=NC(CCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=C1 | 2060.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (2 TMS) | splash10-0fki-3900000000-8197b65f233a917f6f5d | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00dr-3900000000-4a05dead99e371226a6c | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (2 TMS) | splash10-00di-9700000000-b8108f1cb31c26ab942f | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine GC-MS (2 TMS) | splash10-0fe0-5900000000-c04c884eec0846197eb8 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-2910000000-3458f7def44a74d73f7b | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0fki-3900000000-8197b65f233a917f6f5d | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00dr-3900000000-4a05dead99e371226a6c | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-9700000000-b8108f1cb31c26ab942f | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0fe0-5900000000-c04c884eec0846197eb8 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-001j-9200000000-f6dbf3d86200b3f6be5f | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-b77c6433a2a8bdb852dd | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0aor-9600000000-a2a8c75c945ca81ded8a | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-001i-9200000000-fa9fad79e09f38a3450d | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-b9f4341a558b04495c54 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine LC-ESI-QTOF , positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-b9f4341a558b04495c54 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-056r-0900000000-b9f2ff9fde6f1a170d38 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-1900000000-0ad300b172fcdc68e104 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0le9-9000000000-fe751072b0ecf7a0d5bf | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-0900000000-c7b86cf59142756c4f91 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-3900000000-0bed565bcfefeb389d2b | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0arv-9100000000-fc2c7dc356034fe098ae | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-317df42b1c6c53a3cd83 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-6900000000-e29c16ae4d103e7eaa01 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-066u-9000000000-2d8cc6d1c8601ed4eed0 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-1900000000-c5c45bb41ea05838fa94 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-5900000000-68ef55e857c894f92309 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 1-Methylhistamine 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-9000000000-434d60e1525fedada46a | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Feces
- Saliva
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
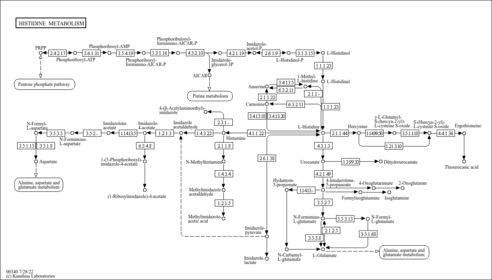
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00034 (0.00021-0.00047) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.002 +/- 0.0005 (0.0015 - 0.0025) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.005 +/- 0.0006 (0.003-0.006) uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 1.12 +/- 0.22 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.007 +/- 0.0005 (0.006 - 0.008) uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.002209 +/- 0.000463 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.00214 +/- 0.0001 uM | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 0.0117 +/- 0.0359 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 0.0125 +/- 0.0348 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 0.0301 +/- 0.0193 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.13 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.098 (0.032-0.18) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | - Geigy Scientific ...
- West Cadwell, N.J...
- Basel, Switzerlan...
| details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.065 (0.32-0.98) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00078 (0.00055-0.00100) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Dermal fibroproliferative disorder (hypertrophic scarring) | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.002431 +/- 0.000461 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | sporadic narcolepsy-cataplexy | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.00276 +/- 0.00013 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Alzheimer's disease | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.00290 +/- 0.00027 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Schizophrenia | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 2.90 +/- 0.27 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Schizophrenia | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Crohns disease | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Ulcerative colitis | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Unclassified IBD | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 0.0203 +/- 0.0254 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Oral cavity disorders | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.73 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Mastocytosis | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Dermal fibroproliferative disorder |
|---|
- Tredget EE, Iwashina T, Scott PG, Ghahary A: Determination of plasma Ntau-methylhistamine in vivo by isotope dilution using benchtop gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1997 Jun 20;694(1):1-9. [PubMed:9234842 ]
| | Alzheimer's disease |
|---|
- Motawaj M, Peoc'h K, Callebert J, Arrang JM: CSF levels of the histamine metabolite tele-methylhistamine are only slightly decreased in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;22(3):861-71. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-100381. [PubMed:20858978 ]
| | Schizophrenia |
|---|
- Prell GD, Green JP, Kaufmann CA, Khandelwal JK, Morrishow AM, Kirch DG, Linnoila M, Wyatt RJ: Histamine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with chronic schizophrenia: their relationships to levels of other aminergic transmitters and ratings of symptoms. Schizophr Res. 1995 Jan;14(2):93-104. [PubMed:7711000 ]
| | Crohn's disease |
|---|
- Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V: Faecal and Serum Metabolomics in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017 Mar 1;11(3):321-334. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw158. [PubMed:27609529 ]
| | Ulcerative colitis |
|---|
- Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V: Faecal and Serum Metabolomics in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017 Mar 1;11(3):321-334. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw158. [PubMed:27609529 ]
| | Mastocytosis |
|---|
- Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Neumann HJ: Determination of 1-methylhistamine and 1-methylimidazoleacetic acid in human urine as a tool for the diagnosis of mastocytosis. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1999 Jan 8;721(1):135-40. [PubMed:10027644 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB022306 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 3488 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C05127 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | N-METHYL-HISTAMINE |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 45171 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Methylhistamine |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 5854 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 3614 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 29009 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | MHISTA |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000278 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Rothschild, Zuleika; Schayer, Richard W. Synthesis and metabolism of a histamine metabolite, 1-methyl-4-(b-aminoethyl)imidazole. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (1958), 30 23-7. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Ito C: The role of the central histaminergic system on schizophrenia. Drug News Perspect. 2004 Jul-Aug;17(6):383-7. [PubMed:15334189 ]
- Khandelwal JK, Hough LB, Morrishow AM, Green JP: Measurement of tele-methylhistamine and histamine in human cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and plasma. Agents Actions. 1982 Dec;12(5-6):583-90. [PubMed:7164933 ]
- Winterkamp S, Weidenhiller M, Otte P, Stolper J, Schwab D, Hahn EG, Raithel M: Urinary excretion of N-methylhistamine as a marker of disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002 Dec;97(12):3071-7. [PubMed:12492192 ]
- Elmore BO, Bollinger JA, Dooley DM: Human kidney diamine oxidase: heterologous expression, purification, and characterization. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2002 Jun;7(6):565-79. Epub 2002 Feb 13. [PubMed:12072962 ]
- Robbins IM, Barst RJ, Rubin LJ, Gaine SP, Price PV, Morrow JD, Christman BW: Increased levels of prostaglandin D(2) suggest macrophage activation in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 2001 Nov;120(5):1639-44. [PubMed:11713147 ]
- O'Sullivan S, Roquet A, Dahlen B, Dahlen S, Kumlin M: Urinary excretion of inflammatory mediators during allergen-induced early and late phase asthmatic reactions. Clin Exp Allergy. 1998 Nov;28(11):1332-9. [PubMed:9824404 ]
- Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Neumann HJ: Determination of 1-methylhistamine and 1-methylimidazoleacetic acid in human urine as a tool for the diagnosis of mastocytosis. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1999 Jan 8;721(1):135-40. [PubMed:10027644 ]
- Theoharides TC, Sant GR, el-Mansoury M, Letourneau R, Ucci AA Jr, Meares EM Jr: Activation of bladder mast cells in interstitial cystitis: a light and electron microscopic study. J Urol. 1995 Mar;153(3 Pt 1):629-36. [PubMed:7861501 ]
- Brumsen C, Papapoulos SE, Lentjes EG, Kluin PM, Hamdy NA: A potential role for the mast cell in the pathogenesis of idiopathic osteoporosis in men. Bone. 2002 Nov;31(5):556-61. [PubMed:12477568 ]
- Rozniecki JJ, Hauser SL, Stein M, Lincoln R, Theoharides TC: Elevated mast cell tryptase in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. Ann Neurol. 1995 Jan;37(1):63-6. [PubMed:7818259 ]
- Alakarppa K, Tupala E, Mantere T, Sarkioja T, Rasanen P, Tarhanen J, Tiihonen J, Tuomisto L: Effect of alcohol abuse on human brain histamine and tele-methylhistamine. Inflamm Res. 2002 Apr;51 Suppl 1:S40-1. [PubMed:12013402 ]
- Tredget EE, Iwashina T, Scott PG, Ghahary A: Determination of plasma Ntau-methylhistamine in vivo by isotope dilution using benchtop gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1997 Jun 20;694(1):1-9. [PubMed:9234842 ]
- van Toorenenbergen AW, Oranje AP: Comparison of serum tryptase and urine N-methylhistamine in patients with suspected mastocytosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2005 Sep;359(1-2):72-7. [PubMed:15913591 ]
- Droogendijk HJ, Kluin-Nelemans HJ, van Doormaal JJ, Oranje AP, van de Loosdrecht AA, van Daele PL: Imatinib mesylate in the treatment of systemic mastocytosis: a phase II trial. Cancer. 2006 Jul 15;107(2):345-51. [PubMed:16779792 ]
- Oranje AP, Mulder PG, Heide R, Tank B, Riezebos P, van Toorenenbergen AW: Urinary N-methylhistamine as an indicator of bone marrow involvement in mastocytosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002 Sep;27(6):502-6. [PubMed:12372095 ]
- Rinne JO, Anichtchik OV, Eriksson KS, Kaslin J, Tuomisto L, Kalimo H, Roytta M, Panula P: Increased brain histamine levels in Parkinson's disease but not in multiple system atrophy. J Neurochem. 2002 Jun;81(5):954-60. [PubMed:12065607 ]
- Fitzpatrick MF, Mackay T, Walters C, Tai PC, Church MK, Holgate ST, Douglas NJ: Circulating histamine and eosinophil cationic protein levels in nocturnal asthma. Clin Sci (Lond). 1992 Aug;83(2):227-32. [PubMed:1327639 ]
- Butterfield JH, Tefferi A, Kozuh GF: Successful treatment of systemic mastocytosis with high-dose interferon-alfa: long-term follow-up of a case. Leuk Res. 2005 Feb;29(2):131-4. [PubMed:15607359 ]
- Winterkamp S, Weidenhiller M, Wilken V, Donhauser N, Schultis HW, Buchwald F, Hahn EG, Raithel M: Standardised evaluation of urinary excretion of N-tele-methylhistamine in different periods of age in a healthy population. Inflamm Res. 2003 Apr;52 Suppl 1:S57-8. [PubMed:12755411 ]
- Coruzzi G, Morini G, Adami M, Grandi D: Role of histamine H3 receptors in the regulation of gastric functions. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2001 Dec;52(4 Pt 1):539-53. [PubMed:11787757 ]
| Show more...
|---|