| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-07-18 20:19:55 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0001311 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0000171
- HMDB00171
- HMDB01311
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | D-Lactic acid |
|---|
| Description | Lactic acid is an organic acid. It is a chiral molecule, consisting of two optical isomers, L-lactic acid and D-lactic acid, with the L-isomer being the most common in living organisms. Lactic acid plays a role in several biochemical processes and is produced in the muscles during intense activity. D-Lactic acid is the end product of the enzyme glyoxalase II (or hydroxyacyl-glutathione hydrolase) (EC 3.1.2.6), which converts the intermediate substrate S-lactoyl-glutathione to reduced glutathione and D-lactate (OMIM: 138790 ). Lactic acid is a microbial metabolite found in Aerococcus, Bacillus, Carnobacterium, Corynebacterium, Enterococcus, Escherichia, Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Leuconostoc, Oenococcus, Pediococcus, Rhizopus, Saccharomyces, Streptococcus, Tetragenococcus, Vagococcus and Weissella (PMID:26287368 ; PMID:26360870 ). |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C3H6O3/c1-2(4)3(5)6/h2,4H,1H3,(H,5,6)/t2-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (-)-Lactic acid | ChEBI | | (R)-(-)-Lactic acid | ChEBI | | D-2-Hydroxypropanoic acid | ChEBI | | D-2-Hydroxypropionic acid | ChEBI | | D-Milchsaeure | ChEBI | | LACTIC ACID | ChEBI | | D-Lactate | Kegg | | (-)-Lactate | Generator | | (R)-(-)-Lactate | Generator | | D-2-Hydroxypropanoate | Generator | | D-2-Hydroxypropionate | Generator | | LACTate | Generator | | L-Lactate | HMDB | | (R)-2-Hydroxypropanoate | HMDB | | (R)-2-Hydroxypropanoic acid | HMDB | | (R)-2-Hydroxypropionate | HMDB | | (R)-2-Hydroxypropionic acid | HMDB | | (R)-a-Hydroxypropionate | HMDB | | (R)-a-Hydroxypropionic acid | HMDB | | (R)-alpha-Hydroxypropionate | HMDB | | (R)-alpha-Hydroxypropionic acid | HMDB | | (R)-Lactate | HMDB | | (R)-Lactic acid | HMDB | | D-(-)-Lactate | HMDB | | D-(-)-Lactic acid | HMDB | | delta-(-)-Lactate | HMDB | | delta-(-)-Lactic acid | HMDB | | delta-2-Hydroxypropanoate | HMDB | | delta-2-Hydroxypropanoic acid | HMDB | | delta-2-Hydroxypropionate | HMDB | | delta-2-Hydroxypropionic acid | HMDB | | delta-Lactate | HMDB | | delta-Lactic acid | HMDB | | DLA | HMDB | | L-(+)-Lactate | HMDB | | Propel | HMDB | | Tisulac | HMDB | | 2 Hydroxypropanoic acid | HMDB | | 2 Hydroxypropionic acid | HMDB | | 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid | HMDB | | Ammonium lactate | HMDB | | L Lactic acid | HMDB | | 2-Hydroxypropionic acid | HMDB | | Sarcolactic acid | HMDB | | D Lactic acid | HMDB | | Lactate, ammonium | HMDB | | L-Lactic acid | HMDB | | D-Lactic acid | ChEBI |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C3H6O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 90.0779 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 90.031694058 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2R)-2-hydroxypropanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | D-lactic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 10326-41-7 |
|---|
| SMILES | C[C@@H](O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C3H6O3/c1-2(4)3(5)6/h2,4H,1H3,(H,5,6)/t2-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UWTATZPHSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha hydroxy acids and derivatives. These are organic compounds containing a carboxylic acid substituted with a hydroxyl group on the adjacent carbon. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Hydroxy acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Alpha hydroxy acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha hydroxy acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-hydroxy acid
- Secondary alcohol
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 52.8 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| D-Lactic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 998.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lactic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 892.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lactic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1064.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lactic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1247.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lactic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1125.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lactic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1501.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00kb-0900000000-fb59ec16914501aa19ab | 2018-05-25 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014j-0900000000-c4d9e12b4b0150eda54b | 2018-05-25 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00kb-0900000000-fb59ec16914501aa19ab | 2018-05-25 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-a3691f383d440fb00e1f | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid GC-MS (2 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-01b9-9620000000-f7faa7db9c1be3d9d975 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-002b-9000000000-50213d6b39ef9741c466 | 2018-05-25 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid Quattro_QQQ 10V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-000i-9000000000-704f8ff33156c82a02d1 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid Quattro_QQQ 25V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-000m-9000000000-023931446d9bb3330e7f | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid Quattro_QQQ 40V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-000l-9000000000-0fb29afb128baea2240b | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid LC-ESI-IT , negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-d7cd347946e49a57860e | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-aee01e43e8ee93db755d | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000f-9000000000-581a00222505e9e4b458 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-5bfd9fdf1c0df2054452 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-006x-9000000000-5f417f4a6d08f0ab00ed | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00dm-9000000000-df7a94bb1a9cf6e78e1a | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-004j-9000000000-dc2a1b965287b9dfee9c | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-c3686a681cc9bbf039e1 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-ddad20647c2ac56efd22 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000000000-b728b45617afcc6b67da | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-b586cb8f053eb4465b4e | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-400a5f1c0dfcc32ef2bb | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0007-9000000000-ad5eb77c7e0a96f3a40a | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0002-9000000000-00ba25458eb6c0cc2940 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0002-9000000000-00ba25458eb6c0cc2940 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lactic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0002-9000000000-00ba25458eb6c0cc2940 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Extracellular
- Mitochondria
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Bladder
- Brain
- Epidermis
- Fibroblasts
- Intestine
- Liver
- Neuron
- Placenta
- Platelet
- Skeletal Muscle
- Spleen
- Testis
|
|---|
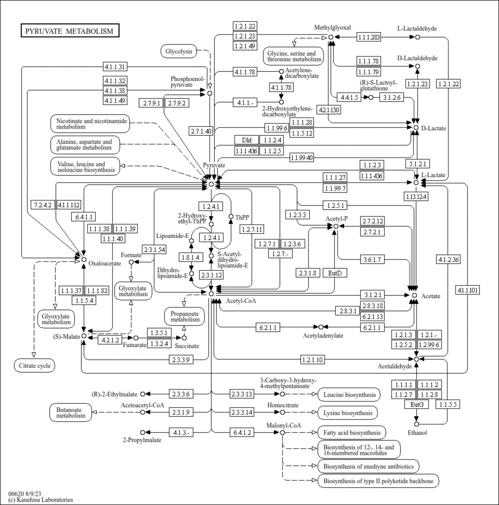
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 11.0 +/- 1.2 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 7.26 +/- 0.481 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 8 +/- 4.6 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 508+/-293 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details |
|
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 20.0 +/- 1.3 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Diabetes | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 4000(2400-5500) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Sepsis | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 13.1 +/- 1.42 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Schizophrenia | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 600 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | D-Lactic Acidosis | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 3100-20200 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | D-Lactic Acidosis and Short Bowel Syndrome | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 4000-10000 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | D-Lactic Acidosis and Short Bowel Syndrome | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 6700 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Male | D-Lactic Acidosis and Short Bowel Syndrome | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 600 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | D-Lactic Acidosis | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | >2300 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Metabolic Disorder | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 466.667-1933.333 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | D-Lactic Acidosis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 6783.6 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | D-Lactic Acidosis and Short Bowel Syndrome | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2190-20000 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | D-Lactic Acidosis and Short Bowel Syndrome | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Diabetes mellitus type 2 |
|---|
- McLellan AC, Phillips SA, Thornalley PJ: Fluorimetric assay of D-lactate. Anal Biochem. 1992 Oct;206(1):12-6. [PubMed:1456422 ]
| | Schizophrenia |
|---|
- Fukushima T, Iizuka H, Yokota A, Suzuki T, Ohno C, Kono Y, Nishikiori M, Seki A, Ichiba H, Watanabe Y, Hongo S, Utsunomiya M, Nakatani M, Sadamoto K, Yoshio T: Quantitative analyses of schizophrenia-associated metabolites in serum: serum D-lactate levels are negatively correlated with gamma-glutamylcysteine in medicated schizophrenia patients. PLoS One. 2014 Jul 8;9(7):e101652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101652. eCollection 2014. [PubMed:25004141 ]
| | D-Lactic Acidosis |
|---|
- Duran M, Van Biervliet JP, Kamerling JP, Wadman SK: D-lactic aciduria, an inborn error of metabolism? Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Feb 1;74(3):297-300. [PubMed:832430 ]
| | Sepsis |
|---|
- Fan SL, Miller NS, Lee J, Remick DG: Diagnosing sepsis - The role of laboratory medicine. Clin Chim Acta. 2016 Sep 1;460:203-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Jul 4. [PubMed:27387712 ]
| | D-Lactic Acidosis and Short Bowel Syndrome |
|---|
- Uribarri J, Oh MS, Carroll HJ: D-lactic acidosis. A review of clinical presentation, biochemical features, and pathophysiologic mechanisms. Medicine (Baltimore). 1998 Mar;77(2):73-82. [PubMed:9556700 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB03066 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB030146 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00019549 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 55423 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00256 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | D-LACTATE |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 34414 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Lactic_acid |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 6150 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 61503 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 42111 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | LAC_D |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Hsieh, Chun Lung; Houng, Jer Yiing. Preparation of D-lactic acid from D,L-lactic acid ester using wheat germ or pancreatic lipase. U.S. (1997), 5 pp. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Hasegawa H, Fukushima T, Lee JA, Tsukamoto K, Moriya K, Ono Y, Imai K: Determination of serum D-lactic and L-lactic acids in normal subjects and diabetic patients by column-switching HPLC with pre-column fluorescence derivatization. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2003 Nov;377(5):886-91. Epub 2003 Jul 19. [PubMed:12879188 ]
- Smith SM, Eng RH, Buccini F: Use of D-lactic acid measurements in the diagnosis of bacterial infections. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):658-64. [PubMed:3528318 ]
- Ellis LC, Groesbeck MD, Farr CH, Tesi RJ: Contractility of seminiferous tubules as related to sperm transport in the male. Arch Androl. 1981 Jun;6(4):283-94. [PubMed:6113819 ]
- Pedersen M: Ciliary activity and pollution. Lung. 1990;168 Suppl:368-76. [PubMed:2117139 ]
- McLellan AC, Phillips SA, Thornalley PJ: Fluorimetric assay of D-lactate. Anal Biochem. 1992 Oct;206(1):12-6. [PubMed:1456422 ]
- Schmid-Schonbein GW: Microlymphatics and lymph flow. Physiol Rev. 1990 Oct;70(4):987-1028. [PubMed:2217560 ]
- Solito R, Alessandrini C, Fruschelli M, Pucci AM, Gerli R: An immunological correlation between the anchoring filaments of initial lymph vessels and the neighboring elastic fibers: a unified morphofunctional concept. Lymphology. 1997 Dec;30(4):194-202. [PubMed:9476251 ]
- Brandt RB, Siegel SA: Methylglyoxal production in human blood. Ciba Found Symp. 1978;(67):211-23. [PubMed:259500 ]
- Zhang YJ, O'Neal WK, Randell SH, Blackburn K, Moyer MB, Boucher RC, Ostrowski LE: Identification of dynein heavy chain 7 as an inner arm component of human cilia that is synthesized but not assembled in a case of primary ciliary dyskinesia. J Biol Chem. 2002 May 17;277(20):17906-15. Epub 2002 Mar 4. [PubMed:11877439 ]
- Tanyel FC, Ulusu NN, Tezcan EF, Buyukpamukcu N: Total calcium content of sacs associated with inguinal hernia, hydrocele or undescended testis reflects differences dictated by programmed cell death. Urol Int. 2003;70(3):211-5. [PubMed:12660459 ]
- Kaneko T, Bando Y, Kurihara H, Satomi K, Nonoyama K, Matsuura N: Fecal microflora in a patient with short-bowel syndrome and identification of dominant lactobacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1997 Dec;35(12):3181-5. [PubMed:9399516 ]
- Hoijer MA, Melief MJ, van Helden-Meeuwsen CG, Eulderink F, Hazenberg MP: Detection of muramic acid in a carbohydrate fraction of human spleen. Infect Immun. 1995 May;63(5):1652-7. [PubMed:7729869 ]
- Juturu V, Wu JC: Microbial production of lactic acid: the latest development. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2016 Dec;36(6):967-977. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2015.1066305. Epub 2015 Aug 11. [PubMed:26287368 ]
- Becker J, Lange A, Fabarius J, Wittmann C: Top value platform chemicals: bio-based production of organic acids. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2015 Dec;36:168-75. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2015.08.022. Epub 2015 Sep 8. [PubMed:26360870 ]
| Show more...
|---|