| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:14:30 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000076 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Dihydrouracil |
|---|
| Description | Dihydrouracil belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidones. Pyrimidones are compounds that contain a pyrimidine ring, which bears a ketone. Pyrimidine is a 6-membered ring consisting of four carbon atoms and two nitrogen centers at the 1- and 3- ring positions. Dihydrouracil is an intermediate breakdown product of uracil. Dihydrouracil exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to plants to humans. Within humans, dihydrouracil participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, dihydrouracil can be biosynthesized from uracil; which is mediated by the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase [NADP(+)]. The breakdown of uracil is a multistep reaction that leads to the production of beta-alanine. The reaction process begins with the enzyme known as dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DHP), which catalyzes the reduction of uracil into dihydrouracil. Then the enzyme known as dihydropyrimidinase hydrolyzes dihydrouracil into N-carbamyl-beta-alanine. Finally, beta-ureidopropionase catalyzes the conversion of N-carbamyl-beta-alanine into beta-alanine. There is at least one metabolic disorder that is associated with altered levels of dihydrouracil. In particular, dihydropyrimidinase deficiency is an inborn metabolic disorder that leads to highly increased concentrations of dihydrouracil and 5,6-dihydrothymine, and moderately increased concentrations of uracil and thymine in urine. Dihydropyrimidinase deficiency can cause neurological and gastrointestinal problems in some affected individuals (OMIM: 222748 ). In particular, patients with dihydropyrimidinase deficiency exhibit a number of neurological abnormalities including intellectual disability, seizures, weak muscle tone (hypotonia), an abnormally small head size (microcephaly), and autistic behaviours that affect communication and social interaction. Gastrointestinal problems that occur in dihydropyrimidinase deficiency include backflow of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus (gastroesophageal reflux) and recurrent episodes of vomiting. |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C4H6N2O2/c7-3-1-2-5-4(8)6-3/h1-2H2,(H2,5,6,7,8) |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 2,4-Dioxotetrahydropyrimidine | ChEBI | | 5,6-Dihydro-2,4-dihydroxypyrimidine | ChEBI | | Dihydro-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione | ChEBI | | DIHYDROPYRIMIDINE-2,4(1H,3H)-dione | ChEBI | | Dihydrouracile | ChEBI | | Hydrouracil | ChEBI | | 5,6-Dihydro-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione | HMDB | | 5,6-Dihydrouracil | HMDB | | Dihydro-pyrimidine-2,4-dione | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C4H6N2O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 114.1026 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 114.042927446 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 1,3-diazinane-2,4-dione |
|---|
| Traditional Name | dihydrouracil |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 504-07-4 |
|---|
| SMILES | O=C1CCNC(=O)N1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C4H6N2O2/c7-3-1-2-5-4(8)6-3/h1-2H2,(H2,5,6,7,8) |
|---|
| InChI Key | OIVLITBTBDPEFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidones. Pyrimidones are compounds that contain a pyrimidine ring, which bears a ketone. Pyrimidine is a 6-membered ring consisting of four carbon atoms and two nitrogen centers at the 1- and 3- ring positions. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Diazines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Pyrimidines and pyrimidine derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Pyrimidones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - N-acyl urea
- Pyrimidone
- Ureide
- 1,3-diazinane
- Dicarboximide
- Urea
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Azacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 279 - 281 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Dihydrouracil,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)NC1=O | 1414.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)NC1=O | 1472.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)NC1=O | 2379.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)CCNC1=O | 1363.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)CCNC1=O | 1393.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)CCNC1=O | 2353.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)C1=O | 1393.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)C1=O | 1500.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)C1=O | 1894.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)NC1=O | 1688.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)NC1=O | 1727.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)NC1=O | 2598.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)CCNC1=O | 1640.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)CCNC1=O | 1635.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)CCNC1=O | 2419.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C1=O | 1849.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C1=O | 1978.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Dihydrouracil,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1CCC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C1=O | 2074.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (2 TMS) | splash10-00di-9700000000-4adeeb2f4f5a1111afb7 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil GC-MS (1 TMS) | splash10-00di-5900000000-8af1b81502646fa5b417 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil GC-MS (2 TMS) | splash10-0fdo-9750000000-d2aaeeba1cf962175f84 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-9700000000-4adeeb2f4f5a1111afb7 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-5900000000-8af1b81502646fa5b417 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0fdo-9750000000-d2aaeeba1cf962175f84 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0f6w-2940000000-3430a0e2d1819021af1d | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-3900000000-79f2d90a419b7469cb61 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-004l-9100000000-55536f0571922b6c69fe | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-03fu-9400000000-5b9edda3479e7d0a0d28 | 2014-09-20 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-03k9-9800000000-da772cea603c785c1df4 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0a4i-9100000000-94a5f543e8c6be7b3204 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0btc-9200000000-e9bf2ae82714a2a3a737 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-5900000000-0fe83e63f6e5d1347894 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil , negative-QTOF | splash10-03xr-6900000000-08aca1bc7f27b0e7cb08 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil LC-ESI-QTOF , positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-5900000000-53ea361c86b4f9fa284b | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil , positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-9300000000-a8599c09cd21e2f84329 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-01b9-9500000000-03c8b6a5b2dc3625d5d3 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0ab9-9000000000-331f648f78f506788b99 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-052f-9000000000-824aa91d3f2de539f0bd | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-2900000000-ad7f91d5265e53403dd6 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0603-9200000000-4b30a83fb454e5bbffb8 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-ce54e3c860a95b0af401 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-9800000000-d705e188f6700a76ef72 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-a26409d69a4259731004 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-f00c4df547660023bee4 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-0900000000-b8f2cf36966bbbbb3285 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-9500000000-44775319047d2eddad49 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-052f-9000000000-3cb7005ca8389854848e | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03dl-7900000000-9d78d5698ad7865d1789 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-997cffdd9ad85c899225 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Dihydrouracil 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-a88e812ae86e53f6c2d6 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Feces
- Saliva
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Fibroblasts
- Kidney
- Liver
- Prostate
|
|---|
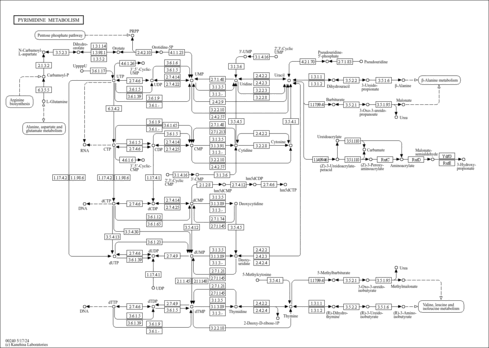
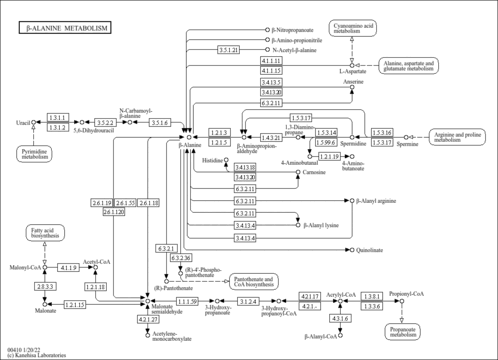
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.31 (0.02-1.63) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.31 (0.02-1.63) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.32 ( 0.10-0.74) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 2.1 +/- 1.0 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 700 +/- 199 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 2168.16 +/- 127.94 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 2000 +/- 223 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 2000 +/- 223 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 2210 +/- 353 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 2240 +/- 380 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 2350 +/- 654 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.79 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 3.8 (2.1-8.3) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.4 +/- 4.7 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 3.0 +/- 2.7 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.5-20 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 12.2 +/- 6.2 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <3.4 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details |
|
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 81.5 (46.0-117.0) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) deficiency | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.4 +/- 1.67 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Hypertension | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 627.0 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.4 +/- 2.00 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Cerebral infarction | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.8 +/- 1.9 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Malignancy | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.7 +/- 1.9 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Liver dysfunction | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.5 +/- 2.00 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Nephropathy | | details |
|
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ: Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 25;11(3):e0152126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27015276 ]
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Ahn J, Shi J, Sinha R: Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2089-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131. Epub 2014 Jul 18. [PubMed:25037050 ]
| | Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency |
|---|
- Sumi S, Kidouchi K, Ohba S, Wada Y: Automated screening system for purine and pyrimidine metabolism disorders using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl. 1995 Oct 20;672(2):233-9. [PubMed:8581129 ]
- Van Kuilenburg AB, Stroomer AE, Van Lenthe H, Abeling NG, Van Gennip AH: New insights in dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency: a pivotal role for beta-aminoisobutyric acid? Biochem J. 2004 Apr 1;379(Pt 1):119-24. [PubMed:14705962 ]
| | Hypertension |
|---|
- Hayashi K, Kidouchi K, Sumi S, Mizokami M, Orito E, Kumada K, Ueda R, Wada Y: Possible prediction of adverse reactions to pyrimidine chemotherapy from urinary pyrimidine levels and a case of asymptomatic adult dihydropyrimidinuria. Clin Cancer Res. 1996 Dec;2(12):1937-41. [PubMed:9816152 ]
| | Cerebral infarction |
|---|
- Hayashi K, Kidouchi K, Sumi S, Mizokami M, Orito E, Kumada K, Ueda R, Wada Y: Possible prediction of adverse reactions to pyrimidine chemotherapy from urinary pyrimidine levels and a case of asymptomatic adult dihydropyrimidinuria. Clin Cancer Res. 1996 Dec;2(12):1937-41. [PubMed:9816152 ]
| | Liver disease |
|---|
- Hayashi K, Kidouchi K, Sumi S, Mizokami M, Orito E, Kumada K, Ueda R, Wada Y: Possible prediction of adverse reactions to pyrimidine chemotherapy from urinary pyrimidine levels and a case of asymptomatic adult dihydropyrimidinuria. Clin Cancer Res. 1996 Dec;2(12):1937-41. [PubMed:9816152 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 114500 (Colorectal cancer)
- 274270 (Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency)
- 145500 (Hypertension)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01849 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB030556 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 629 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00429 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | DI-H-URACIL |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 34956 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Dihydrouracil |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 285 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 649 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 15901 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | 56DURA |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000040 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Bhat, K. S.; Rao, A. S. Synthesis of uracil, 6-methyluracil and some dihydrouracils. Organic Preparations and Procedures International (1983), 15(5), 303-13. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) |
|---|
| General References | - Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Hofmann U, Schwab M, Seefried S, Marx C, Zanger UM, Eichelbaum M, Murdter TE: Sensitive method for the quantification of urinary pyrimidine metabolites in healthy adults by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2003 Jul 5;791(1-2):371-80. [PubMed:12798197 ]
- Van Kuilenburg AB, Stroomer AE, Van Lenthe H, Abeling NG, Van Gennip AH: New insights in dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency: a pivotal role for beta-aminoisobutyric acid? Biochem J. 2004 Apr 1;379(Pt 1):119-24. [PubMed:14705962 ]
- Grem JL: Intratumoral molecular or genetic markers as predictors of clinical outcome with chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. Semin Oncol. 2005 Feb;32(1):120-7. [PubMed:15726514 ]
- Assmann B, Hoffmann GF, Wagner L, Brautigam C, Seyberth HW, Duran M, Van Kuilenburg AB, Wevers R, Van Gennip AH: Dihydropyrimidinase deficiency and congenital microvillous atrophy: coincidence or genetic relation? J Inherit Metab Dis. 1997 Sep;20(5):681-8. [PubMed:9323563 ]
- Megyeri A, Bacso Z, Shields A, Eliason JF: Development of a stereological method to measure levels of fluoropyrimidine metabolizing enzymes in tumor sections using laser scanning cytometry. Cytometry A. 2005 Apr;64(2):62-71. [PubMed:15729713 ]
- Nakamura A, Kikuchi K, Ohishi T, Masuike T: [Assay method for uracil, dihydrouracil, 5-fluorouracil and 5-fluoro-5, 6-dihydrouracil by high-performance liquid chromatography]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2004 Mar;31(3):381-6. [PubMed:15045945 ]
- van Lenthe H, van Kuilenburg AB, Ito T, Bootsma AH, van Cruchten A, Wada Y, van Gennip AH: Defects in pyrimidine degradation identified by HPLC-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry of urine specimens or urine-soaked filter paper strips. Clin Chem. 2000 Dec;46(12):1916-22. [PubMed:11106323 ]
- Sumi S, Kidouchi K, Ohba S, Wada Y: Automated screening system for purine and pyrimidine metabolism disorders using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl. 1995 Oct 20;672(2):233-9. [PubMed:8581129 ]
- Shen GP, Galick H, Inoue M, Wallace SS: Decline of nuclear and mitochondrial oxidative base excision repair activity in late passage human diploid fibroblasts. DNA Repair (Amst). 2003 Jun 11;2(6):673-93. [PubMed:12767347 ]
- Tan BR, McLeod HL: Pharmacogenetic influences on treatment response and toxicity in colorectal cancer. Semin Oncol. 2005 Feb;32(1):113-9. [PubMed:15726513 ]
- Garcia AA, Blessing JA, Lenz HJ, Darcy KM, Mannel RS, Miller DS, Husseinzadeh N: Phase II clinical trial of capecitabine in ovarian carcinoma recurrent 6-12 months after completion of primary chemotherapy, with exploratory TS, DPD, and TP correlates: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol. 2005 Mar;96(3):810-7. [PubMed:15721430 ]
- Schneider S, Uchida K, Brabender J, Baldus SE, Yochim J, Danenberg KD, Salonga D, Chen P, Tsao-Wei D, Groshen S, Hoelscher AH, Schneider PM, Danenberg PV: Downregulation of TS, DPD, ERCC1, GST-Pi, EGFR, and HER2 gene expression after neoadjuvant three-modality treatment in patients with esophageal cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2005 Mar;200(3):336-44. [PubMed:15737843 ]
- Jiang H, Jiang J, Hu P, Hu Y: Measurement of endogenous uracil and dihydrouracil in plasma and urine of normal subjects by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002 Mar 25;769(1):169-76. [PubMed:11936689 ]
|
|---|