| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:03 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000518 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Chenodeoxycholic acid |
|---|
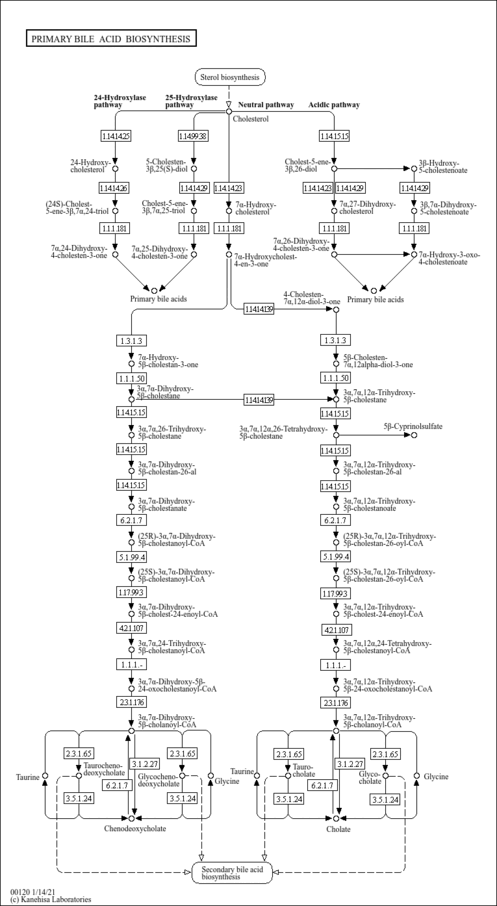
| Description | Chenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid. Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals. The distinction between different bile acids is minute, depending only on the presence or absence of hydroxyl groups on positions 3, 7, and 12. Bile acids are physiological detergents that facilitate excretion, absorption, and transport of fats and sterols in the intestine and liver. Bile acids are also steroidal amphipathic molecules derived from the catabolism of cholesterol. They modulate bile flow and lipid secretion, are essential for the absorption of dietary fats and vitamins, and have been implicated in the regulation of all the key enzymes involved in cholesterol homeostasis. Bile acids recirculate through the liver, bile ducts, small intestine and portal vein to form an enterohepatic circuit. They exist as anions at physiological pH and, consequently, require a carrier for transport across the membranes of the enterohepatic tissues. The unique detergent properties of bile acids are essential for the digestion and intestinal absorption of hydrophobic nutrients. Bile acids have potent toxic properties (e.g. membrane disruption) and there are a plethora of mechanisms to limit their accumulation in blood and tissues (PMID: 11316487 , 16037564 , 12576301 , 11907135 ). Usually conjugated with either glycine or taurine. It acts as a detergent to solubilize fats for intestinal absorption and is reabsorbed by the small intestine. It is used as cholagogue, a choleretic laxative, and to prevent or dissolve gallstones. |
|---|
| Structure | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O InChI=1S/C24H40O4/c1-14(4-7-21(27)28)17-5-6-18-22-19(9-11-24(17,18)3)23(2)10-8-16(25)12-15(23)13-20(22)26/h14-20,22,25-26H,4-13H2,1-3H3,(H,27,28)/t14-,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20-,22+,23+,24-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 3alpha,7alpha-Dihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid | ChEBI | | 7alpha-Hydroxylithocholic acid | ChEBI | | Anthropodeoxycholic acid | ChEBI | | Anthropodesoxycholic acid | ChEBI | | CDCA | ChEBI | | Chenic acid | ChEBI | | Chenix | ChEBI | | Chenodiol | ChEBI | | Gallodesoxycholic acid | ChEBI | | 3a,7a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholanate | Generator | | 3a,7a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholanic acid | Generator | | 3alpha,7alpha-Dihydroxy-5beta-cholanate | Generator | | 3Α,7α-dihydroxy-5β-cholanate | Generator | | 3Α,7α-dihydroxy-5β-cholanic acid | Generator | | 7a-Hydroxylithocholate | Generator | | 7a-Hydroxylithocholic acid | Generator | | 7alpha-Hydroxylithocholate | Generator | | 7Α-hydroxylithocholate | Generator | | 7Α-hydroxylithocholic acid | Generator | | Anthropodeoxycholate | Generator | | Anthropodesoxycholate | Generator | | Chenate | Generator | | Gallodesoxycholate | Generator | | Chenodeoxycholate | Generator | | (+)-Chenodeoxycholate | HMDB | | (+)-Chenodeoxycholic acid | HMDB | | (3a,5b,7a)-3,7-Dihydroxy-cholan-24-Oate | HMDB | | (3a,5b,7a)-3,7-Dihydroxy-cholan-24-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3a,7a-Dihydroxy-5b,14a,17b-cholanate | HMDB | | 3a,7a-Dihydroxy-5b,14a,17b-cholanic acid | HMDB | | 3a,7a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholan-24-Oate | HMDB | | 3a,7a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholan-24-Oic acid | HMDB | | 7a-Hydroxy-desoxycholsaeure | HMDB | | Chenodesoxycholsaeure | HMDB | | Acid, chenique | HMDB | | Chenofalk | HMDB | | Chenophalk | HMDB | | Acid, chenodeoxycholic | HMDB | | Chenodeoxycholate, sodium | HMDB | | Quenocol | HMDB | | Solvay brand OF chenodeoxycholic acid | HMDB | | Antigen brand OF chenodeoxycholic acid | HMDB | | Falk brand OF chenodeoxycholic acid | HMDB | | Quenobilan | HMDB | | Sodium chenodeoxycholate | HMDB | | Tramedico brand OF chenodeoxycholic acid | HMDB | | Zambon brand OF chenodeoxycholic acid | HMDB | | Acid, chenic | HMDB | | Acid, gallodesoxycholic | HMDB | | Chenique acid | HMDB | | Estedi brand OF chenodeoxycholic acid | HMDB | | Henohol | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C24H40O4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 392.572 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 392.292659768 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (4R)-4-[(1S,2S,5R,7S,9R,10R,11S,14R,15R)-5,9-dihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadecan-14-yl]pentanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (4R)-4-[(1S,2S,5R,7S,9R,10R,11S,14R,15R)-5,9-dihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadecan-14-yl]pentanoic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 474-25-9 |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C24H40O4/c1-14(4-7-21(27)28)17-5-6-18-22-19(9-11-24(17,18)3)23(2)10-8-16(25)12-15(23)13-20(22)26/h14-20,22,25-26H,4-13H2,1-3H3,(H,27,28)/t14-,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20-,22+,23+,24-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | RUDATBOHQWOJDD-BSWAIDMHSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as dihydroxy bile acids, alcohols and derivatives. Dihydroxy bile acids, alcohols and derivatives are compounds containing or derived from a bile acid or alcohol, and which bears exactly two carboxylic acid groups. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Steroids and steroid derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Bile acids, alcohols and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Dihydroxy bile acids, alcohols and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Dihydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- 3-hydroxysteroid
- Hydroxysteroid
- 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid
- 7-hydroxysteroid
- Cyclic alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Aliphatic homopolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homopolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 165 - 167 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 0.09 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | 4.15 | SANGSTER (1993) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 7.52 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 14.9358 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 1.99 minutes | 32390414 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 77.5 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Long = Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 2825.2 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Lipids = Ascentis Express C18 with (60:40 water:ACN):(90:10 IPA:ACN) and 10mM NH4COOH + 0.1% Formic Acid | 230.4 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_Old = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:(20:80 acetone:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 213.6 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_New = RP Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:(30:70 MeOH:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 175.0 seconds | 40023050 | | RIKEN = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 529.0 seconds | 40023050 | | Eawag_XBridgeC18 = XBridge C18 3.5u 2.1x50 mm with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 670.8 seconds | 40023050 | | BfG_NTS_RP1 =Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm x 150 mm, 3.5 um) with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 633.1 seconds | 40023050 | | HILIC_BDD_2 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN(0.1% formic acid):water(16 mM ammonium formate) | 112.5 seconds | 40023050 | | UniToyama_Atlantis = RP Waters Atlantis T3 (2.1 x 150 mm, 5 um) with ACN:Water and 0.1% Formic Acid | 1126.2 seconds | 40023050 | | BDD_C18 = Hypersil Gold 1.9µm C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 540.3 seconds | 40023050 | | UFZ_Phenomenex = Kinetex Core-Shell C18 2.6 um, 3.0 x 100 mm, Phenomenex with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 1648.4 seconds | 40023050 | | SNU_RIKEN_POS = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 372.9 seconds | 40023050 | | RPMMFDA = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 455.7 seconds | 40023050 | | MTBLS87 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water and :ammonium carbonate | 256.2 seconds | 40023050 | | KI_GIAR_zic_HILIC_pH2_7 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN:Water and 0.1% FA | 301.3 seconds | 40023050 | | Meister zic-pHILIC pH9.3 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water 5mM NH4Ac pH9.3 and 5mM ammonium acetate in water | 68.6 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Chenodeoxycholic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3313.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3372.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3313.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3232.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3259.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3321.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C | 3235.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3530.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3592.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3577.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3702.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3698.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O | 3813.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Chenodeoxycholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](CC[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3915.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|
| Disease References | | Cystic fibrosis |
|---|
- Smith JL, Lewindon PJ, Hoskins AC, Pereira TN, Setchell KD, O'Connell NC, Shepherd RW, Ramm GA: Endogenous ursodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid in liver disease due to cystic fibrosis. Hepatology. 2004 Jun;39(6):1673-82. [PubMed:15185309 ]
| | Biliary atresia |
|---|
- Gustafsson J, Alvelius G, Bjorkhem I, Nemeth A: Bile acid metabolism in extrahepatic biliary atresia: lithocholic acid in stored dried blood collected at neonatal screening. Ups J Med Sci. 2006;111(1):131-6. [PubMed:16553252 ]
- Nittono H, Obinata K, Nakatsu N, Watanabe T, Niijima S, Sasaki H, Arisaka O, Kato H, Yabuta K, Miyano T: Sulfated and nonsulfated bile acids in urine of patients with biliary atresia: analysis of bile acids by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1986 Jan;5(1):23-9. [PubMed:3944741 ]
| | Cirrhosis |
|---|
- Cao H, Huang H, Xu W, Chen D, Yu J, Li J, Li L: Fecal metabolome profiling of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma patients by ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2011 Apr 8;691(1-2):68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.02.038. Epub 2011 Feb 23. [PubMed:21458633 ]
- Huang HJ, Zhang AY, Cao HC, Lu HF, Wang BH, Xie Q, Xu W, Li LJ: Metabolomic analyses of faeces reveals malabsorption in cirrhotic patients. Dig Liver Dis. 2013 Aug;45(8):677-82. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2013.01.001. Epub 2013 Feb 4. [PubMed:23384618 ]
| | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
|---|
- Cao H, Huang H, Xu W, Chen D, Yu J, Li J, Li L: Fecal metabolome profiling of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma patients by ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2011 Apr 8;691(1-2):68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.02.038. Epub 2011 Feb 23. [PubMed:21458633 ]
| | Primary biliary cirrhosis |
|---|
- Batta AK, Arora R, Salen G, Tint GS, Eskreis D, Katz S: Characterization of serum and urinary bile acids in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis by gas-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: effect of ursodeoxycholic acid treatment. J Lipid Res. 1989 Dec;30(12):1953-62. [PubMed:2621422 ]
|
|
|---|
| General References | - Tadano T, Kanoh M, Matsumoto M, Sakamoto K, Kamano T: Studies of serum and feces bile acids determination by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Rinsho Byori. 2006 Feb;54(2):103-10. [PubMed:16548228 ]
- Smith JL, Lewindon PJ, Hoskins AC, Pereira TN, Setchell KD, O'Connell NC, Shepherd RW, Ramm GA: Endogenous ursodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid in liver disease due to cystic fibrosis. Hepatology. 2004 Jun;39(6):1673-82. [PubMed:15185309 ]
- Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Morelli A: Nitric oxide and portal hypertension: a nitric oxide-releasing derivative of ursodeoxycholic acid that selectively releases nitric oxide in the liver. Dig Liver Dis. 2003 May;35 Suppl 2:S61-9. [PubMed:12846445 ]
- Meyers RL, Book LS, O'Gorman MA, Jackson WD, Black RE, Johnson DG, Matlak ME: High-dose steroids, ursodeoxycholic acid, and chronic intravenous antibiotics improve bile flow after Kasai procedure in infants with biliary atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 2003 Mar;38(3):406-11. [PubMed:12632357 ]
- Soderdahl G, Nowak G, Duraj F, Wang FH, Einarsson C, Ericzon BG: Ursodeoxycholic acid increased bile flow and affects bile composition in the early postoperative phase following liver transplantation. Transpl Int. 1998;11 Suppl 1:S231-8. [PubMed:9664985 ]
- Nobilis M, Pour M, Kunes J, Kopecky J, Kvetina J, Svoboda Z, Sladkova K, Vortel J: High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of ursodeoxycholic acid after solid phase extraction of blood serum and detection-oriented derivatization. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2001 Mar;24(5-6):937-46. [PubMed:11248487 ]
- Dohmen K, Mizuta T, Nakamuta M, Shimohashi N, Ishibashi H, Yamamoto K: Fenofibrate for patients with asymptomatic primary biliary cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Mar 15;10(6):894-8. [PubMed:15040040 ]
- Lupton JR, Steinbach G, Chang WC, O'Brien BC, Wiese S, Stoltzfus CL, Glober GA, Wargovich MJ, McPherson RS, Winn RJ: Calcium supplementation modifies the relative amounts of bile acids in bile and affects key aspects of human colon physiology. J Nutr. 1996 May;126(5):1421-8. [PubMed:8618139 ]
- Hillaire S, Ballet F, Franco D, Setchell KD, Poupon R: Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid on human hepatocytes in primary culture. Hepatology. 1995 Jul;22(1):82-7. [PubMed:7601437 ]
- Kitani K, Kanai S, Ivy GO, Carrillo MC: Pharmacological modifications of endogenous antioxidant enzymes with special reference to the effects of deprenyl: a possible antioxidant strategy. Mech Ageing Dev. 1999 Nov;111(2-3):211-21. [PubMed:10656538 ]
- Reyes H, Sjovall J: Bile acids and progesterone metabolites in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Ann Med. 2000 Mar;32(2):94-106. [PubMed:10766400 ]
- Stark M, Jornvall H, Johansson J: Isolation and characterization of hydrophobic polypeptides in human bile. Eur J Biochem. 1999 Nov;266(1):209-14. [PubMed:10542066 ]
- Hofmann AF: The continuing importance of bile acids in liver and intestinal disease. Arch Intern Med. 1999 Dec 13-27;159(22):2647-58. [PubMed:10597755 ]
- Morton DH, Salen G, Batta AK, Shefer S, Tint GS, Belchis D, Shneider B, Puffenberger E, Bull L, Knisely AS: Abnormal hepatic sinusoidal bile acid transport in an Amish kindred is not linked to FIC1 and is improved by ursodiol. Gastroenterology. 2000 Jul;119(1):188-95. [PubMed:10889168 ]
- Virovic L, Supanc V, Duvnjak M: [Primary sclerosing cholangitis--diagnosis and therapy]. Acta Med Croatica. 2003;57(3):207-19. [PubMed:14582467 ]
- Gatzen M, Pausch J: [Treatment of cholestatic liver diseases]. Med Klin (Munich). 2002 Mar 15;97(3):152-9. [PubMed:11957790 ]
- Eriksson LS, Olsson R, Glauman H, Prytz H, Befrits R, Ryden BO, Einarsson K, Lindgren S, Wallerstedt S, Weden M: Ursodeoxycholic acid treatment in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. A Swedish multicentre, double-blind, randomized controlled study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997 Feb;32(2):179-86. [PubMed:9051880 ]
- Lindblad A, Glaumann H, Strandvik B: A two-year prospective study of the effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on urinary bile acid excretion and liver morphology in cystic fibrosis-associated liver disease. Hepatology. 1998 Jan;27(1):166-74. [PubMed:9425933 ]
- Kowdley KV: Ursodeoxycholic acid therapy in hepatobiliary disease. Am J Med. 2000 Apr 15;108(6):481-6. [PubMed:10781781 ]
- Azer SA, Coverdale SA, Byth K, Farrell GC, Stacey NH: Sequential changes in serum levels of individual bile acids in patients with chronic cholestatic liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996 Mar;11(3):208-15. [PubMed:8742915 ]
- St-Pierre MV, Kullak-Ublick GA, Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ: Transport of bile acids in hepatic and non-hepatic tissues. J Exp Biol. 2001 May;204(Pt 10):1673-86. [PubMed:11316487 ]
- Claudel T, Staels B, Kuipers F: The Farnesoid X receptor: a molecular link between bile acid and lipid and glucose metabolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 Oct;25(10):2020-30. Epub 2005 Jul 21. [PubMed:16037564 ]
- Chiang JY: Bile acid regulation of hepatic physiology: III. Bile acids and nuclear receptors. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Mar;284(3):G349-56. [PubMed:12576301 ]
- Davis RA, Miyake JH, Hui TY, Spann NJ: Regulation of cholesterol-7alpha-hydroxylase: BAREly missing a SHP. J Lipid Res. 2002 Apr;43(4):533-43. [PubMed:11907135 ]
|
|---|