| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-05-30 20:55:51 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000535 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB00535
- HMDB0061883
- HMDB61883
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Caproic acid |
|---|
| Description | Caproic acid, also known as hexanoic acid or C6:0, is a medium-chain fatty acid. Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 6 to 12 carbons, which can form medium-chain triglycerides. Caproic acid is a colourless oily liquid that smells like cheese with an overlying waxy or barnyard odor like that of goats or other barnyard animals. Its name comes from the Latin word capra, meaning "goat". Two other fatty acids are named after goats: caprylic acid (C8) and capric acid (C10). Along with caproic acid, they account for 15% of the fat in goat's milk. Caproic acid is a fatty acid found naturally in various animal fats and oils. While generally more abundant in animals, caproic acid is found in all organisms ranging from bacteria to plants to animals. Caproic acid is one of the chemicals that gives the decomposing fleshy seed coat of the ginkgo fruit its characteristic unpleasant odor. It is also one of the components of vanilla and cheese. Industrially, the primary use of caproic acid is in the manufacture of its esters for use as artificial flavors and in the manufacture of hexyl derivatives, such as hexylphenols. Caproic acid has been associated with medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, which is an inborn error of metabolism. As a relatively volatile organic compound, caproic acid has been identified as a fecal biomarker of Clostridium difficile infection (PMID: 30986230 ). |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C6H12O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6(7)8/h2-5H2,1H3,(H,7,8) |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 1-Hexanoic acid | ChEBI | | 1-Pentanecarboxylic acid | ChEBI | | 6:0 | ChEBI | | Butylacetic acid | ChEBI | | C6:0 | ChEBI | | Capronic acid | ChEBI | | CH3-[CH2]4-COOH | ChEBI | | Hexanoate | ChEBI | | Hexoic acid | ChEBI | | Hexylic acid | ChEBI | | N-Caproic acid | ChEBI | | N-Hexanoic acid | ChEBI | | N-Hexoic acid | ChEBI | | N-Hexylic acid | ChEBI | | Pentanecarboxylic acid | ChEBI | | Pentiformic acid | ChEBI | | Pentylformic acid | ChEBI | | 1-Hexanoate | Generator | | 1-Pentanecarboxylate | Generator | | Butylacetate | Generator | | Capronate | Generator | | Hexanoic acid | Generator | | Hexoate | Generator | | Hexylate | Generator | | N-Caproate | Generator | | N-Hexanoate | Generator | | N-Hexoate | Generator | | N-Hexylate | Generator | | Pentanecarboxylate | Generator | | Pentiformate | Generator | | Pentylformate | Generator | | Caproate | Generator | | Hexanoic acid, calcium salt | MeSH, HMDB | | Hexanoic acid, sodium salt, 1-(11)C-labeled | MeSH, HMDB | | Hexanoic acid, nickel (2+) salt | MeSH, HMDB | | Hexanoic acid, sodium salt | MeSH, HMDB | | Bismuth(III)hexanoate | MeSH, HMDB | | Hexanoic acid, copper (2+) salt | MeSH, HMDB | | Hexanoic acid, manganese (2+) salt | MeSH, HMDB | | Bi(ohex)3 | MeSH, HMDB | | Hexanoic acid, barium salt | MeSH, HMDB | | Hexanoic acid, potassium salt | MeSH, HMDB | | Hexanoic acid, rhodium (2+) salt | MeSH, HMDB | | FA(6:0) | HMDB | | Calcium N-hexanoate | MeSH, HMDB | | Hexanoic acid, sodium salt (1:1) | MeSH, HMDB | | Sodium capronate | MeSH, HMDB | | Calcium hexanoate | MeSH, HMDB | | Caproic acid sodium salt | MeSH, HMDB | | Sodium caproate | MeSH, HMDB | | Sodium hexanoate | MeSH, HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H12O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 116.1583 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 116.083729628 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | hexanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | hexanoic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 142-62-1 |
|---|
| SMILES | CCCCCC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H12O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6(7)8/h2-5H2,1H3,(H,7,8) |
|---|
| InChI Key | FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
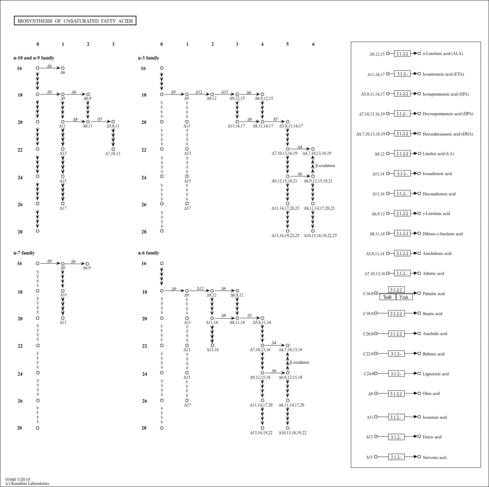
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as medium-chain fatty acids. These are fatty acids with an aliphatic tail that contains between 4 and 12 carbon atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acids and conjugates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Medium-chain fatty acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Medium-chain fatty acid
- Straight chain fatty acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | Not Available |
|---|
| Role | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 3.78 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 12.1123 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 4.93 minutes | 32390414 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 37.7 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized |
|---|
| Disease References | | Ulcerative colitis |
|---|
- Garner CE, Smith S, de Lacy Costello B, White P, Spencer R, Probert CS, Ratcliffe NM: Volatile organic compounds from feces and their potential for diagnosis of gastrointestinal disease. FASEB J. 2007 Jun;21(8):1675-88. Epub 2007 Feb 21. [PubMed:17314143 ]
- Le Gall G, Noor SO, Ridgway K, Scovell L, Jamieson C, Johnson IT, Colquhoun IJ, Kemsley EK, Narbad A: Metabolomics of fecal extracts detects altered metabolic activity of gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. J Proteome Res. 2011 Sep 2;10(9):4208-18. doi: 10.1021/pr2003598. Epub 2011 Aug 8. [PubMed:21761941 ]
- De Preter V, Machiels K, Joossens M, Arijs I, Matthys C, Vermeire S, Rutgeerts P, Verbeke K: Faecal metabolite profiling identifies medium-chain fatty acids as discriminating compounds in IBD. Gut. 2015 Mar;64(3):447-58. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306423. Epub 2014 May 8. [PubMed:24811995 ]
- Ahmed I, Greenwood R, Costello B, Ratcliffe N, Probert CS: Investigation of faecal volatile organic metabolites as novel diagnostic biomarkers in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Mar;43(5):596-611. doi: 10.1111/apt.13522. Epub 2016 Jan 25. [PubMed:26806034 ]
| | Irritable bowel syndrome |
|---|
- Le Gall G, Noor SO, Ridgway K, Scovell L, Jamieson C, Johnson IT, Colquhoun IJ, Kemsley EK, Narbad A: Metabolomics of fecal extracts detects altered metabolic activity of gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. J Proteome Res. 2011 Sep 2;10(9):4208-18. doi: 10.1021/pr2003598. Epub 2011 Aug 8. [PubMed:21761941 ]
| | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
|---|
- Raman M, Ahmed I, Gillevet PM, Probert CS, Ratcliffe NM, Smith S, Greenwood R, Sikaroodi M, Lam V, Crotty P, Bailey J, Myers RP, Rioux KP: Fecal microbiome and volatile organic compound metabolome in obese humans with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Jul;11(7):868-75.e1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.02.015. Epub 2013 Feb 27. [PubMed:23454028 ]
| | Celiac disease |
|---|
- Di Cagno R, De Angelis M, De Pasquale I, Ndagijimana M, Vernocchi P, Ricciuti P, Gagliardi F, Laghi L, Crecchio C, Guerzoni ME, Gobbetti M, Francavilla R: Duodenal and faecal microbiota of celiac children: molecular, phenotype and metabolome characterization. BMC Microbiol. 2011 Oct 4;11:219. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-219. [PubMed:21970810 ]
| | Autism |
|---|
- De Angelis M, Piccolo M, Vannini L, Siragusa S, De Giacomo A, Serrazzanetti DI, Cristofori F, Guerzoni ME, Gobbetti M, Francavilla R: Fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. PLoS One. 2013 Oct 9;8(10):e76993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076993. eCollection 2013. [PubMed:24130822 ]
| | Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified |
|---|
- De Angelis M, Piccolo M, Vannini L, Siragusa S, De Giacomo A, Serrazzanetti DI, Cristofori F, Guerzoni ME, Gobbetti M, Francavilla R: Fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. PLoS One. 2013 Oct 9;8(10):e76993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076993. eCollection 2013. [PubMed:24130822 ]
| | Crohn's disease |
|---|
- De Preter V, Machiels K, Joossens M, Arijs I, Matthys C, Vermeire S, Rutgeerts P, Verbeke K: Faecal metabolite profiling identifies medium-chain fatty acids as discriminating compounds in IBD. Gut. 2015 Mar;64(3):447-58. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306423. Epub 2014 May 8. [PubMed:24811995 ]
- Ahmed I, Greenwood R, Costello B, Ratcliffe N, Probert CS: Investigation of faecal volatile organic metabolites as novel diagnostic biomarkers in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Mar;43(5):596-611. doi: 10.1111/apt.13522. Epub 2016 Jan 25. [PubMed:26806034 ]
| | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ: Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 25;11(3):e0152126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27015276 ]
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Ahn J, Shi J, Sinha R: Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2089-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131. Epub 2014 Jul 18. [PubMed:25037050 ]
| | Clostridium difficile infection |
|---|
- Patel M, Fowler D, Sizer J, Walton C: Faecal volatile biomarkers of Clostridium difficile infection. PLoS One. 2019 Apr 15;14(4):e0215256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215256. eCollection 2019. [PubMed:30986230 ]
| | Perillyl alcohol administration for cancer treatment |
|---|
- Silva CL, Passos M, Camara JS: Solid phase microextraction, mass spectrometry and metabolomic approaches for detection of potential urinary cancer biomarkers--a powerful strategy for breast cancer diagnosis. Talanta. 2012 Jan 30;89:360-8. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2011.12.041. Epub 2011 Dec 22. [PubMed:22284503 ]
| | Medium Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency |
|---|
- Gregersen N, Kolvraa S, Rasmussen K, Mortensen PB, Divry P, David M, Hobolth N: General (medium-chain) acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (non-ketotic dicarboxylic aciduria): quantitative urinary excretion pattern of 23 biologically significant organic acids in three cases. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Aug 15;132(2):181-91. [PubMed:6616873 ]
|
|
|---|
| General References | - Ohdoi C, Nyhan WL, Kuhara T: Chemical diagnosis of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry detection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2003 Jul 15;792(1):123-30. [PubMed:12829005 ]
- Jakobs C, Sweetman L, Nyhan WL: Hydroxy acid metabolites of branched-chain amino acids in amniotic fluid. Clin Chim Acta. 1984 Jul 16;140(2):157-66. [PubMed:6467607 ]
- Schoots AC, Mikkers FE, Cramers CA, Ringoir S: Profiling of uremic serum by high-resolution gas chromatography-electron-impact, chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr. 1979 Sep 11;164(1):1-8. [PubMed:541389 ]
- Epps JM, Phillips JO, Mestecky J: IgA-mediated clearance and tissue deposition of dinitrophenylated human serum albumin at various DNP:HSA ratios. Mol Immunol. 1988 Aug;25(8):731-8. [PubMed:3185569 ]
- Varani J, Orr W, Ward PA: Cell-associated proteases affect tumour cell migration in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1979 Apr;36:241-52. [PubMed:457809 ]
- Nilsen SL, Castellino FJ: Expression of human plasminogen in Drosophila Schneider S2 cells. Protein Expr Purif. 1999 Jun;16(1):136-43. [PubMed:10336871 ]
- Varani J, Orr W, Ward PA: Comparison of cell attachment and caseinolytic activities of five tumour cell types. J Cell Sci. 1978 Dec;34:133-44. [PubMed:748334 ]
- Hoverstad T, Fausa O, Bjorneklett A, Bohmer T: Short-chain fatty acids in the normal human feces. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 May;19(3):375-81. [PubMed:6740214 ]
- Harkness RA: Lesch-Nyhan syndrome: reduced amino acid concentrations in CSF and brain. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1989;253A:159-63. [PubMed:2624185 ]
- Traul KA, Driedger A, Ingle DL, Nakhasi D: Review of the toxicologic properties of medium-chain triglycerides. Food Chem Toxicol. 2000 Jan;38(1):79-98. [PubMed:10685018 ]
- Simons K, Toomre D: Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;1(1):31-9. [PubMed:11413487 ]
- Watson AD: Thematic review series: systems biology approaches to metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. Lipidomics: a global approach to lipid analysis in biological systems. J Lipid Res. 2006 Oct;47(10):2101-11. Epub 2006 Aug 10. [PubMed:16902246 ]
- Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig AJ: Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue function and plasticity orchestrate nutritional adaptation. J Lipid Res. 2007 Jun;48(6):1253-62. Epub 2007 Mar 20. [PubMed:17374880 ]
- Lingwood D, Simons K: Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science. 2010 Jan 1;327(5961):46-50. doi: 10.1126/science.1174621. [PubMed:20044567 ]
- Patel M, Fowler D, Sizer J, Walton C: Faecal volatile biomarkers of Clostridium difficile infection. PLoS One. 2019 Apr 15;14(4):e0215256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215256. eCollection 2019. [PubMed:30986230 ]
- Elshenawy S, Pinney SE, Stuart T, Doulias PT, Zura G, Parry S, Elovitz MA, Bennett MJ, Bansal A, Strauss JF 3rd, Ischiropoulos H, Simmons RA: The Metabolomic Signature of the Placenta in Spontaneous Preterm Birth. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3). pii: ijms21031043. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031043. [PubMed:32033212 ]
- Gunstone, Frank D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra (2007). The lipid handbook with CD-ROM. CRC Press.
|
|---|