| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:15:25 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0001051 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Glyceraldehyde |
|---|
| Description | Glyceraldehyde is a triose monosaccharide with chemical formula C3H6O3. It is the simplest of all common aldoses. It is a sweet, colourless crystalline solid that is an intermediate compound in carbohydrate metabolism. The word "glyceraldehyde" comes from combining glycerine and aldehyde, as glyceraldehyde is merely glycerine with one hydroxide changed to an aldehyde. Glyceraldehyde is produced from the action of the enzyme glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase, which converts glycerol to glyceraldehyde using NADP as a cofactor. When present at sufficiently high levels, glyceraldehyde can be a cytotoxin and a mutagen. A cytotoxin is a compound that kills cells. A mutagen is a compound that causes mutations in DNA. Glyceraldehyde is a highly reactive compound that can modify and cross-link proteins. Glyceraldehyde-modified proteins appear to be cytotoxic, depress intracellular glutathione levels, and induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (PMID:14981296 ). Glyceraldehyde has been shown to cause chromosome damage to human cells in culture and is mutagenic in the Ames bacterial test. |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C3H6O3/c4-1-3(6)2-5/h1,3,5-6H,2H2 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (+-)-Glyceraldehyde | ChEBI | | 2,3-Dihydroxypropanal | ChEBI | | 2,3-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde | ChEBI | | Aldotriose | ChEBI | | alpha,beta-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde | ChEBI | | DL-Glyceraldehyde | ChEBI | | Gliceraldehido | ChEBI | | Glyceraldehyd | ChEBI | | Glyceric aldehyde | ChEBI | | Glycerinaldehyd | ChEBI | | Glycerinaldehyde | ChEBI | | Glycerinformal | ChEBI | | Glycerose | ChEBI | | Glyzerinaldehyd | ChEBI | | a,b-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde | Generator | | Α,β-dihydroxypropionaldehyde | Generator | | (+/-)-2,3-dihydroxy-propanal | HMDB | | (+/-)-glyceraldehyde | HMDB | | D-(+)-Glyceraldehyde | HMDB | | D-2,3-Dihydroxypropanal | HMDB | | D-2,3-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde | HMDB | | D-Aldotriose | HMDB | | D-Glyceraldehyde | HMDB | | D-Glycerose | HMDB | | delta-(+)-Glyceraldehyde | HMDB | | delta-2,3-Dihydroxypropanal | HMDB | | delta-2,3-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde | HMDB | | delta-Aldotriose | HMDB | | delta-Glyceraldehyde | HMDB | | delta-Glycerose | HMDB | | Dihydroxypropionaldehyde | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C3H6O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 90.0779 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 90.031694058 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2,3-dihydroxypropanal |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (+/-)-glyceraldehyde |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 56-82-6 |
|---|
| SMILES | OCC(O)C=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C3H6O3/c4-1-3(6)2-5/h1,3,5-6H,2H2 |
|---|
| InChI Key | MNQZXJOMYWMBOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are compounds containing one carbohydrate unit not glycosidically linked to another such unit, and no set of two or more glycosidically linked carbohydrate units. Monosaccharides have the general formula CnH2nOn. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Monosaccharides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Monosaccharide
- Alpha-hydroxyaldehyde
- Secondary alcohol
- 1,2-diol
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Short-chain aldehyde
- Primary alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Aldehyde
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | Not Available |
|---|
| Role | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 145 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 17 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 1.07 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 8.8203 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 2.34 minutes | 32390414 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 235.3 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Glyceraldehyde,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OCC(O)C=O | 1058.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(C=O)CO | 1014.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC=C(O)CO | 1111.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OCC(C=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1181.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC=C(O)CO[Si](C)(C)C | 1231.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC=C(CO)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1204.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC=C(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1358.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC=C(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1266.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC=C(CO[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1242.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC(O)C=O | 1290.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(C=O)CO | 1267.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC=C(O)CO | 1341.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC(C=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1619.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC=C(O)CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1682.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC=C(CO)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1672.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC=C(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1937.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC=C(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1880.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glyceraldehyde,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC=C(CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1672.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0udj-1900000000-66c3a7fb073f6c5c86a0 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0udi-1900000000-3fd8dc5205f5abb770ca | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0udi-0900000000-228dd3700017b511ddd9 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0w2a-0910000000-74411a9433752c08b424 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0udj-1900000000-66c3a7fb073f6c5c86a0 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0udi-1900000000-3fd8dc5205f5abb770ca | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-03gl-9000000000-04537fb12b74f4857059 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (2 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0g4r-9730000000-bb9b8a35e01fa42c3f2e | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TBDMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TBDMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TBDMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde GC-MS (TBDMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-03di-9000000000-25cf3a1adcc93448a673 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0006-9000000000-c5b3efaddb77bd3470a0 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-01ox-9000000000-ff6b63535e8104e1a60f | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde , negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-ca32a106d1461e63eea5 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-af49bbc2fc7043fc3c04 | 2016-09-14 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-006x-9000000000-876e932a7b8564c247dd | 2016-09-14 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0596-9000000000-9dc05bb3457ad5d98b3b | 2016-09-14 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-7749188cec001a162f6b | 2016-09-14 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-08daa6fe14473ac5bc2e | 2016-09-14 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-bb4eb4e9f59323f2cae5 | 2016-09-14 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0079-9000000000-3cb73efbb0ef4186837f | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-41e64da2b99cd707e835 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-a516ef0decbed3a53fd6 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-05fv-9000000000-58125ea4710c5863a7cc | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-052b-9000000000-a014d8affc7e437e8106 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glyceraldehyde 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-052g-9000000000-1f025d763cc3b0d6b99a | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm (predicted from logP)
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
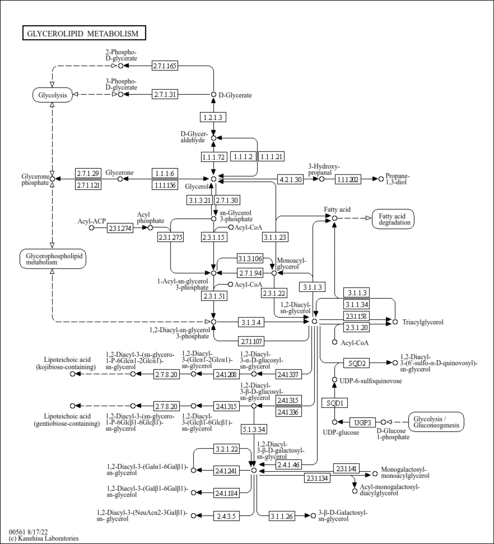
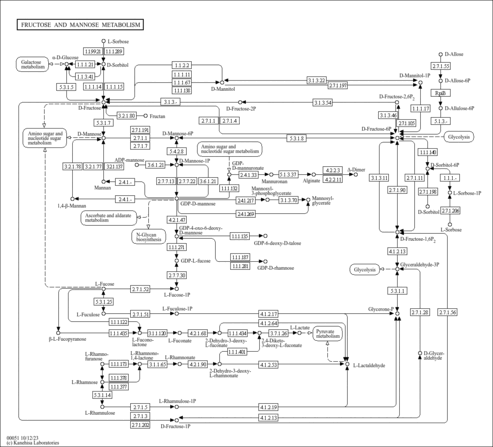
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1476.0 +/- 655.0 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 50.00 +/- 50.00 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details |
|
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Interstitial cystitis | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Both | Crohns disease | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Both | Ulcerative colitis | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Crohns disease | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Ulcerative colitis | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Unclassified IBD | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 6407.7 +/- 6030.8 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Renal fanconi syndrome | | details |
|
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Bladder infections |
|---|
- Braundmeier-Fleming A, Russell NT, Yang W, Nas MY, Yaggie RE, Berry M, Bachrach L, Flury SC, Marko DS, Bushell CB, Welge ME, White BA, Schaeffer AJ, Klumpp DJ: Stool-based biomarkers of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Sci Rep. 2016 May 18;6:26083. doi: 10.1038/srep26083. [PubMed:27188581 ]
| | Crohn's disease |
|---|
- Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V: Faecal and Serum Metabolomics in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017 Mar 1;11(3):321-334. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw158. [PubMed:27609529 ]
| | Ulcerative colitis |
|---|
- Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V: Faecal and Serum Metabolomics in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017 Mar 1;11(3):321-334. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw158. [PubMed:27609529 ]
| | Fanconi syndrome |
|---|
- Jonas AJ, Lin SN, Conley SB, Schneider JA, Williams JC, Caprioli RC: Urine glyceraldehyde excretion is elevated in the renal Fanconi syndrome. Kidney Int. 1989 Jan;35(1):99-104. [PubMed:2709665 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB022392 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00007413 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 731 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C02154 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CPD0-1551 |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Glyceraldehyde |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 751 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 5445 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | Not Available |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Wan, Xin-Jun; Song, Ming-You; Wu, Rong; Chu, Dao-Bao. Synthesis of glyceraldehyde by indirect electrooxidation. Yingyong Huaxue (2003), 20(6), 578-581. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) |
|---|
| General References | - Gugliucci A: A practical method to study functional impairment of proteins by glycation and effects of inhibitors using current coagulation/fibrinolysis reagent kits. Clin Biochem. 2003 Mar;36(2):155-8. [PubMed:12633766 ]
- Beard KM, Shangari N, Wu B, O'Brien PJ: Metabolism, not autoxidation, plays a role in alpha-oxoaldehyde- and reducing sugar-induced erythrocyte GSH depletion: relevance for diabetes mellitus. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003 Oct;252(1-2):331-8. [PubMed:14577607 ]
- Iwata H, Ukeda H, Maruyama T, Fujino T, Sawamura M: Effect of carbonyl compounds on red blood cells deformability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Aug 27;321(3):700-6. [PubMed:15358163 ]
- Zakrzewska I, Prokopowicz J, Worowski K, Skrzydlewska E, Puchalski Z, Piotrowski Z: Low molecular organic inactivators in differentiating organ origin of alpha-amylase in humans. Part I. Mater Med Pol. 1989 Oct-Dec;21(4):274-6. [PubMed:2518736 ]
- Phillipou G, Seaborn CJ, Phillips PJ: Re-evaluation of the fructosamine reaction. Clin Chem. 1988 Aug;34(8):1561-4. [PubMed:3402055 ]
- Fujita T, Funako T, Hayashi H: 8-Hydroxydaidzein, an aldose reductase inhibitor from okara fermented with Aspergillus sp. HK-388. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2004 Jul;68(7):1588-90. [PubMed:15277768 ]
- Haraguchi H, Hayashi R, Ishizu T, Yagi A: A flavone from Manilkara indica as a specific inhibitor against aldose reductase in vitro. Planta Med. 2003 Sep;69(9):853-5. [PubMed:14598214 ]
- Yamagishi S, Nakamura K, Inoue H, Kikuchi S, Takeuchi M: Serum or cerebrospinal fluid levels of glyceraldehyde-derived advanced glycation end products (AGEs) may be a promising biomarker for early detection of Alzheimer's disease. Med Hypotheses. 2005;64(6):1205-7. [PubMed:15823718 ]
- Choei H, Sasaki N, Takeuchi M, Yoshida T, Ukai W, Yamagishi S, Kikuchi S, Saito T: Glyceraldehyde-derived advanced glycation end products in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2004 Sep;108(3):189-93. Epub 2004 Jun 17. [PubMed:15221334 ]
- Jonas AJ, Lin SN, Conley SB, Schneider JA, Williams JC, Caprioli RC: Urine glyceraldehyde excretion is elevated in the renal Fanconi syndrome. Kidney Int. 1989 Jan;35(1):99-104. [PubMed:2709665 ]
- Takeuchi M, Yamagishi S: Alternative routes for the formation of glyceraldehyde-derived AGEs (TAGE) in vivo. Med Hypotheses. 2004;63(3):453-5. [PubMed:15288367 ]
- Nagaraj RH, Oya-Ito T, Padayatti PS, Kumar R, Mehta S, West K, Levison B, Sun J, Crabb JW, Padival AK: Enhancement of chaperone function of alpha-crystallin by methylglyoxal modification. Biochemistry. 2003 Sep 16;42(36):10746-55. [PubMed:12962499 ]
- Usui T, Shizuuchi S, Watanabe H, Hayase F: Cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by the glyceraldehyde-related Maillard reaction products for HL-60 cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2004 Feb;68(2):333-40. [PubMed:14981296 ]
|
|---|