| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2007-05-22 19:40:54 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2021-09-14 15:47:52 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0006254 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid |
|---|
| Description | 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid belongs to the class of organic compounds known as retinoids. These are oxygenated derivatives of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene and derivatives thereof. Based on a literature review a significant number of articles have been published on 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid. |
|---|
| Structure | C\C(\C=C\C1=C(C)C(O)CCC1(C)C)=C/C=C/C(/C)=C/C(O)=O InChI=1S/C20H28O3/c1-14(7-6-8-15(2)13-19(22)23)9-10-17-16(3)18(21)11-12-20(17,4)5/h6-10,13,18,21H,11-12H2,1-5H3,(H,22,23)/b8-6+,10-9+,14-7+,15-13+ |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-3-hydroxy-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid | ChEBI | | (2E,4E,6E,8E)-9-(3-Hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid | ChEBI | | (7E,9E,11E,13E)-4-Hydroxyretinoic acid | ChEBI | | 4-Hydroxy-(7E,9E,11E,13E)-retinoic acid | ChEBI | | 4-Hydroxy-all-trans-retinoic acid | ChEBI | | (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-3-hydroxy-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoate | Generator | | (2E,4E,6E,8E)-9-(3-Hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoate | Generator | | (7E,9E,11E,13E)-4-Hydroxyretinoate | Generator | | 4-Hydroxy-(7E,9E,11E,13E)-retinoate | Generator | | 4-Hydroxy-all-trans-retinoate | Generator | | 4-Hydroxyretinoate | Generator | | 4-Hydroxy-13-cis-retinoate | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxy-13-cis-retinoic acid | HMDB, MeSH | | 4-Hydroxy-retinoate | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxy-retinoic acid | HMDB | | 4-OH-Retinoate | HMDB | | 4-OH-Retinoic acid | HMDB | | all-trans-4-Hydroxyretinoate | HMDB | | all-trans-4-Hydroxyretinoic acid | HMDB | | rac-4-Hydroxy-all-trans-retinoate | HMDB | | rac-4-Hydroxy-all-trans-retinoic acid | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxy-13-retinoic acid | MeSH, HMDB | | 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid, (13-cis)-isomer | MeSH, HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H28O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 316.4345 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 316.203844762 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2E,4E,6E,8E)-9-(3-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-dimethylnona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 4-hydroxyretinoic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 66592-72-1 |
|---|
| SMILES | C\C(\C=C\C1=C(C)C(O)CCC1(C)C)=C/C=C/C(/C)=C/C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H28O3/c1-14(7-6-8-15(2)13-19(22)23)9-10-17-16(3)18(21)11-12-20(17,4)5/h6-10,13,18,21H,11-12H2,1-5H3,(H,22,23)/b8-6+,10-9+,14-7+,15-13+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | KGUMXGDKXYTTEY-FRCNGJHJSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as retinoids. These are oxygenated derivatives of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene and derivatives thereof. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Retinoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Retinoids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Retinoic acid
- Diterpenoid
- Retinoid skeleton
- Medium-chain fatty acid
- Branched fatty acid
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Methyl-branched fatty acid
- Unsaturated fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Fatty acid
- Secondary alcohol
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O)C(C)(C)CCC1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2807.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1O | 2841.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2814.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O)C(C)(C)CCC1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3038.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1O | 3059.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)CCC1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3254.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0k92-1093000000-7f88a5d83645fa2a79e9 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid GC-MS (2 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0092-5008900000-f94c9a4b723e495dbc22 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00kb-0292000000-4d5a6c9335a4fa5db05e | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0zg1-0590000000-0b50fabd74e810e935c0 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0pba-3920000000-8958845f26cb19e0194b | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-0089000000-cdb17ed778c9480eb63e | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0gi1-0094000000-b75b3689212cfa9472cb | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-4390000000-5614482c4d64bf67afaf | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000t-0291000000-7a67cccc8b73d68d76e3 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0f8i-0490000000-891d9992953ed919a7c3 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000l-5920000000-8f663f06367ea569c02e | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-0096000000-123a0c931fe8f0c0d401 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0190000000-3eec1ef4274b19e5f537 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 4-Hydroxyretinoic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-016r-4910000000-9e73ac1032f900dd901d | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Membrane
- Nucleus
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
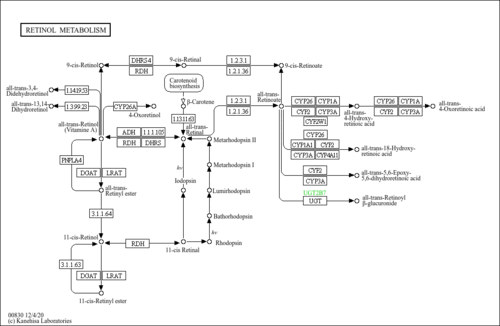
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Expected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Available | Not Available | Normal | | details | | Urine | Expected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Available | Not Available | Normal | | details |
|
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | None |
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | None |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB023862 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 4943093 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C16677 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 2299866 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 6438629 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 63795 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | CE2956 |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Rosenberger, Michael. Retinoic acid metabolites. 1. Total synthesis of 4-hydroxy- and 4-oxoretinoic acid. Journal of Organic Chemistry (1982), 47(9), 1698-701. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Napoli JL, Posch KP, Fiorella PD, Boerman MH: Physiological occurrence, biosynthesis and metabolism of retinoic acid: evidence for roles of cellular retinol-binding protein (CRBP) and cellular retinoic acid-binding protein (CRABP) in the pathway of retinoic acid homeostasis. Biomed Pharmacother. 1991;45(4-5):131-43. [PubMed:1932598 ]
- Roberts ES, Vaz AD, Coon MJ: Role of isozymes of rabbit microsomal cytochrome P-450 in the metabolism of retinoic acid, retinol, and retinal. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;41(2):427-33. [PubMed:1538719 ]
- Spear PA, Garcin H, Narbonne JF: Increased retinoic acid metabolism following 3,3',4,4',5,5'-hexabromobiphenyl injection. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;66(9):1181-6. [PubMed:2851384 ]
|
|---|