| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2007-05-22 21:57:36 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:31 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0006292 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0002325
- HMDB02325
- HMDB06292
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Chenodeoxycholoyl-CoA |
|---|
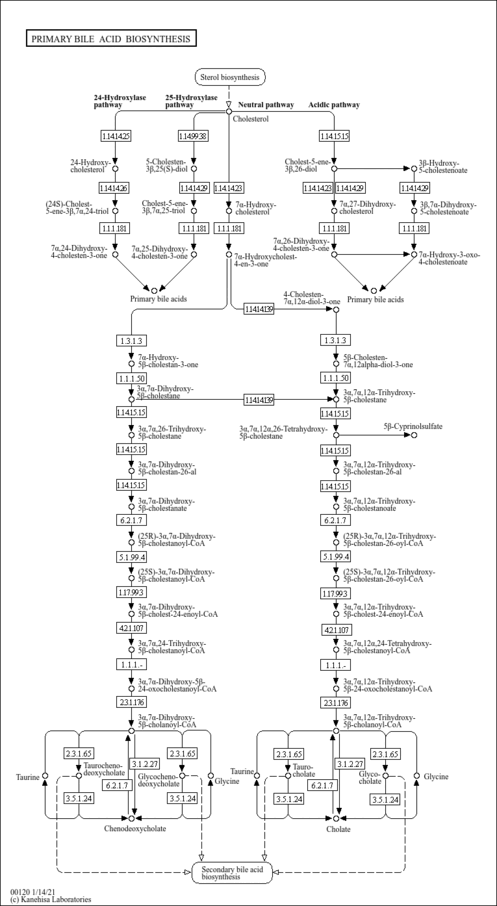
| Description | Chenodeoxycholoyl-CoA is bile acid Coenzyme A ester. In humans, bile acids conjugated with glycine and taurine are the major solutes in bile, and unconjugated bile acids are almost nondetectable in normal bile. Conjugated bile acids are less toxic and are more efficient promoters of intestinal absorption of dietary lipid than unconjugated bile acids. The synthesis of bile acid and amino acid conjugates in human liver is the result of two independent enzymatic reactions with a bile acid coenzyme A thioester intermediate formation of bile acid-CoA esters, considered the rate-limiting step in bile acid amidation and catalyzed by an ATP-dependent microsomal enzyme, bile acid-CoA synthetase (EC 6.2.1.7). In the second reaction, the thioester bond is cleaved, and an amide bond is formed between the bile acid and the amino acids glycine or taurine. The bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.65) catalyzes this reaction in the cytosol prior to secretion into bile. In human liver the formation of bile acid-CoA thioesters is localized both to the microsomal fraction catalysed by an ATP-dependent synthetase and to the peroxisomal fraction catalysed by the thiolase in the last step of the beta-oxidative cleavage of the 5beta-cholestanoyl side chain. The highest specific amidation activity of both chenodeoxycholoyl-CoA is always found in the most peroxisome-rich subcellular fractions. (PMID: 2722825 , 10817395 , 11673457 , 10884298 ). |
|---|
| Structure | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)C(O)C(C)(C)COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N InChI=1S/C45H74N7O19P3S/c1-24(27-7-8-28-34-29(11-14-45(27,28)5)44(4)13-10-26(53)18-25(44)19-30(34)54)6-9-33(56)75-17-16-47-32(55)12-15-48-41(59)38(58)43(2,3)21-68-74(65,66)71-73(63,64)67-20-31-37(70-72(60,61)62)36(57)42(69-31)52-23-51-35-39(46)49-22-50-40(35)52/h22-31,34,36-38,42,53-54,57-58H,6-21H2,1-5H3,(H,47,55)(H,48,59)(H,63,64)(H,65,66)(H2,46,49,50)(H2,60,61,62)/t24-,25+,26-,27-,28+,29+,30-,31-,34+,36-,37-,38?,42-,44+,45-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 5'-{3-[(3R)-4-{[3-({2-[(3alpha,7alpha-dihydroxy-5beta-cholan-24-oyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}amino)-3-oxopropyl]amino}-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxobutyl] dihydrogen diphosphate}3'-phosphoadenosine | HMDB | | Chenodeoxycholoyl coenzyme A | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C45H74N7O19P3S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 1142.091 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 1141.397303447 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | {[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-2-({[({[3-({2-[(2-{[(4R)-4-[(1S,2S,5R,7S,9R,10R,11S,14R,15R)-5,9-dihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0²,⁷.0¹¹,¹⁵]heptadecan-14-yl]pentanoyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]ethyl}carbamoyl)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylpropoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}methyl)-4-hydroxyoxolan-3-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-2-[({[3-({2-[(2-{[(4R)-4-[(1S,2S,5R,7S,9R,10R,11S,14R,15R)-5,9-dihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0²,⁷.0¹¹,¹⁵]heptadecan-14-yl]pentanoyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]ethyl}carbamoyl)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylpropoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)methyl]-4-hydroxyoxolan-3-yl]oxyphosphonic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 60731-52-4 |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)C(O)C(C)(C)COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C45H74N7O19P3S/c1-24(27-7-8-28-34-29(11-14-45(27,28)5)44(4)13-10-26(53)18-25(44)19-30(34)54)6-9-33(56)75-17-16-47-32(55)12-15-48-41(59)38(58)43(2,3)21-68-74(65,66)71-73(63,64)67-20-31-37(70-72(60,61)62)36(57)42(69-31)52-23-51-35-39(46)49-22-50-40(35)52/h22-31,34,36-38,42,53-54,57-58H,6-21H2,1-5H3,(H,47,55)(H,48,59)(H,63,64)(H,65,66)(H2,46,49,50)(H2,60,61,62)/t24-,25+,26-,27-,28+,29+,30-,31-,34+,36-,37-,38?,42-,44+,45-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | IIWDDMINEZBCTG-POZCYTSJSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 2,3,4-saturated fatty acyl coas. These are acyl-CoAs carrying a 2,3,4-saturated fatty acyl chain. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acyl thioesters |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 2,3,4-saturated fatty acyl CoAs |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Coenzyme a or derivatives
- Purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside diphosphate
- Steroidal glycoside
- Dihydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- Hydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- Cholane-skeleton
- Bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- 3-hydroxysteroid
- Hydroxysteroid
- 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid
- 7-hydroxysteroid
- Steroid
- Ribonucleoside 3'-phosphate
- Pentose phosphate
- Pentose-5-phosphate
- Beta amino acid or derivatives
- Glycosyl compound
- N-glycosyl compound
- Organic pyrophosphate
- 6-aminopurine
- Pentose monosaccharide
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Purine
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Aminopyrimidine
- Pyrimidine
- Monosaccharide
- N-acyl-amine
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Fatty amide
- N-substituted imidazole
- Imidolactam
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Alkyl phosphate
- Azole
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Cyclic alcohol
- Imidazole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Carbothioic s-ester
- Carboxamide group
- Thiocarboxylic acid ester
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Secondary alcohol
- Thiocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Oxacycle
- Sulfenyl compound
- Azacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Primary amine
- Alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Gas |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | 1.41 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 4.88 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 13.5107 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 6.49 minutes | 32390414 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 512.6 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Long = Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 2682.9 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Lipids = Ascentis Express C18 with (60:40 water:ACN):(90:10 IPA:ACN) and 10mM NH4COOH + 0.1% Formic Acid | 126.0 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_Old = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:(20:80 acetone:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 199.7 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_New = RP Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:(30:70 MeOH:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 173.9 seconds | 40023050 | | RIKEN = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 236.5 seconds | 40023050 | | Eawag_XBridgeC18 = XBridge C18 3.5u 2.1x50 mm with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 475.0 seconds | 40023050 | | BfG_NTS_RP1 =Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm x 150 mm, 3.5 um) with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 635.7 seconds | 40023050 | | HILIC_BDD_2 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN(0.1% formic acid):water(16 mM ammonium formate) | 974.4 seconds | 40023050 | | UniToyama_Atlantis = RP Waters Atlantis T3 (2.1 x 150 mm, 5 um) with ACN:Water and 0.1% Formic Acid | 927.2 seconds | 40023050 | | BDD_C18 = Hypersil Gold 1.9µm C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 619.8 seconds | 40023050 | | UFZ_Phenomenex = Kinetex Core-Shell C18 2.6 um, 3.0 x 100 mm, Phenomenex with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 985.4 seconds | 40023050 | | SNU_RIKEN_POS = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 344.4 seconds | 40023050 | | RPMMFDA = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 343.4 seconds | 40023050 | | MTBLS87 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water and :ammonium carbonate | 407.2 seconds | 40023050 | | KI_GIAR_zic_HILIC_pH2_7 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN:Water and 0.1% FA | 332.4 seconds | 40023050 | | Meister zic-pHILIC pH9.3 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water 5mM NH4Ac pH9.3 and 5mM ammonium acetate in water | 321.5 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesNot Available |
|---|