| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2008-08-14 18:05:41 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:34 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0006890 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA |
|---|
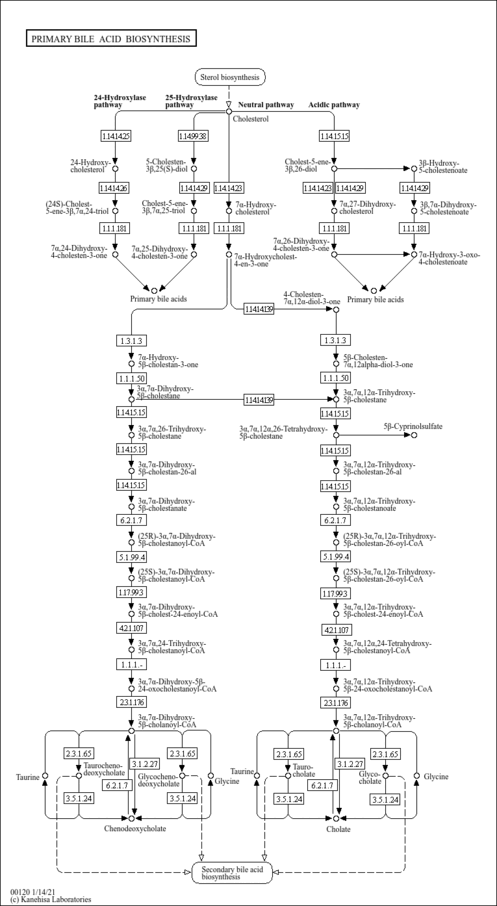
| Description | 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA is an intermediate in bile acid synthesis. Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals. The distinction between different bile acids is minute, depending only on the presence or absence of hydroxyl groups on positions 3, 7, and 12. Bile acids are physiological detergents that facilitate excretion, absorption, and transport of fats and sterols in the intestine and liver. Bile acids are also steroidal amphipathic molecules derived from the catabolism of cholesterol. They modulate bile flow and lipid secretion, are essential for the absorption of dietary fats and vitamins, and have been implicated in the regulation of all the key enzymes involved in cholesterol homeostasis. Bile acids recirculate through the liver, bile ducts, small intestine and portal vein to form an enterohepatic circuit. They exist as anions at physiological pH and, consequently, require a carrier for transport across the membranes of the enterohepatic tissues. The unique detergent properties of bile acids are essential for the digestion and intestinal absorption of hydrophobic nutrients. Bile acids have potent toxic properties (e.g. membrane disruption) and there are a plethora of mechanisms to limit their accumulation in blood and tissues (PMID: 11316487 , 16037564 , 12576301 , 11907135 ). |
|---|
| Structure | [H][C@@]12C[C@H](O)CCC1(C)C1C[C@H](O)C3(C)C(CCC3C1[C@H](O)C2)C(C)CCC(O)C(C)C(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)C(O)C(C)(C)COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N InChI=1S/C48H80N7O21P3S/c1-24(28-8-9-29-36-30(19-34(59)48(28,29)6)47(5)13-11-27(56)17-26(47)18-32(36)58)7-10-31(57)25(2)45(64)80-16-15-50-35(60)12-14-51-43(63)40(62)46(3,4)21-73-79(70,71)76-78(68,69)72-20-33-39(75-77(65,66)67)38(61)44(74-33)55-23-54-37-41(49)52-22-53-42(37)55/h22-34,36,38-40,44,56-59,61-62H,7-21H2,1-6H3,(H,50,60)(H,51,63)(H,68,69)(H,70,71)(H2,49,52,53)(H2,65,66,67)/t24?,25?,26-,27+,28?,29?,30?,31?,32+,33+,34-,36?,38+,39+,40?,44+,47?,48?/m0/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (24R,25R)-3-alpha,7-alpha,12-alpha,24-Tetrahydroxy-5-beta-cholestanoyl-CoA | HMDB | | (24R,25R)-3-alpha,7-alpha,12-alpha,24-Tetrahydroxy-5-beta-cholestanoyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a,24Z-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a,24Z-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha,24-Tetrahydroxy-5beta-cholestanoyl-CoA | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha,24-Tetrahydroxy-5beta-cholestanoyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha,24Zeta-Tetrahydroxy-5beta-cholestanoyl-CoA | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha,24Zeta-Tetrahydroxy-5beta-cholestanoyl-coenzyme A | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C48H80N7O21P3S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 1216.169 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 1215.434082883 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | {[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-2-({[hydroxy({[hydroxy({3-hydroxy-3-[(2-{[2-({3-hydroxy-2-methyl-6-[(5R,7S,9R,16S)-5,9,16-trihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0²,⁷.0¹¹,¹⁵]heptadecan-14-yl]heptanoyl}sulfanyl)ethyl]carbamoyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]-2,2-dimethylpropoxy})phosphoryl]oxy})phosphoryl]oxy}methyl)oxolan-3-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-2-[({hydroxy[hydroxy(3-hydroxy-3-[(2-{[2-({3-hydroxy-2-methyl-6-[(5R,7S,9R,16S)-5,9,16-trihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0²,⁷.0¹¹,¹⁵]heptadecan-14-yl]heptanoyl}sulfanyl)ethyl]carbamoyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]-2,2-dimethylpropoxy)phosphoryl]oxyphosphoryl}oxy)methyl]oxolan-3-yl]oxyphosphonic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]12C[C@H](O)CCC1(C)C1C[C@H](O)C3(C)C(CCC3C1[C@H](O)C2)C(C)CCC(O)C(C)C(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)C(O)C(C)(C)COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C48H80N7O21P3S/c1-24(28-8-9-29-36-30(19-34(59)48(28,29)6)47(5)13-11-27(56)17-26(47)18-32(36)58)7-10-31(57)25(2)45(64)80-16-15-50-35(60)12-14-51-43(63)40(62)46(3,4)21-73-79(70,71)76-78(68,69)72-20-33-39(75-77(65,66)67)38(61)44(74-33)55-23-54-37-41(49)52-22-53-42(37)55/h22-34,36,38-40,44,56-59,61-62H,7-21H2,1-6H3,(H,50,60)(H,51,63)(H,68,69)(H,70,71)(H2,49,52,53)(H2,65,66,67)/t24?,25?,26-,27+,28?,29?,30?,31?,32+,33+,34-,36?,38+,39+,40?,44+,47?,48?/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | PXHZOQNODUPJKC-QVXJXFLKSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as galnacb1-4galb1-4glc- (ganglio series). These are neutral glycosphingolipids in which the root sequence is GalNAcb1-4Galb1-4Glc. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Sphingolipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Glycosphingolipids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | GalNAcb1-4Galb1-4Glc- (Ganglio series) |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Galnacb1-4galb1-4glcb-cer_backbone
- Neuaca2-3galb1-4glcb-cer_backbone
- Glycosyl-n-acylsphingosine
- Oligosaccharide
- N-acylneuraminic acid or derivatives
- N-acylneuraminic acid
- Neuraminic acid
- Fatty acyl glycoside
- N-acyl-alpha-hexosamine
- C-glucuronide
- Alkyl glycoside
- C-glycosyl compound
- Glycosyl compound
- O-glycosyl compound
- Ketal
- Fatty amide
- N-acyl-amine
- Fatty acyl
- Oxane
- Pyran
- Acetamide
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxamide group
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Polyol
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Acetal
- Oxacycle
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Organic oxide
- Primary alcohol
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross Sections| Predictor | Adduct Type | CCS Value (Å2) | Reference |
|---|
| DeepCCS | [M-2H]- | 339.865 | 30932474 | | DeepCCS | [M+Na]+ | 314.249 | 30932474 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesNot Available |
|---|
| MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0019-0900021100-db98da7d8ab78149b774 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-0900033200-4e40e95020ecbab364eb | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-0900010100-bc331afee717427603b9 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00o1-2920542410-30866330296bf943ea51 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-003r-3900221010-7ada8638d3c58ca47b75 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-057i-5900100000-d436b0895a28f04af0aa | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0190000000-e32a88ac11b923b100fb | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03fs-2960602200-504b9e1a2c922b031ef6 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-05r9-6424903800-5b0b1a85c5b0f282ef2a | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014j-0891000000-63c467835708cde6d37f | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-001s-0920000112-3138fb4e2d1a852f31b5 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3a,7a,12a,24-Tetrahydroxy-5b-cholestanoyl-CoA 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0100011900-14a814e67cbe3b021d5c | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|