| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-05-30 20:55:58 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000300 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Uracil |
|---|
| Description | Uracil, also known as U, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidones. Pyrimidones are compounds that contain a pyrimidine ring, which bears a ketone. Pyrimidine is a 6-membered ring consisting of four carbon atoms and two nitrogen centers at the 1- and 3- ring positions. Uracil is a common naturally occurring pyrimidine found in RNA. It base pairs with adenine and is replaced by thymine in DNA. Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in RNA that are represented by the letters A, G, C and U. Methylation of uracil produces thymine. The name "uracil" was coined in 1885 by the German chemist Robert Behrend, who was attempting to synthesize derivatives of uric acid. Originally discovered in 1900, uracil was isolated by hydrolysis of yeast nuclein that was found in bovine thymus and spleen, herring sperm, and wheat germ. Uracil exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to plants to humans. Uracil's use in the body is to help carry out the synthesis of many enzymes necessary for cell function through bonding with riboses and phosphates. Uracil serves as an allosteric regulator and a coenzyme for many important biochemical reactions. Uracil (via the nucleoside uridine) can be phosphorylated by various kinases to produce UMP, UDP and UTP. UDP and UTP regulate carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPSase II) activity in animals. Uracil is also involved in the biosynthesis of polysaccharides and in the transport of sugars containing aldehydes. Within humans, uracil participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, uracil and ribose 1-phosphate can be biosynthesized from uridine; which is mediated by the enzyme uridine phosphorylase 2. In addition, uracil can be converted into dihydrouracil through the action of the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase [NADP(+)]. Uracil is rarely found in DNA, and this may have been an evolutionary change to increase genetic stability. This is because cytosine can deaminate spontaneously to produce uracil through hydrolytic deamination. Therefore, if there were an organism that used uracil in its DNA, the deamination of cytosine (which undergoes base pairing with guanine) would lead to formation of uracil (which would base pair with adenine) during DNA synthesis. Uracil can be used for drug delivery and as a pharmaceutical. When elemental fluorine reacts with uracil, it produces 5-fluorouracil. 5-Fluorouracil is an anticancer drug (antimetabolite) that mimics uracil during the nucleic acid (i.e. RNA) synthesis and transcription process. Because 5-fluorouracil is similar in shape to, but does not undergo the same chemistry as, uracil, the drug inhibits RNA replication enzymes, thereby blocking RNA synthesis and stopping the growth of cancerous cells. | Read more...
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C4H4N2O2/c7-3-1-2-5-4(8)6-3/h1-2H,(H2,5,6,7,8) |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 2,4(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinedione | ChEBI | | 2,4-Dioxopyrimidine | ChEBI | | 2,4-Pyrimidinedione | ChEBI | | U | ChEBI | | Ura | ChEBI | | Urazil | ChEBI | | 2,4-Dihydroxypyrimidine | HMDB | | 2,4-Pyrimidinediol | HMDB | | Hybar X | HMDB | | Pirod | HMDB | | Pyrod | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C4H4N2O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 112.0868 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 112.027277382 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-2,4-dione |
|---|
| Traditional Name | uracil |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 66-22-8 |
|---|
| SMILES | O=C1NC=CC(=O)N1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C4H4N2O2/c7-3-1-2-5-4(8)6-3/h1-2H,(H2,5,6,7,8) |
|---|
| InChI Key | ISAKRJDGNUQOIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidones. Pyrimidones are compounds that contain a pyrimidine ring, which bears a ketone. Pyrimidine is a 6-membered ring consisting of four carbon atoms and two nitrogen centers at the 1- and 3- ring positions. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Diazines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Pyrimidines and pyrimidine derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Pyrimidones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Pyrimidone
- Hydropyrimidine
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Vinylogous amide
- Urea
- Lactam
- Azacycle
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 330 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 3.6 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | -1.07 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Uracil,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)[NH]C1=O | 1525.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)[NH]C1=O | 1532.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)[NH]C1=O | 1880.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)C=C[NH]C1=O | 1447.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)C=C[NH]C1=O | 1487.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)C=C[NH]C1=O | 1857.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)C1=O | 1655.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)C1=O | 1673.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)C1=O | 1697.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)[NH]C1=O | 1793.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)[NH]C1=O | 1753.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)[NH]C1=O | 2007.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)C=C[NH]C1=O | 1658.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)C=C[NH]C1=O | 1724.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C(=O)C=C[NH]C1=O | 1940.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C1=O | 2002.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C1=O | 2095.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Uracil,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C=CC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C1=O | 1915.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-5950000000-18425875415ad150c4fc | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (2 TMS) | splash10-006t-9740000000-e884a4b98e7e9dc75e5f | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil GC-MS (2 TMS) | splash10-052e-7790000000-026cb6beb5cde6a61b80 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-02tc-9200000000-4a57c4e06fd552d6a9bf | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-03xu-9400000000-1c29f070a8135b06f88b | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-5950000000-18425875415ad150c4fc | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-006t-9740000000-e884a4b98e7e9dc75e5f | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-052e-7790000000-026cb6beb5cde6a61b80 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-6940000000-a726178341f6443e60cc | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-03xu-9300000000-6a96f6ce1ef731689107 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Uracil GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-03xu-9400000000-d7ffe72f606f1af3349b | 2014-09-20 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-03di-3900000000-e422eda255a4b6414f86 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-006y-9000000000-130eb5f4414426e03667 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0006-9100000000-c096d08ca715d97cd732 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil EI-B (HITACHI M-60) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-02tc-9200000000-83a0a6ad4fc1b407e570 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil EI-B (HITACHI M-80) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-03xu-9400000000-acd0cfd54af7d6a55283 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-309fe212c929f3c6a930 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-6900000000-55a7de75a40eab61da8b | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-1c3caab26eb7e359db92 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-7494d4e611a73ecb79ea | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-ed4046b040337db620d8 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-ff54f3083ce4ccccfd95 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-6728c1eb6f68b40c09f8 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-309fe212c929f3c6a930 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-6900000000-55a7de75a40eab61da8b | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-1c3caab26eb7e359db92 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-7494d4e611a73ecb79ea | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-ed4046b040337db620d8 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil LC-ESI-QTOF , negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-6728c1eb6f68b40c09f8 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil , negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-a21102c708f8d5eaf262 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-1900000000-0029cbdcaa1377a4d03e | 2015-05-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0229-9400000000-c227e1deb392170cb323 | 2015-05-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-3cf6f9fc3ab6890266ac | 2015-05-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-4900000000-67a3d94ab649e28bda13 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9100000000-bbf50de54fc413b6588e | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Uracil 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-98042b91f1087b0c2563 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Amniotic Fluid
- Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Feces
- Saliva
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - All Tissues
- Placenta
- Prostate
|
|---|
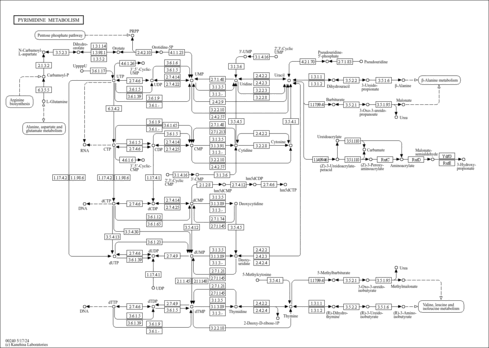
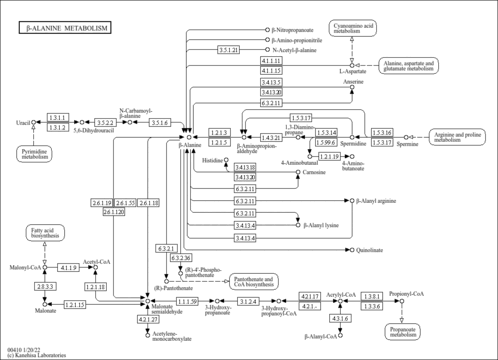
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Amniotic Fluid | Detected and Quantified | 0.87 +/- 0.69 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.17 (0.097-0.26) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.10 +/- 1.02 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | <2 uM | Children (3 months - 6 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.1 +/- 0.2 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 38.89 +/- 12.38 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 7.914-33.918 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.5 (2.37-3.5) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 15.01 +/-4.73 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 7-29 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 8-78 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0-0.8 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0-0.9 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 10.13 +/- 5.43 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0-2.8 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 6.81 +/- 5.09 umol/mmol creatinine | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 12.29 +/- 5.78 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <20.85 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 9.5 (2.6-22.8) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 11.021 +/- 9.32 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.400-3.600 umol/mmol creatinine | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <3 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 3.05 (1.76-4.24) umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 4.99 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0-26 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 8-110 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.25 +/- 0.98 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Canavan disease | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.250 +/- 1.380 uM | Children (3 months - 6 years old) | Not Specified | Uremia | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal Cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | asymptomatic diverticulosis | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Crohns disease | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Ulcerative colitis | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (6 - 18 years old) | Not Specified | Unclassified IBD | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Attachment loss | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Missing teeth | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Periodontal Probing Depth | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 495.881 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 624.657 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Male | Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 12.0 (2.0-22.0) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Argininemia | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 35.0 (20.0-50.0) umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Argininemia | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 265.0 (30.0-500.0) umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 6.00 +/- 4.00 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Hypertension | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 5.00 +/- 4.00 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Cerebral infarction | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 8.00 +/- 13.00 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Malignancy | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 7.00 +/- 6.00 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Liver dysfunction | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 20.24 +/- 7.24 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Canavan disease | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 6.6 +/- 2.5 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Nephropathy | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Bladder cancer | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 38.573 +/- 84.754 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Eosinophilic esophagitis | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 48 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | Molybdenium co-factor deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 321.0904 (290.564-368.576) umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Arginase Deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 144.265 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | Argininemia | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Canavan disease |
|---|
- Tavazzi B, Lazzarino G, Leone P, Amorini AM, Bellia F, Janson CG, Di Pietro V, Ceccarelli L, Donzelli S, Francis JS, Giardina B: Simultaneous high performance liquid chromatographic separation of purines, pyrimidines, N-acetylated amino acids, and dicarboxylic acids for the chemical diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism. Clin Biochem. 2005 Nov;38(11):997-1008. Epub 2005 Sep 1. [PubMed:16139832 ]
| | Uremia |
|---|
- Vanholder R, De Smet R, Glorieux G, Argiles A, Baurmeister U, Brunet P, Clark W, Cohen G, De Deyn PP, Deppisch R, Descamps-Latscha B, Henle T, Jorres A, Lemke HD, Massy ZA, Passlick-Deetjen J, Rodriguez M, Stegmayr B, Stenvinkel P, Tetta C, Wanner C, Zidek W: Review on uremic toxins: classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003 May;63(5):1934-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00924.x. [PubMed:12675874 ]
| | Crohn's disease |
|---|
- Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V: Faecal and Serum Metabolomics in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017 Mar 1;11(3):321-334. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw158. [PubMed:27609529 ]
| | Ulcerative colitis |
|---|
- Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V: Faecal and Serum Metabolomics in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017 Mar 1;11(3):321-334. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw158. [PubMed:27609529 ]
| | Diverticular disease |
|---|
- Tursi A, Mastromarino P, Capobianco D, Elisei W, Miccheli A, Capuani G, Tomassini A, Campagna G, Picchio M, Giorgetti G, Fabiocchi F, Brandimarte G: Assessment of Fecal Microbiota and Fecal Metabolome in Symptomatic Uncomplicated Diverticular Disease of the Colon. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016 Oct;50 Suppl 1:S9-S12. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000626. [PubMed:27622378 ]
| | Attachment loss |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Missing teeth |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Periodontal Probing Depth |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Argininemia |
|---|
- Naylor EW, Cederbaum SD: Urinary pyrimidine excretion in arginase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1981;4(4):207-10. [PubMed:6796772 ]
- Brockstedt M, Smit LM, de Grauw AJ, van der Klei-van Moorsel JM, Jakobs C: A new case of hyperargininaemia: neurological and biochemical findings prior to and during dietary treatment. Eur J Pediatr. 1990 Feb;149(5):341-3. [PubMed:2311630 ]
- G.Frauendienst-Egger, Friedrich K. Trefz (2017). MetaGene: Metabolic & Genetic Information Center (MIC: http://www.metagene.de). METAGENE consortium.
| | Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase Deficiency |
|---|
- G.Frauendienst-Egger, Friedrich K. Trefz (2017). MetaGene: Metabolic & Genetic Information Center (MIC: http://www.metagene.de). METAGENE consortium.
| | Hypertension |
|---|
- Hayashi K, Kidouchi K, Sumi S, Mizokami M, Orito E, Kumada K, Ueda R, Wada Y: Possible prediction of adverse reactions to pyrimidine chemotherapy from urinary pyrimidine levels and a case of asymptomatic adult dihydropyrimidinuria. Clin Cancer Res. 1996 Dec;2(12):1937-41. [PubMed:9816152 ]
| | Cerebral infarction |
|---|
- Hayashi K, Kidouchi K, Sumi S, Mizokami M, Orito E, Kumada K, Ueda R, Wada Y: Possible prediction of adverse reactions to pyrimidine chemotherapy from urinary pyrimidine levels and a case of asymptomatic adult dihydropyrimidinuria. Clin Cancer Res. 1996 Dec;2(12):1937-41. [PubMed:9816152 ]
| | Liver disease |
|---|
- Hayashi K, Kidouchi K, Sumi S, Mizokami M, Orito E, Kumada K, Ueda R, Wada Y: Possible prediction of adverse reactions to pyrimidine chemotherapy from urinary pyrimidine levels and a case of asymptomatic adult dihydropyrimidinuria. Clin Cancer Res. 1996 Dec;2(12):1937-41. [PubMed:9816152 ]
| | Eosinophilic esophagitis |
|---|
- Slae, M., Huynh, H., Wishart, D.S. (2014). Analysis of 30 normal pediatric urine samples via NMR spectroscopy (unpublished work). NA.
| | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Ni Y, Xie G, Jia W: Metabonomics of human colorectal cancer: new approaches for early diagnosis and biomarker discovery. J Proteome Res. 2014 Sep 5;13(9):3857-70. doi: 10.1021/pr500443c. Epub 2014 Aug 14. [PubMed:25105552 ]
- Brown DG, Rao S, Weir TL, O'Malia J, Bazan M, Brown RJ, Ryan EP: Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016 Jun 6;4:11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0151-y. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27275383 ]
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ: Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 25;11(3):e0152126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27015276 ]
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Ahn J, Shi J, Sinha R: Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2089-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131. Epub 2014 Jul 18. [PubMed:25037050 ]
| | Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency |
|---|
- Brockstedt M, Jakobs C, Smit LM, van Gennip AH, Berger R: A new case of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1990;13(1):121-4. [PubMed:2109146 ]
| | Molybdenium co-factor deficiency |
|---|
- Nagappa M, Bindu PS, Taly AB, Sinha S, Bharath RD: Child Neurology: Molybdenum cofactor deficiency. Neurology. 2015 Dec 8;85(23):e175-8. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002194. [PubMed:26644055 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 271900 (Canavan disease)
- 266600 (Crohn's disease)
- 207800 (Argininemia)
- 237300 (Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase Deficiency)
- 145500 (Hypertension)
- 610247 (Eosinophilic esophagitis)
- 114500 (Colorectal cancer)
- 274270 (Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency)
- 252150 (Molybdenium co-factor deficiency)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB03419 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB006426 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00001513 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 1141 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00106 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | URACIL |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 33879 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Uracil |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 258 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 1174 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 17568 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | URA |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000139 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Burckhalter, J. H.; Scarborough, Homer C. The synthesis of uracils as anticonvulsants. Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association (1912-1977) (1955), 44 545-50. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Sweatman BC, Farrant RD, Holmes E, Ghauri FY, Nicholson JK, Lindon JC: 600 MHz 1H-NMR spectroscopy of human cerebrospinal fluid: effects of sample manipulation and assignment of resonances. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1993 Aug;11(8):651-64. [PubMed:8257730 ]
- Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Hofmann U, Schwab M, Seefried S, Marx C, Zanger UM, Eichelbaum M, Murdter TE: Sensitive method for the quantification of urinary pyrimidine metabolites in healthy adults by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2003 Jul 5;791(1-2):371-80. [PubMed:12798197 ]
- van Lenthe H, van Kuilenburg AB, Ito T, Bootsma AH, van Cruchten A, Wada Y, van Gennip AH: Defects in pyrimidine degradation identified by HPLC-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry of urine specimens or urine-soaked filter paper strips. Clin Chem. 2000 Dec;46(12):1916-22. [PubMed:11106323 ]
- Jiang H, Jiang J, Hu P, Hu Y: Measurement of endogenous uracil and dihydrouracil in plasma and urine of normal subjects by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002 Mar 25;769(1):169-76. [PubMed:11936689 ]
- Allgayer H, Kolb M, Stuber V, Kruis W: Effects of bile acids on base hydroxylation in a model of human colonic mucosal DNA. Cancer Detect Prev. 2002;26(1):85-9. [PubMed:12088208 ]
- Jakobs C, Sweetman L, Nyhan WL, Gruenke L, Craig JC, Wadman SK: Stable isotope dilution analysis of orotic acid and uracil in amniotic fluid. Clin Chim Acta. 1984 Nov 15;143(2):123-33. [PubMed:6391739 ]
- van Kuilenburg AB, van Lenthe H, Loffler M, van Gennip AH: Analysis of pyrimidine synthesis "de novo" intermediates in urine and dried urine filter- paper strips with HPLC-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2004 Nov;50(11):2117-24. Epub 2004 Sep 16. [PubMed:15375016 ]
- Spector T, Harrington JA, Porter DJ: 5-Ethynyluracil (776C85): inactivation of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Dec 14;46(12):2243-8. [PubMed:8274158 ]
- Mani S, Kugler JW, Sciortino DF, Garcia JC, Ansari RH, Humerickhouse R, Michelassi F, Posner MC, Shulman KL, Schilsky RL, List M, Vokes EE, Benner S: Phase II trial of uracil/tegafur (UFT) plus leucovorin in patients with advanced pancreatic carcinoma: a University of Chicago phase II consortium study. Ann Oncol. 1998 Sep;9(9):1035-7. [PubMed:9818081 ]
- Tomita T, Tajima T, Ishibashi M, Tagaya N, Aoki H, Itoh S, Kadowaki A, Kogure H, Tajima Y: [Study on the concentrations of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), tegafur (ET) and uracil in bile: comparison of UFT or FT]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1989 Dec;16(12):3755-62. [PubMed:2512859 ]
- Duthie SJ, McMillan P: Uracil misincorporation in human DNA detected using single cell gel electrophoresis. Carcinogenesis. 1997 Sep;18(9):1709-14. [PubMed:9328165 ]
- Bayer AS, Galpin JE, Theofilopoulos AN, Guze LB: Neurological disease associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonitis: demonstration of viable Mycoplasma pneumoniae in cerebrospinal fluid and blood by radioisotopic and immunofluorescent tissue culture techniques. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jan;94(1):15-20. [PubMed:6778283 ]
- Feliu J, Mel R, Borrega P, Lopez Gomez L, Escudero P, Dorta J, Castro J, Vazquez-Estevez SE, Bolanos M, Espinosa E, Gonzalez Baron M: Phase II study of a fixed dose-rate infusion of gemcitabine associated with uracil/tegafur in advanced carcinoma of the pancreas. Ann Oncol. 2002 Nov;13(11):1756-62. [PubMed:12419748 ]
- Mashiyama ST, Courtemanche C, Elson-Schwab I, Crott J, Lee BL, Ong CN, Fenech M, Ames BN: Uracil in DNA, determined by an improved assay, is increased when deoxynucleosides are added to folate-deficient cultured human lymphocytes. Anal Biochem. 2004 Jul 1;330(1):58-69. [PubMed:15183762 ]
- DeAngelis LM, Kreis W, Chan K, Dantis E, Akerman S: Pharmacokinetics of ara-C and ara-U in plasma and CSF after high-dose administration of cytosine arabinoside. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1992;29(3):173-7. [PubMed:1733548 ]
- Stover PJ, Garza C: Bringing individuality to public health recommendations. J Nutr. 2002 Aug;132(8 Suppl):2476S-2480S. [PubMed:12163715 ]
- Duthie SJ, Hawdon A: DNA instability (strand breakage, uracil misincorporation, and defective repair) is increased by folic acid depletion in human lymphocytes in vitro. FASEB J. 1998 Nov;12(14):1491-7. [PubMed:9806758 ]
- Hanaue H, Kurosawa T, Kitano Y, Miyakawa S, Nemoto A, Yamamoto H, Asagoe T, Takada T, Yasuda H, Shikata J: Anticancer drug distribution in lymph and blood during adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery for gastric carcinoma. A study with a combined preparation of 1-(2-tetrahydrofuryl)-5-fluorouracil and uracil. Cancer. 1987 May 1;59(9):1571-6. [PubMed:3103905 ]
- Elshenawy S, Pinney SE, Stuart T, Doulias PT, Zura G, Parry S, Elovitz MA, Bennett MJ, Bansal A, Strauss JF 3rd, Ischiropoulos H, Simmons RA: The Metabolomic Signature of the Placenta in Spontaneous Preterm Birth. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3). pii: ijms21031043. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031043. [PubMed:32033212 ]
| Show more...
|---|