| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:14:52 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000491 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0001962
- HMDB0002254
- HMDB0003736
- HMDB0004750
- HMDB00491
- HMDB01962
- HMDB02254
- HMDB03736
- HMDB04750
| Show more accession numbers
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid |
|---|
| Description | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid (CAS: 1460-34-0) is an abnormal metabolite that arises from the incomplete breakdown of branched-chain amino acids. 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid is a neurotoxin, an acidogen, and a metabotoxin. A neurotoxin causes damage to nerve cells and nerve tissues. An acidogen is an acidic compound that induces acidosis, which has multiple adverse effects on many organ systems. A metabotoxin is an endogenously produced metabolite that causes adverse health effects at chronically high levels. Chronically high levels of 3-methyl-2-oxovaleric acid are associated with maple syrup urine disease. MSUD is a metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC), leading to a buildup of the branched-chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) and their toxic by-products (ketoacids) in the blood and urine. The symptoms of MSUD often show in infancy and lead to severe brain damage if untreated. MSUD may also present later depending on the severity of the disease. If left untreated in older individuals, during times of metabolic crisis, symptoms of the condition include uncharacteristically inappropriate, extreme, or erratic behaviour and moods, hallucinations, anorexia, weight loss, anemia, diarrhea, vomiting, dehydration, lethargy, oscillating hypertonia and hypotonia, ataxia, seizures, hypoglycemia, ketoacidosis, opisthotonus, pancreatitis, rapid neurological decline, and coma. In maple syrup urine disease, the brain concentration of branched-chain ketoacids can increase 10- to 20-fold. This leads to a depletion of glutamate and a consequent reduction in the concentration of brain glutamine, aspartate, alanine, and other amino acids. The result is a compromise of energy metabolism because of a failure of the malate-aspartate shuttle and a diminished rate of protein synthesis (PMID: 15930465 ). 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid is a keto-acid, which is a subclass of organic acids. Abnormally high levels of organic acids in the blood (organic acidemia), urine (organic aciduria), the brain, and other tissues lead to general metabolic acidosis. Acidosis typically occurs when arterial pH falls below 7.35. In infants with acidosis, the initial symptoms include poor feeding, vomiting, loss of appetite, weak muscle tone (hypotonia), and lack of energy (lethargy). These can progress to heart, liver, and kidney abnormalities, seizures, coma, and possibly death. These are also the characteristic symptoms of untreated MSUD. Many affected children with organic acidemias experience intellectual disability or delayed development. | Read more...
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C6H10O3/c1-3-4(2)5(7)6(8)9/h4H,3H2,1-2H3,(H,8,9)/t4-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (3S)-2-oxo-3-Methyl-N-valeric acid | ChEBI | | (3S)-3-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid | ChEBI | | (S)-2-oxo-3-Methylpentanoic acid | ChEBI | | (S)-3-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid | ChEBI | | (S)-OMV | ChEBI | | (3S)-3-Methyl-2-oxopentanoate | Kegg | | (3S)-2-oxo-3-Methyl-N-valerate | Generator | | (S)-2-oxo-3-Methylpentanoate | Generator | | (S)-3-Methyl-2-oxopentanoate | ChEBI | | 3S-Methyl-2-oxo-pentanoate | Generator | | 2-Oxo-3-methyl-n-valeric acid | HMDB | | 2-Oxo-3-methylpentanoic acid | HMDB | | 2-Oxo-3-methylvaleric acid | HMDB | | 2-Oxoisoleucine | HMDB | | 3-Methyl-2-ketovaleric acid | HMDB | | 3-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid | HMDB | | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid | HMDB | | L-2-Keto-3-Methylvalerate | HMDB | | L-2-keto-3-Methylvaleric acid | HMDB | | L-alpha-keto-beta-Methylvaleric acid | HMDB | | L-α-keto-β-Methylvaleric acid | HMDB | | alpha-keto-beta-Methylvaleric acid | HMDB | | alpha-Oxo-beta-methyl-n-valeric acid | HMDB | | alpha-Oxo-beta-methylvaleric acid | HMDB | | alpha-keto-beta-Methyl-n-valeric acid | HMDB | | α-keto-β-Methylvaleric acid | HMDB | | α-Oxo-β-methyl-n-valeric acid | HMDB | | α-Oxo-β-methylvaleric acid | HMDB | | α-keto-β-Methyl-n-valeric acid | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H10O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 130.1418 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 130.062994186 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (3S)-3-methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (S)-omv |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 24809-08-3 |
|---|
| SMILES | CC[C@H](C)C(=O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H10O3/c1-3-4(2)5(7)6(8)9/h4H,3H2,1-2H3,(H,8,9)/t4-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | JVQYSWDUAOAHFM-BYPYZUCNSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as short-chain keto acids and derivatives. These are keto acids with an alkyl chain the contains less than 6 carbon atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Short-chain keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Short-chain keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Branched fatty acid
- Methyl-branched fatty acid
- Short-chain keto acid
- Alpha-keto acid
- Fatty acyl
- Alpha-hydroxy ketone
- Ketone
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 915.5 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | CC[C@H](C)C(=O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1150.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | CCC(C)=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1205.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | CCC(C)=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1305.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | CCC(C)=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1306.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | CCC(C)=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1277.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC[C@H](C)C(=O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1366.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CCC(C)=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1464.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CCC(C)=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1739.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CCC(C)=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1726.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CCC(C)=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1618.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (3 TMS) | splash10-000i-9610000000-d2ffd4c2796688c555ee | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (3 TMS) | splash10-000i-9720000000-9cbc934e100bedd87f17 | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-000i-9720000000-5acbdc73aee24c023763 | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-000i-6930000000-8c2cf1d8df538010611b | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-000i-6930000000-7bef6751c4c607393e5e | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0hg9-4950000000-3e1c700a6f553bf63afb | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-000i-9610000000-d2ffd4c2796688c555ee | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-000i-9720000000-9cbc934e100bedd87f17 | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-000i-9720000000-5acbdc73aee24c023763 | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-000i-6930000000-8c2cf1d8df538010611b | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-056r-9100000000-b8f5074d17649d2ecf26 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-000w-9300000000-0a6ff60455403c38be39 | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0002-9000000000-7ee6d2fb63c6ea4cccfa | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-002b-9000000000-47d18dff23b741029581 | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid LC-ESI-ITFT , negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-ae9da2a9acfa56fc6091 | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid LC-ESI-IT , negative-QTOF | splash10-004r-5900000000-a3f740a5c859439255be | 2020-09-08 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-08gr-8900000000-4655fc2c3f2400debce5 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4r-9100000000-815187e3b65ba4681518 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-5336f451fc038f8f52e0 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004r-5900000000-ac576644eaaed7403309 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-01ri-9600000000-665ad7969f567554366d | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0aor-9000000000-5ddf098628cacea63000 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-b869f38a64c0c2b97fca | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-7900000000-fd047f4f444bcf29d644 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-9d9f015d81ffe62b835b | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-08gr-9600000000-653f0f404b417cca473f | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-ec479cb60b6749261d76 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-95cfabed6b44084d9111 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2020-09-08 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2020-09-08 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Membrane
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Feces
- Saliva
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
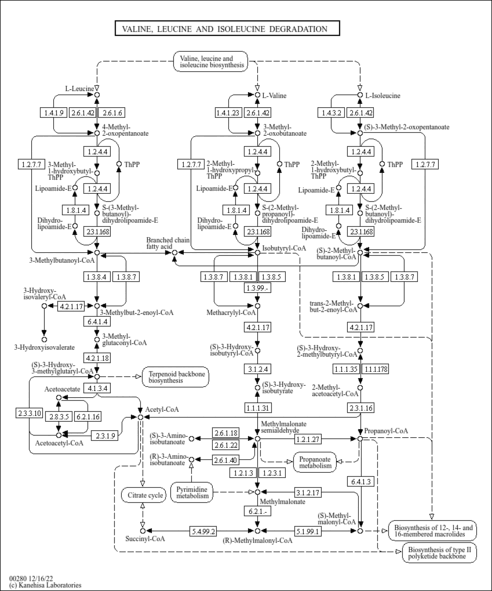
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 18.0 (8.0-31.0) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 22.7 +/- 4.6 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 2.0 +/- 2.0 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0-7 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.55-0.95 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 6.005 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.53-0.88 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.2 (0.4-4.8) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.3 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.24 (0.11 - 0.55) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.54 (0.12 - 1.42) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 368 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Maple syrup urine disease | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 142.0 +/- 9.0 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 101 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Maple syrup urine disease | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal Cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Attachment loss | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Missing teeth | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Periodontal Probing Depth | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Prosthesis/Missing teeth | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Cardiosvacular risk | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 4.333 +/- 3.83 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Eosinophilic esophagitis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 209.0 +/- 35.0 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Bladder cancer | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Maple syrup urine disease |
|---|
- Schadewaldt P, Hammen HW, Ott AC, Wendel U: Renal clearance of branched-chain L-amino and 2-oxo acids in maple syrup urine disease. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1999 Aug;22(6):706-22. [PubMed:10472531 ]
- Wendel, U., Becker, K., Przyrembel, H. et al. (1980). Peritoneal dialysis in maple-syrup-urine disease: Studies on branched-chain amino and keto acids. Eur J Pediatr (1980) 134: 57. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442404. Eur J Pediatr.
| | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Brown DG, Rao S, Weir TL, O'Malia J, Bazan M, Brown RJ, Ryan EP: Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016 Jun 6;4:11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0151-y. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27275383 ]
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ: Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 25;11(3):e0152126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27015276 ]
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Ahn J, Shi J, Sinha R: Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2089-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131. Epub 2014 Jul 18. [PubMed:25037050 ]
| | Attachment loss |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Missing teeth |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Periodontal Probing Depth |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Prosthesis/Missing teeth |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Eosinophilic esophagitis |
|---|
- Slae, M., Huynh, H., Wishart, D.S. (2014). Analysis of 30 normal pediatric urine samples via NMR spectroscopy (unpublished work). NA.
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 248600 (Maple syrup urine disease)
- 114500 (Colorectal cancer)
- 610247 (Eosinophilic esophagitis)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB030164 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 388419 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00671 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | 2-KETO-3-METHYL-VALERATE |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 5478 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 439286 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 15614 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | Not Available |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000175 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Kondo, Shigeo; Sudo, Tetsuji; Ogiwara, Mitsuo; Takeuchi, Hiroshi. a-Oxo-b-methyl-n-valeric acid and its salts. Jpn. Kokai Tokkyo Koho (1979), 3 pp. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Wendel U, Even G, Langenbeck U, Schadewaldt P, Hummel W: Determination of (S)- and (R)-2-oxo-3-methylvaleric acid in plasma of patients with maple syrup urine disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1992 Jun 15;208(1-2):85-91. [PubMed:1638756 ]
- Przyrembel H, Bremer HJ, Duran M, Bruinvis L, Ketting D, Wadman SK, Baumgartner R, Irle U, Bachmann C: Propionyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency with overflow of metabolites of isoleucine catabolism at all levels. Eur J Pediatr. 1979 Jan 18;130(1):1-14. [PubMed:759179 ]
- Yudkoff M, Daikhin Y, Nissim I, Horyn O, Luhovyy B, Lazarow A, Nissim I: Brain amino acid requirements and toxicity: the example of leucine. J Nutr. 2005 Jun;135(6 Suppl):1531S-8S. [PubMed:15930465 ]
- Elshenawy S, Pinney SE, Stuart T, Doulias PT, Zura G, Parry S, Elovitz MA, Bennett MJ, Bansal A, Strauss JF 3rd, Ischiropoulos H, Simmons RA: The Metabolomic Signature of the Placenta in Spontaneous Preterm Birth. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3). pii: ijms21031043. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031043. [PubMed:32033212 ]
|
|---|