| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:04 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000601 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0003873
- HMDB00601
- HMDB03873
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Coprocholic acid |
|---|
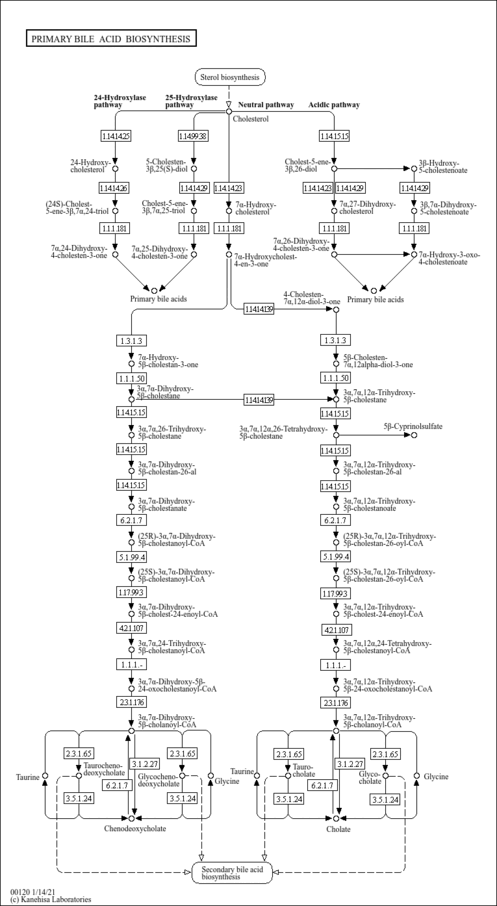
| Description | Coprocholic acid, also called 3α,7α,12α-Trihydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-oic acid, is a bile acid. Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals. The distinction between different bile acids is minute, depending only on the presence or absence of hydroxyl groups on positions 3, 7, and 12. Bile acids are physiological detergents that facilitate excretion, absorption, and transport of fats and sterols in the intestine and liver. Bile acids are also steroidal amphipathic molecules derived from the catabolism of cholesterol. They modulate bile flow and lipid secretion, are essential for the absorption of dietary fats and vitamins, and have been implicated in the regulation of all the key enzymes involved in cholesterol homeostasis. Bile acids recirculate through the liver, bile ducts, small intestine, and the portal vein to form an enterohepatic circuit. They exist as anions at physiological pH, and consequently require a carrier for transport across the membranes of the enterohepatic tissues. The unique detergent properties of bile acids are essential for the digestion and intestinal absorption of hydrophobic nutrients. Bile acids have potent toxic properties (e.g. membrane disruption) and there are a plethora of mechanisms to limit their accumulation in blood and tissues (PMID: 11316487 , 16037564 , 12576301 , 11907135 ). |
|---|
| Structure | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])C[C@H](O)[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCCC(C)C(O)=O InChI=1S/C27H46O5/c1-15(6-5-7-16(2)25(31)32)19-8-9-20-24-21(14-23(30)27(19,20)4)26(3)11-10-18(28)12-17(26)13-22(24)29/h15-24,28-30H,5-14H2,1-4H3,(H,31,32)/t15-,16?,17+,18-,19-,20+,21+,22-,23+,24+,26+,27-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (3alpha,5beta,7alpha,12alpha)-3,7,12-Trihydroxycholestan-26-Oic acid | ChEBI | | 3,7,12-Trihydroxycholestan-26-Oic acid | ChEBI | | (3a,5b,7a,12a)-3,7,12-Trihydroxycholestan-26-Oate | Generator | | (3a,5b,7a,12a)-3,7,12-Trihydroxycholestan-26-Oic acid | Generator | | (3alpha,5beta,7alpha,12alpha)-3,7,12-Trihydroxycholestan-26-Oate | Generator | | (3Α,5β,7α,12α)-3,7,12-trihydroxycholestan-26-Oate | Generator | | (3Α,5β,7α,12α)-3,7,12-trihydroxycholestan-26-Oic acid | Generator | | 3,7,12-Trihydroxycholestan-26-Oate | Generator | | Coprocholate | Generator | | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-(6ci,7ci,8ci)5b-cholestan-26-Oate | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-(6ci,7ci,8ci)5b-cholestan-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholestan-26-Oate | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholestan-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxycoprostanate | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxycoprostanic acid | HMDB | | 5b-Cholestane-3a,7a,12a-triol-26-Oate | HMDB | | 5b-Cholestane-3a,7a,12a-triol-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha-Trihydroxy-5-beta-cholestan-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3,7,12-Trihydroxycholestan-26-Oic acid, (25R)-isomer | HMDB | | 3,7,12-Trihydroxycholestan-26-Oic acid, (25S)-isomer | HMDB | | 3Α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3Α,7α,12α-trihydroxycoprostanic acid | HMDB | | 5Β-cholestane-3α,7α,12α-triol-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-Trihydroxy-5beta-cholestan-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-Trihydroxycoprostanic acid | HMDB | | 5beta-Cholestane-3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-triol-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | Trihydroxycoprostanic acid | HMDB | | Trihydroxycoprostanoic acid | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholestanoic acid | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholestanoate | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-Trihydroxy-5beta-cholestanoate | HMDB | | 3Α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholestanoate | HMDB | | 3Α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholestanoic acid | HMDB | | Coprocholic acid | HMDB, ChEBI |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C27H46O5 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 450.6511 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 450.334524582 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (6R)-2-methyl-6-[(1S,2S,5R,7S,9R,10R,11S,14R,15R,16S)-5,9,16-trihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadecan-14-yl]heptanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (6R)-2-methyl-6-[(1S,2S,5R,7S,9R,10R,11S,14R,15R,16S)-5,9,16-trihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadecan-14-yl]heptanoic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 547-98-8 |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])C[C@H](O)[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCCC(C)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C27H46O5/c1-15(6-5-7-16(2)25(31)32)19-8-9-20-24-21(14-23(30)27(19,20)4)26(3)11-10-18(28)12-17(26)13-22(24)29/h15-24,28-30H,5-14H2,1-4H3,(H,31,32)/t15-,16?,17+,18-,19-,20+,21+,22-,23+,24+,26+,27-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | CNWPIIOQKZNXBB-VCVMUKOKSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as trihydroxy bile acids, alcohols and derivatives. These are prenol lipids structurally characterized by a bile acid or alcohol which bears three hydroxyl groups. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Steroids and steroid derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Bile acids, alcohols and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Trihydroxy bile acids, alcohols and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Trihydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- Steroid acid
- 3-hydroxysteroid
- 12-hydroxysteroid
- 7-hydroxysteroid
- 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid
- Hydroxysteroid
- Medium-chain fatty acid
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Fatty acid
- Cyclic alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Polyol
- Organooxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic homopolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homopolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Coprocholic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3626.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O | 3699.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,1TMS,isomer #3 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O | 3688.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,1TMS,isomer #4 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3619.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3572.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3564.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3503.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #4 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O | 3588.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #5 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3576.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TMS,isomer #6 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3580.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3520.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #2 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3508.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #3 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3491.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,3TMS,isomer #4 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3508.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,4TMS,isomer #1 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3499.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3836.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O | 3909.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O | 3898.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3872.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3990.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3980.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3964.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O | 4016.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4061.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4046.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 4171.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4183.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4158.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Coprocholic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]21C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1C[C@H]3O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4213.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0a4i-0353900000-c3bc744526d90b133841 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0udi-1341349000-6c72d8109d5d5eae56d4 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_6) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_3_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TMS_4_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_2_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00lr-0001900000-852d3949fa0da999fbb4 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-015i-0007900000-7eea489d1d7efa89ad83 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-1209400000-32cc970b446d3852e318 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0000900000-7e444665cccf50f6f849 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-001s-0003900000-1b58b94657c3cc05dac8 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-052r-8008900000-3cc12b0a94eafaef10e5 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0uyi-1003900000-5c888251913ae8a80b47 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00kr-4298800000-c11d607bba9f2dc3c53b | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9542000000-bd6635a22cb471b48c15 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0000900000-a004816f1a3eaa6588ef | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0001900000-21ca99c0ac4af23573b3 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coprocholic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-2023900000-84c3d77a80ad34457a20 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Disease References | | Infantile Refsum's disease |
|---|
- Poll-The BT, Saudubray JM, Ogier H, Schutgens RB, Wanders RJ, Schrakamp G, van den Bosch H, Trijbels JM, Poulos A, Moser HW, et al.: Infantile Refsum's disease: biochemical findings suggesting multiple peroxisomal dysfunction. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1986;9(2):169-74. [PubMed:2427795 ]
| | Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata |
|---|
- Baumgartner MR, Poll-The BT, Verhoeven NM, Jakobs C, Espeel M, Roels F, Rabier D, Levade T, Rolland MO, Martinez M, Wanders RJ, Saudubray JM: Clinical approach to inherited peroxisomal disorders: a series of 27 patients. Ann Neurol. 1998 Nov;44(5):720-30. [PubMed:9818927 ]
| | Peroxisomal biogenesis defect |
|---|
- Baumgartner MR, Poll-The BT, Verhoeven NM, Jakobs C, Espeel M, Roels F, Rabier D, Levade T, Rolland MO, Martinez M, Wanders RJ, Saudubray JM: Clinical approach to inherited peroxisomal disorders: a series of 27 patients. Ann Neurol. 1998 Nov;44(5):720-30. [PubMed:9818927 ]
| | Refsum's disease |
|---|
- Poll-The BT, Saudubray JM, Ogier H, Schutgens RB, Wanders RJ, Schrakamp G, van den Bosch H, Trijbels JM, Poulos A, Moser HW, et al.: Infantile Refsum's disease: biochemical findings suggesting multiple peroxisomal dysfunction. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1986;9(2):169-74. [PubMed:2427795 ]
| | D-Bifunctional protein deficiency |
|---|
- Rizzo C, Boenzi S, Wanders RJ, Duran M, Caruso U, Dionisi-Vici C: Characteristic acylcarnitine profiles in inherited defects of peroxisome biogenesis: a novel tool for screening diagnosis using tandem mass spectrometry. Pediatr Res. 2003 Jun;53(6):1013-8. doi: 10.1203/01.PDR.0000064902.59052.0F. Epub 2003 Mar 19. [PubMed:12646728 ]
|
|
|---|