| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-05-22 15:12:34 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:16:32 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0003125 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0006491
- HMDB03125
- HMDB06491
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Hydrogen peroxide |
|---|
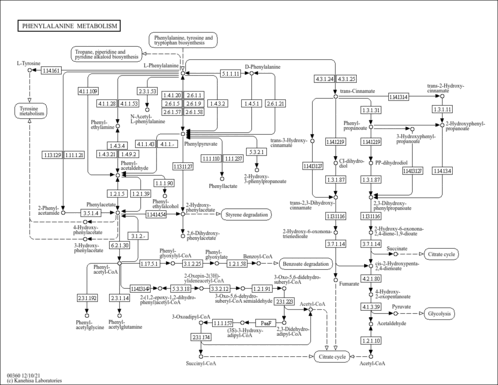
| Description | Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a very pale blue liquid that appears colourless in a dilute solution. H2O2 is slightly more viscous than water and is a weak acid. H2O2 is unstable and slowly decomposes in the presence of light. It has strong oxidizing properties and is, therefore, a powerful bleaching agent that is mostly used for bleaching paper. H2O2 has also found use as a disinfectant and as an oxidizer. H2O2 in the form of carbamide peroxide is widely used for tooth whitening (bleaching), both in professionally- and in self-administered products. H2O2 is a well-documented component of living cells and is a normal metabolite of oxygen in the aerobic metabolism of cells and tissues. A total of 31 human cellular H2O2 generating enzymes has been identified so far (PMID: 25843657 ). H2O2 plays important roles in host defence and oxidative biosynthetic reactions. At high levels (>100 nM) H2O2 is toxic to most cells due to its ability to non-specifically oxidize proteins, membranes and DNA, leading to general cellular damage and dysfunction. However, at low levels (<10 nM), H2O2 functions as a signalling agent, particularly in higher organisms. In plants, H2O2 plays a role in signalling to cause cell shape changes such as stomatal closure and root growth. As a messenger molecule in vertebrates, H2O2 diffuses through cells and tissues to initiate cell shape changes, to drive vascular remodelling, and to activate cell proliferation and recruitment of immune cells. H2O2 also plays a role in redox sensing, signalling, and redox regulation (PMID: 28110218 ). This is normally done through molecular redox “switches” such as thiol-containing proteins. The production and decomposition of H2O2 are tightly regulated (PMID: 17434122 ). In humans, H2O2 can be generated in response to various stimuli, including cytokines and growth factors. H2O2 is degraded by several enzymes including catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD), both of which play important roles in keeping the amount of H2O2 in the body below toxic levels. H2O2 also appears to play a role in vitiligo. Vitiligo is a skin pigment disorder leading to patchy skin colour, especially among dark-skinned individuals. Patients with vitiligo have low catalase levels in their skin, leading to higher levels of H2O2. High levels of H2O2 damage the epidermal melanocytes, leading to a loss of pigment (PMID: 10393521 ). Accumulating evidence suggests that hydrogen peroxide H2O2 plays an important role in cancer development. Experimental data have shown that cancer cells produce high amounts of H2O2. An increase in the cellular levels of H2O2 has been linked to several key alterations in cancer, including DNA changes, cell proliferation, apoptosis resistance, metastasis, angiogenesis and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) activation (PMID: 17150302 , 17335854 , 16677071 , 16607324 , 16514169 ). H2O2 is found in most cells, tissues, and biofluids. H2O2 levels in the urine can be significantly increased with the consumption of coffee and other polyphenolic-containing beverages (wine, tea) (PMID: 12419961 ). In particular, roasted coffee has high levels of 1,2,4-benzenetriol which can, on its own, lead to the production of H2O2. Normal levels of urinary H2O2 in non-coffee drinkers or fasted subjects are between 0.5-3 uM/mM creatinine whereas, for those who drink coffee, the levels are between 3-10 uM/mM creatinine (PMID: 12419961 ). It is thought that H2O2 in urine could act as an antibacterial agent and that H2O2 is involved in the regulation of glomerular function (PMID: 10766414 ). |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| [OH(OH)] | ChEBI | | Dihydrogen dioxide | ChEBI | | H2O2 | ChEBI | | HOOH | ChEBI | | Oxydol | ChEBI | | Perhydrol | ChEBI | | Oxyfull | Kegg | | Adeka super el | HMDB | | Albone | HMDB | | Albone 35 | HMDB | | Albone DS | HMDB | | Anti-keim 50 | HMDB | | Asepticper | HMDB | | Baquashock | HMDB | | CIX | HMDB | | Clarigel gold | HMDB | | Crestal whitestrips | HMDB | | Crystacide | HMDB | | Dentasept | HMDB | | Deslime LP | HMDB | | Hioxyl | HMDB | | Hipox | HMDB | | Hybrite | HMDB | | Hydrogen dioxide | HMDB | | Inhibine | HMDB | | Lase peroxide | HMDB | | Lensan a | HMDB | | Magic bleaching | HMDB | | Metrokur | HMDB | | Mirasept | HMDB | | Nite white excel 2 | HMDB | | Odosat D | HMDB | | Opalescence xtra | HMDB | | Oxigenal | HMDB | | Oxysept | HMDB | | Oxysept I | HMDB | | Pegasyl | HMDB | | Perone | HMDB | | Peroxaan | HMDB | | Peroxclean | HMDB | | Quasar brite | HMDB | | Select bleach | HMDB | | Superoxol | HMDB | | T-Stuff | HMDB | | Whiteness HP | HMDB | | Whitespeed | HMDB | | Xtra white | HMDB | | Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) | HMDB | | Hydroperoxide | HMDB | | Peroxide, hydrogen | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | H2O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 34.0147 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 34.005479308 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | peroxol |
|---|
| Traditional Name | hydrogen peroxide |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 7722-84-1 |
|---|
| SMILES | OO |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/H2O2/c1-2/h1-2H |
|---|
| InChI Key | MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as homogeneous other non-metal compounds. These are inorganic non-metallic compounds in which the largest atom belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds |
|---|
| Class | Homogeneous other non-metal compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Homogeneous other non-metal compounds |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | Not Available |
|---|
| Substituents | - Homogeneous other non metal
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Not Available |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Not Available | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Liquid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | -0.43 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 1000 mg/mL at 25 °C | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross Sections| Predictor | Adduct Type | CCS Value (Å2) | Reference |
|---|
| DeepCCS | [M+H]+ | 109.478 | 30932474 | | DeepCCS | [M-H]- | 107.747 | 30932474 | | DeepCCS | [M-2H]- | 142.886 | 30932474 | | DeepCCS | [M+Na]+ | 116.212 | 30932474 |
Predicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 9.102 minutes | 33406817 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 290.2 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Long = Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 972.9 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Lipids = Ascentis Express C18 with (60:40 water:ACN):(90:10 IPA:ACN) and 10mM NH4COOH + 0.1% Formic Acid | 434.2 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_Old = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:(20:80 acetone:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 156.1 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_New = RP Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:(30:70 MeOH:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 347.9 seconds | 40023050 | | RIKEN = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 210.2 seconds | 40023050 | | Eawag_XBridgeC18 = XBridge C18 3.5u 2.1x50 mm with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 315.8 seconds | 40023050 | | BfG_NTS_RP1 =Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm x 150 mm, 3.5 um) with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 386.0 seconds | 40023050 | | HILIC_BDD_2 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN(0.1% formic acid):water(16 mM ammonium formate) | 655.9 seconds | 40023050 | | UniToyama_Atlantis = RP Waters Atlantis T3 (2.1 x 150 mm, 5 um) with ACN:Water and 0.1% Formic Acid | 675.0 seconds | 40023050 | | BDD_C18 = Hypersil Gold 1.9µm C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 121.9 seconds | 40023050 | | UFZ_Phenomenex = Kinetex Core-Shell C18 2.6 um, 3.0 x 100 mm, Phenomenex with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 822.6 seconds | 40023050 | | SNU_RIKEN_POS = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 281.8 seconds | 40023050 | | RPMMFDA = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 397.7 seconds | 40023050 | | MTBLS87 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water and :ammonium carbonate | 756.9 seconds | 40023050 | | KI_GIAR_zic_HILIC_pH2_7 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN:Water and 0.1% FA | 313.1 seconds | 40023050 | | Meister zic-pHILIC pH9.3 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water 5mM NH4Ac pH9.3 and 5mM ammonium acetate in water | 359.4 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized| Metabolite | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Hydrogen peroxide | OO | 1295.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Hydrogen peroxide | OO | 452.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Hydrogen peroxide | OO | 382.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|
| General References | - Lopez-Lazaro M: Dual role of hydrogen peroxide in cancer: possible relevance to cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Cancer Lett. 2007 Jul 8;252(1):1-8. Epub 2006 Dec 5. [PubMed:17150302 ]
- Schallreuter KU, Elwary S: Hydrogen peroxide regulates the cholinergic signal in a concentration dependent manner. Life Sci. 2007 May 30;80(24-25):2221-6. Epub 2007 Jan 25. [PubMed:17335854 ]
- Stone JR, Yang S: Hydrogen peroxide: a signaling messenger. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006 Mar-Apr;8(3-4):243-70. [PubMed:16677071 ]
- Tredwin CJ, Naik S, Lewis NJ, Scully C: Hydrogen peroxide tooth-whitening (bleaching) products: review of adverse effects and safety issues. Br Dent J. 2006 Apr 8;200(7):371-6. [PubMed:16607324 ]
- Ardanaz N, Pagano PJ: Hydrogen peroxide as a paracrine vascular mediator: regulation and signaling leading to dysfunction. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2006 Mar;231(3):237-51. [PubMed:16514169 ]
- Go YM, Chandler JD, Jones DP: The cysteine proteome. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Jul;84:227-245. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.03.022. Epub 2015 Apr 3. [PubMed:25843657 ]
- Sies H: Hydrogen peroxide as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:613-619. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.035. Epub 2017 Jan 5. [PubMed:28110218 ]
- Veal EA, Day AM, Morgan BA: Hydrogen peroxide sensing and signaling. Mol Cell. 2007 Apr 13;26(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.03.016. [PubMed:17434122 ]
- Schallreuter KU: Successful treatment of oxidative stress in vitiligo. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 1999 May-Jun;12(3):132-8. doi: 10.1159/000029867. [PubMed:10393521 ]
- Hiramoto K, Kida T, Kikugawa K: Increased urinary hydrogen peroxide levels caused by coffee drinking. Biol Pharm Bull. 2002 Nov;25(11):1467-71. doi: 10.1248/bpb.25.1467. [PubMed:12419961 ]
- Long LH, Halliwell B: Coffee drinking increases levels of urinary hydrogen peroxide detected in healthy human volunteers. Free Radic Res. 2000 May;32(5):463-7. [PubMed:10766414 ]
|
|---|