| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-08-12 19:09:36 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:16:36 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0003344 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0002165
- HMDB02165
- HMDB03344
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Glycolaldehyde |
|---|
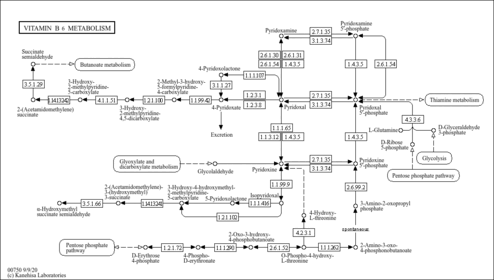
| Description | Glycolaldehyde (HOCH2-CH=O, IUPAC name 2-hydroxyethanal) is a type of diose (2-carbon monosaccharide). Glycolaldehyde is readily converted to acetyl coenzyme A. It has an aldehyde and a hydroxyl group. However, it is not actually a sugar, because there is only one hydroxyl group. Glycolaldehyde is formed from many sources, including the amino acid glycine and from purone catabolism. It can form by action of ketolase on fructose 1,6-bisphosphate in an alternate glycolysis pathway. This compound is transferred by thiamin pyrophosphate during the pentose phosphate shunt. |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C2H4O2/c3-1-2-4/h1,4H,2H2 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| GLYCOALDEHYDE | ChEBI | | Glycolic aldehyde | ChEBI | | Glycollaldehyde | ChEBI | | Hydroxyacetaldehyde | ChEBI | | Methylol formaldehyde | ChEBI | | Monomethylolformaldehyde | ChEBI | | 2-Hydroxyacetaldehyde | HMDB | | 2-Hydroxyethanal | HMDB | | 2-OH-Acetaldehyde | HMDB | | 2-Oxoethanol | HMDB | | Diose | HMDB | | Hydroxyethanal | HMDB | | Methylolformaldehyde | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C2H4O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 60.052 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 60.021129372 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-hydroxyacetaldehyde |
|---|
| Traditional Name | glycolaldehyde |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 141-46-8 |
|---|
| SMILES | OCC=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C2H4O2/c3-1-2-4/h1,4H,2H2 |
|---|
| InChI Key | WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as short-chain aldehydes. These are an aldehyde with a chain length containing between 2 and 5 carbon atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbonyl compounds |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Short-chain aldehydes |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Short-chain aldehyde
- Primary alcohol
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 97 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 0.67 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 8.1483 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 2.95 minutes | 32390414 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 232.8 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Long = Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 614.9 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Lipids = Ascentis Express C18 with (60:40 water:ACN):(90:10 IPA:ACN) and 10mM NH4COOH + 0.1% Formic Acid | 349.8 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_Old = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:(20:80 acetone:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 113.5 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_New = RP Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:(30:70 MeOH:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 265.9 seconds | 40023050 | | RIKEN = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 93.1 seconds | 40023050 | | Eawag_XBridgeC18 = XBridge C18 3.5u 2.1x50 mm with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 257.5 seconds | 40023050 | | BfG_NTS_RP1 =Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm x 150 mm, 3.5 um) with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 283.8 seconds | 40023050 | | HILIC_BDD_2 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN(0.1% formic acid):water(16 mM ammonium formate) | 331.3 seconds | 40023050 | | UniToyama_Atlantis = RP Waters Atlantis T3 (2.1 x 150 mm, 5 um) with ACN:Water and 0.1% Formic Acid | 551.5 seconds | 40023050 | | BDD_C18 = Hypersil Gold 1.9µm C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 57.2 seconds | 40023050 | | UFZ_Phenomenex = Kinetex Core-Shell C18 2.6 um, 3.0 x 100 mm, Phenomenex with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 726.2 seconds | 40023050 | | SNU_RIKEN_POS = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 228.7 seconds | 40023050 | | RPMMFDA = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 295.7 seconds | 40023050 | | MTBLS87 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water and :ammonium carbonate | 622.4 seconds | 40023050 | | KI_GIAR_zic_HILIC_pH2_7 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN:Water and 0.1% FA | 301.4 seconds | 40023050 | | Meister zic-pHILIC pH9.3 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water 5mM NH4Ac pH9.3 and 5mM ammonium acetate in water | 268.6 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized| Metabolite | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Glycolaldehyde | OCC=O | 1268.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde | OCC=O | 520.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde | OCC=O | 578.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
Derivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Glycolaldehyde,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OCC=O | 836.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC=CO | 867.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC=CO[Si](C)(C)C | 992.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC=CO[Si](C)(C)C | 920.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC=CO[Si](C)(C)C | 1010.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC=O | 1042.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC=CO | 1085.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC=CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1420.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC=CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1384.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Glycolaldehyde,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC=CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1321.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-c2f1922c3cfc298b56e6 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0109-9200000000-6143e9afd72b9d7c5b6c | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-001i-9000000000-86c6c734f49f41d961f7 | 2015-03-01 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde LC-ESI-QTOF 10V, positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-4900000000-49b53ff321501e621bff | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde LC-ESI-QTOF 20V, positive-QTOF | splash10-00dl-9400000000-2bd428d561e19271ec88 | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde LC-ESI-QTOF 40V, positive-QTOF | splash10-00kf-9000000000-73ede536fea5e4ad63d0 | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-4900000000-bb83469432ecea1f97fa | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00dl-9400000000-ddfc724456c2aac5ea03 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00kf-9000000000-1eb34df93b3cd472f40d | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-9000000000-9aad7766f88c7ab6028b | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-9000000000-8dee0ff3027177f894d7 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-f167702c9efe9cfcd0a8 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-666acd064bdf4b7e4e17 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-f129f99fe312906de2f3 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-052f-9000000000-a4339f6764dcb3e35133 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-1d4ca7190bbdd61a3001 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-588ee6697087d4260422 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-6ffb9541e24882de3fac | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-ee98b120aa7fd044da72 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-87bbaed151efac084591 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glycolaldehyde 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-87bbaed151efac084591 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|