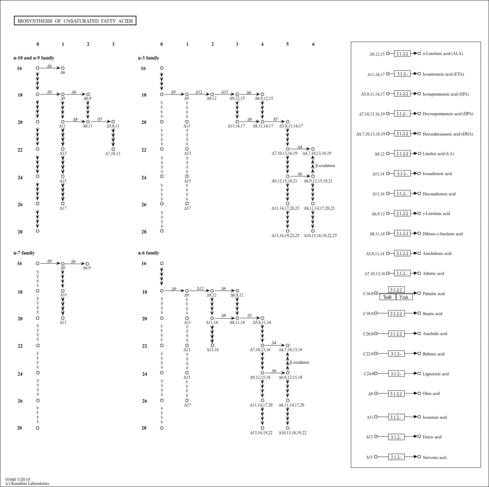
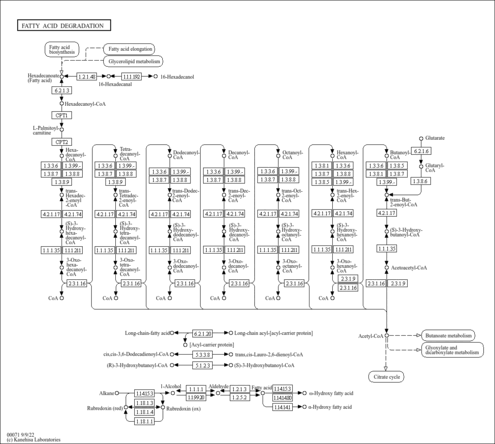
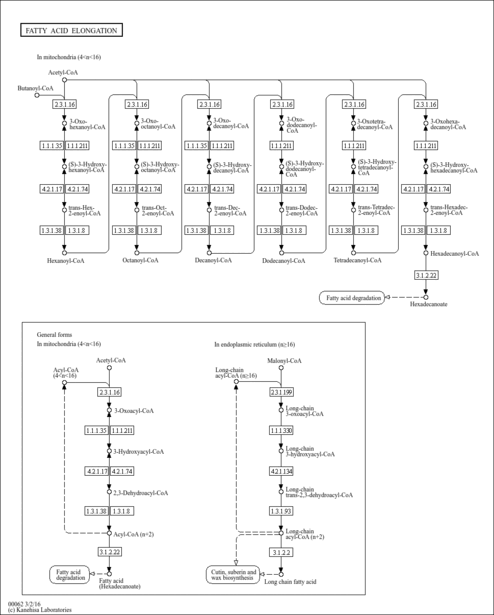
Showing metabocard for Lauroyl-CoA (HMDB0003571)
Only showing the first 10 proteins. There are 112 proteins in total.
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups other than amino-acyl groups
- Specific function:
- Abolishes BNIP3-mediated apoptosis and mitochondrial damage.
- Gene Name:
- ACAA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P42765
- Molecular weight:
- 41923.82
Reactions
| Lauroyl-CoA + Acetyl-CoA → Coenzyme A + 3-Oxotetradecanoyl-CoA | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Plays a role in valine and pyrimidine metabolism. Binds fatty acyl-CoA.
- Gene Name:
- ALDH6A1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q02252
- Molecular weight:
- 57839.31
- General function:
- Involved in acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- ACADS
- Uniprot ID:
- P16219
- Molecular weight:
- 44296.705
- General function:
- Involved in acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the desaturation of acyl-CoAs to 2-trans-enoyl-CoAs. Isoform 1 shows highest activity against medium-chain fatty acyl-CoAs and activity decreases with increasing chain length. Isoform 2 is active against a much broader range of substrates and shows activity towards very long-chain acyl-CoAs. Isoform 2 is twice as active as isoform 1 against 16-hydroxy-palmitoyl-CoA and is 25% more active against 1,16-hexadecanodioyl-CoA.
- Gene Name:
- ACOX1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15067
- Molecular weight:
- 70135.205
Reactions
| Lauroyl-CoA + FAD → (2E)-Dodecenoyl-CoA + FADH | details |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Oxidizes the CoA esters of the bile acid intermediates di- and tri-hydroxycholestanoic acids.
- Gene Name:
- ACOX2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99424
- Molecular weight:
- 76826.14
- General function:
- Involved in acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- IVD
- Uniprot ID:
- P26440
- Molecular weight:
- 43055.325
Transporters
- General function:
- Lipid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in translocation of long-chain fatty acids (LFCA) across the plasma membrane. The LFCA import appears to be hormone-regulated in a tissue-specific manner. In adipocytes, but not myocytes, insulin induces a rapid translocation of FATP1 from intracellular compartments to the plasma membrane, paralleled by increased LFCA uptake. May act directly as a bona fide transporter, or alternatively, in a cytoplasmic or membrane- associated multimeric protein complex to trap and draw fatty acids towards accumulation. Plays a pivotal role in regulating available LFCA substrates from exogenous sources in tissues undergoing high levels of beta-oxidation or triglyceride synthesis. May be involved in regulation of cholesterol metabolism. Has acyl-CoA ligase activity for long-chain and very-long-chain fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- SLC27A1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6PCB7
- Molecular weight:
- 71107.5
Only showing the first 10 proteins. There are 112 proteins in total.