| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-13 12:02:10 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:51:26 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0012453 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid |
|---|
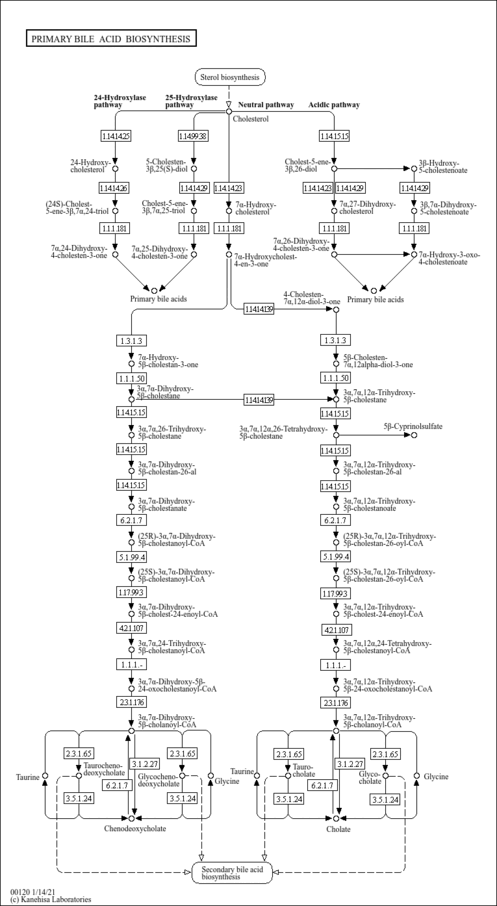
| Description | 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid (CAS: 6561-58-6) belongs to the class of organic compounds known as monohydroxy bile acids, alcohols, and derivatives. These are bile acids, alcohols or any of their derivatives bearing a hydroxyl group. 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid is found in the primary bile acid biosynthesis pathway. 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid is created from cholest-5-ene-3 beta,26-diol through the action of CYP27A (EC 1.14.13.15). 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid is then converted into 3beta,7alpha-dihydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid by the action of CYP7B (EC 1.14.13.100). 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid was identified as one of forty plasma metabolites that could be used to predict gut microbiome Shannon diversity (PMID: 31477923 ). Shannon diversity is a metric that summarizes both species abundance and evenness, and it has been suggested as a marker for microbiome health. |
|---|
| Structure | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC[C@@H](C)C(O)=O InChI=1S/C27H44O3/c1-17(6-5-7-18(2)25(29)30)22-10-11-23-21-9-8-19-16-20(28)12-14-26(19,3)24(21)13-15-27(22,23)4/h8,17-18,20-24,28H,5-7,9-16H2,1-4H3,(H,29,30)/t17-,18-,20+,21+,22-,23+,24+,26+,27-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 3b-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoate | Generator | | 3b-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid | Generator | | 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoate | Generator | | 3Β-hydroxy-5-cholestenoate | Generator | | 3Β-hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid | Generator | | 5-Cholesten-3-ol-25-carboxylic acid | HMDB | | (25R)-3b-Hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oate | HMDB | | (25R)-3b-Hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | (25R)-3beta-Hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oate | HMDB | | (25R)-3Β-hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oate | HMDB | | (25R)-3Β-hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | (3beta)-3-Hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | (3beta,25R)-3-Hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | (3Β)-3-hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | (3Β,25R)-3-hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3beta-Hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3beta-Hydroxycholest-5-en-27-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3Β-hydroxycholest-5-en-26-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3Β-hydroxycholest-5-en-27-Oic acid | HMDB | | 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C27H44O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 416.646 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 416.329045277 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2R,6R)-6-[(1S,2R,5S,10S,11S,14R,15R)-5-hydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadec-7-en-14-yl]-2-methylheptanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (2R,6R)-6-[(1S,2R,5S,10S,11S,14R,15R)-5-hydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadec-7-en-14-yl]-2-methylheptanoic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 56845-87-5 |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC[C@@H](C)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C27H44O3/c1-17(6-5-7-18(2)25(29)30)22-10-11-23-21-9-8-19-16-20(28)12-14-26(19,3)24(21)13-15-27(22,23)4/h8,17-18,20-24,28H,5-7,9-16H2,1-4H3,(H,29,30)/t17-,18-,20+,21+,22-,23+,24+,26+,27-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | WVXOMPRLWLXFAP-KQOPCUSDSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as monohydroxy bile acids, alcohols and derivatives. These are bile acids, alcohols or any of their derivatives bearing a hydroxyl group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Steroids and steroid derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Bile acids, alcohols and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Monohydroxy bile acids, alcohols and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Monohydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- Steroid acid
- 3-hydroxy-delta-5-steroid
- 3-hydroxysteroid
- 3-beta-hydroxysteroid
- 3-beta-hydroxy-delta-5-steroid
- Hydroxysteroid
- Delta-5-steroid
- Medium-chain fatty acid
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Cyclic alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic homopolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homopolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 9.14 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 21.3978 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 1.44 minutes | 32390414 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 52.1 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Long = Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 3331.5 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Lipids = Ascentis Express C18 with (60:40 water:ACN):(90:10 IPA:ACN) and 10mM NH4COOH + 0.1% Formic Acid | 491.2 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_Old = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:(20:80 acetone:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 264.1 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_New = RP Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:(30:70 MeOH:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 205.5 seconds | 40023050 | | RIKEN = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 633.7 seconds | 40023050 | | Eawag_XBridgeC18 = XBridge C18 3.5u 2.1x50 mm with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 941.2 seconds | 40023050 | | BfG_NTS_RP1 =Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm x 150 mm, 3.5 um) with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 893.0 seconds | 40023050 | | HILIC_BDD_2 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN(0.1% formic acid):water(16 mM ammonium formate) | 107.7 seconds | 40023050 | | UniToyama_Atlantis = RP Waters Atlantis T3 (2.1 x 150 mm, 5 um) with ACN:Water and 0.1% Formic Acid | 1678.9 seconds | 40023050 | | BDD_C18 = Hypersil Gold 1.9µm C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 630.9 seconds | 40023050 | | UFZ_Phenomenex = Kinetex Core-Shell C18 2.6 um, 3.0 x 100 mm, Phenomenex with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 1886.4 seconds | 40023050 | | SNU_RIKEN_POS = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 558.2 seconds | 40023050 | | RPMMFDA = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 553.5 seconds | 40023050 | | MTBLS87 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water and :ammonium carbonate | 249.7 seconds | 40023050 | | KI_GIAR_zic_HILIC_pH2_7 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN:Water and 0.1% FA | 514.5 seconds | 40023050 | | Meister zic-pHILIC pH9.3 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water 5mM NH4Ac pH9.3 and 5mM ammonium acetate in water | 8.9 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C)C(=O)O | 3596.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3480.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3498.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C)C(=O)O | 3813.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@H](CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3756.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 3beta-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@H](CCC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4025.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|