| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:15:29 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0001167 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Pyruvaldehyde |
|---|
| Description | Pyruvaldehyde, also known as 2-oxopropanal or 1,2-propanedione, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha ketoaldehydes. These are organic compounds containing an aldehyde substituted with a keto group on the adjacent carbon. Pyruvaldehyde is an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Pyruvaldehyde exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. In humans, pyruvaldehyde is involved in spermidine and spermine biosynthesis. Outside of the human body, Pyruvaldehyde has been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as prairie turnips, chervils, japanese walnuts, corns, and calabash. This could make pyruvaldehyde a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C3H4O2/c1-3(5)2-4/h2H,1H3 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 1,2-Propanedione | ChEBI | | 2-Ketopropionaldehyde | ChEBI | | 2-Oxopropanal | ChEBI | | 2-Oxopropionaldehyde | ChEBI | | Acetylformaldehyde | ChEBI | | Acetylformyl | ChEBI | | alpha-Ketopropionaldehyde | ChEBI | | CH3COCHO | ChEBI | | Pyruvic aldehyde | ChEBI | | a-Ketopropionaldehyde | Generator | | Α-ketopropionaldehyde | Generator | | 1-Ketopropionaldehyde | HMDB | | 2-Keto propionaldehyde | HMDB | | 2-oxo-Propionaldehyde | HMDB | | Ketopropionaldehyde | HMDB | | Methylglyoxal | HMDB | | Propanedione | HMDB | | Propanolone | HMDB | | Pyroracemic aldehyde | HMDB | | Aldehyde, pyruvic | HMDB | | Oxopropanal | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C3H4O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 72.0627 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 72.021129372 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-oxopropanal |
|---|
| Traditional Name | methylglyoxal |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 78-98-8 |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(=O)C=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C3H4O2/c1-3(5)2-4/h2H,1H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | AIJULSRZWUXGPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha ketoaldehydes. These are organic compounds containing an aldehyde substituted with a keto group on the adjacent carbon. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbonyl compounds |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha ketoaldehydes |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-ketoaldehyde
- Ketone
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Short-chain aldehyde
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | < 25 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Pyruvaldehyde,1TMS,isomer #1 | C=C(C=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 841.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyruvaldehyde,1TMS,isomer #1 | C=C(C=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 785.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyruvaldehyde,1TMS,isomer #1 | C=C(C=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1045.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Pyruvaldehyde,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | C=C(C=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1100.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyruvaldehyde,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | C=C(C=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1012.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyruvaldehyde,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | C=C(C=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1235.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-43f9b3c94058c64733b5 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-00dj-9000000000-964129275940a60a617d | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-006y-9000000000-0ae1e5fd2d50b28f967c | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-00dj-9000000000-964129275940a60a617d | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000000000-110d6fcd891f2c54a2cb | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-05fr-9000000000-bec3651f9ea6825cf4f7 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-8db5b1ba128748e220c3 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000000000-f968a2358e6fd85ae268 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000000000-0797bdeaa575b54943c5 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0uk9-9000000000-89ef1c082b2ef672eb67 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000000000-5b936b9153956c2f64be | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000000000-9190b139940adf0d92c6 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-570ca33f905cecb028a1 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-482389dce4f05675f174 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-79267be0bc618dc8018f | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyruvaldehyde 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-87bbaed151efac084591 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Eye Lens
- Fibroblasts
- Kidney
- Liver
|
|---|
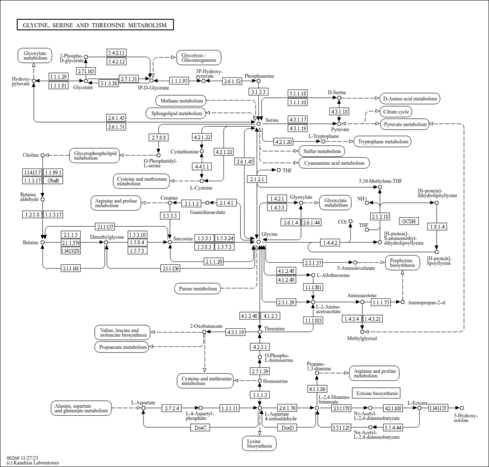
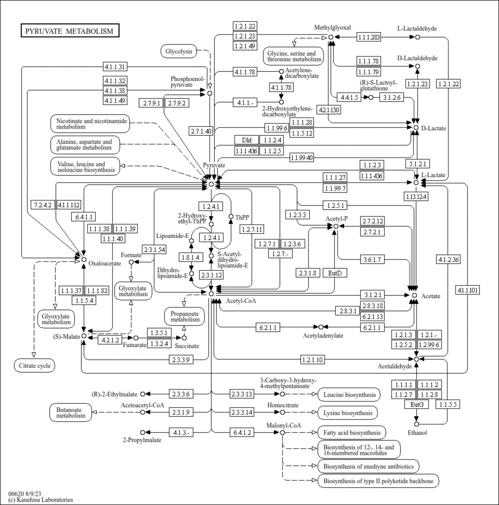
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 110.0 +/- 77.0 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.653 +/- 0.167 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.59 (0.44-0.74) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details |
|
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.528 +/- 0.250 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Uremia | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 3.0 (2.4-3.6) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Diabetes | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.22 (0.16-0.23) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Diabetes | | details |
|
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Diabetes mellitus type 2 |
|---|
- Khuhawar MY, Zardari LA, Laghari AJ: Capillary gas chromatographic determination of methylglyoxal from serum of diabetic patients by precolumn derivatization with 1,2-diamonopropane. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008 Sep 15;873(1):15-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.04.048. Epub 2008 May 17. [PubMed:18760976 ]
| | Uremia |
|---|
- Vanholder R, De Smet R, Glorieux G, Argiles A, Baurmeister U, Brunet P, Clark W, Cohen G, De Deyn PP, Deppisch R, Descamps-Latscha B, Henle T, Jorres A, Lemke HD, Massy ZA, Passlick-Deetjen J, Rodriguez M, Stegmayr B, Stenvinkel P, Tetta C, Wanner C, Zidek W: Review on uremic toxins: classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003 May;63(5):1934-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00924.x. [PubMed:12675874 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 125853 (Diabetes mellitus type 2)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB03587 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB031000 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00007562 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 857 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00546 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | METHYL-GLYOXAL |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 35307 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Methylglyoxal |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 6049 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 880 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 17158 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | MTHGXL |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00029995 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Zhang, Jing-An; Chen, Yu-Ping. Synthesis of pyruvaldehyde. Jingxi Huagong (2000), 17(9), 507-510. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) |
|---|
| General References | - Wondrak GT, Cervantes-Laurean D, Roberts MJ, Qasem JG, Kim M, Jacobson EL, Jacobson MK: Identification of alpha-dicarbonyl scavengers for cellular protection against carbonyl stress. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002 Feb 1;63(3):361-73. [PubMed:11853687 ]
- Mottaran E, Stewart SF, Rolla R, Vay D, Cipriani V, Moretti M, Vidali M, Sartori M, Rigamonti C, Day CP, Albano E: Lipid peroxidation contributes to immune reactions associated with alcoholic liver disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002 Jan 1;32(1):38-45. [PubMed:11755315 ]
- Lo TW, Selwood T, Thornalley PJ: The reaction of methylglyoxal with aminoguanidine under physiological conditions and prevention of methylglyoxal binding to plasma proteins. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Nov 16;48(10):1865-70. [PubMed:7986197 ]
- Gildersleeve DL, Tobes MC, Natale RB: Rapid analysis for methylglyoxal bis(guanylhydrazone) by reversed-phase ion-pair liquid chromatography. Clin Chem. 1985 Dec;31(12):1979-84. [PubMed:4064286 ]
- Ahmed N, Thornalley PJ, Dawczynski J, Franke S, Strobel J, Stein G, Haik GM: Methylglyoxal-derived hydroimidazolone advanced glycation end-products of human lens proteins. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 Dec;44(12):5287-92. [PubMed:14638728 ]
- Seppanen P, Alhonen-Hongisto L, Janne J: Polyamine deprivation-induced enhanced uptake of methylglyoxal bis(guanylhydrazone) by tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 5;674(2):169-77. [PubMed:6786360 ]
- Ahmed MU, Brinkmann Frye E, Degenhardt TP, Thorpe SR, Baynes JW: N-epsilon-(carboxyethyl)lysine, a product of the chemical modification of proteins by methylglyoxal, increases with age in human lens proteins. Biochem J. 1997 Jun 1;324 ( Pt 2):565-70. [PubMed:9182719 ]
- Riley ML, Harding JJ: The reaction of methylglyoxal with human and bovine lens proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Jan 25;1270(1):36-43. [PubMed:7827133 ]
- Beisswenger PJ, Drummond KS, Nelson RG, Howell SK, Szwergold BS, Mauer M: Susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy is related to dicarbonyl and oxidative stress. Diabetes. 2005 Nov;54(11):3274-81. [PubMed:16249455 ]
- Nemet I, Varga-Defterdarovic L, Turk Z: Preparation and quantification of methylglyoxal in human plasma using reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Clin Biochem. 2004 Oct;37(10):875-81. [PubMed:15369718 ]
- Thornalley PJ, Argirova M, Ahmed N, Mann VM, Argirov O, Dawnay A: Mass spectrometric monitoring of albumin in uremia. Kidney Int. 2000 Nov;58(5):2228-34. [PubMed:11044246 ]
- Baskaran S, Rajan DP, Balasubramanian KA: Formation of methylglyoxal by bacteria isolated from human faeces. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Mar;28(3):211-5. [PubMed:2926792 ]
- Kuhla B, Luth HJ, Haferburg D, Boeck K, Arendt T, Munch G: Methylglyoxal, glyoxal, and their detoxification in Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Jun;1043:211-6. [PubMed:16037241 ]
- Schupp N, Schinzel R, Heidland A, Stopper H: Genotoxicity of advanced glycation end products: involvement of oxidative stress and of angiotensin II type 1 receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Jun;1043:685-95. [PubMed:16037294 ]
- Haik GM Jr, Lo TW, Thornalley PJ: Methylglyoxal concentration and glyoxalase activities in the human lens. Exp Eye Res. 1994 Oct;59(4):497-500. [PubMed:7859825 ]
- Shamsi FA, Lin K, Sady C, Nagaraj RH: Methylglyoxal-derived modifications in lens aging and cataract formation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998 Nov;39(12):2355-64. [PubMed:9804144 ]
- Jan CR, Chen CH, Wang SC, Kuo SY: Effect of methylglyoxal on intracellular calcium levels and viability in renal tubular cells. Cell Signal. 2005 Jul;17(7):847-55. Epub 2004 Dec 8. [PubMed:15763427 ]
- Ahmed N, Dobler D, Dean M, Thornalley PJ: Peptide mapping identifies hotspot site of modification in human serum albumin by methylglyoxal involved in ligand binding and esterase activity. J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 18;280(7):5724-32. Epub 2004 Nov 22. [PubMed:15557329 ]
| Show more...
|---|